The working equipment of the excavator. Excavators - types and equipment. How are units classified
They are performed in a large power range.
performance and versatility. The excavator consists of a worker and
power equipment, control systems, transmissions, turntables for accommodating mechanisms, various
devices, apparatus and undercarriage. The working equipment of excavators with a direct and reverse shovel consists of a working body, an arrow and a handle. The working equipment of excavators with dragline has no handle, and the bucket is suspended from the boom on the rope with the help of a harness. Work equipment also includes blocks, guides, and ropes that transmit movement to various elements of work equipment. For excavation work of a different nature in different conditions, construction excavators are supplied with buckets and other interchangeable working equipment. Small-capacity excavators are used for small amounts of earthworks, as well as for various auxiliary and preparatory construction works - felling and clearing forests, pile driving, compaction of pavements, installation and loading and unloading. If at least three types of interchangeable equipment can be installed on an excavator - a direct shovel (hereinafter referred to simply as a shovel), a backhoe and a dragline, such excavators can be supplied with other types of working equipment and they are called universal. However, more often, the set of replacement equipment includes equipment for shovels, reverse shovels,
Several factors can help excavator operators increase productivity during everyday construction tasks, but one of the biggest factors contributing to a return to choosing the right excavator bucket is applicable to the application. Some excavator operators may tend to use a standard bucket in all applications. However, this approach may adversely affect operator performance. For example, using a standard bucket rather than a trench bucket in trenches or deep digging can reduce efficiency.
dragline, grab and crane. The smaller the size of the excavator, the greater the number of interchangeable buckets (up to 30) and other types of working equipment (up to 15) it can have. For more effective use of the excavator in different conditions and soils of different strength, excavators Equipped with buckets of different capacity, arrows and handles. Changing the length of arrows and handles is usually carried out by special inserts. Dragline - work equipment for excavation below the level of the excavator with a bucket suspended on the ropes and digging in the direction of the excavator. The depth of digging, the height at which the bucket is unloaded and the distance that the bucket (digging radius) of the dragline can be thrown is much greater than that of the forward and reverse shovels. Therefore, the dragline is used for digging large trenches and trenches, as well as for dumping embankments, in particular in the construction of canals, roads and railways. The dragline works in the following way. Bucket / lower the bottom of the excavation or trench, and then drag it to the car traction rope; at the same time the ladle is filled with the cut-off soil. Then the loaded bucket is lifted with a hoisting rope, at the same time turning the platform to the place of unloading of the bucket. After unloading the bucket, turn the platform with the arrow to the bottom and simultaneously lower the bucket. The boom is a welded lattice design, which reduces its weight and makes it possible to make it longer, whose booms are straight and reverse shovels, using a bucket of the same capacity. By extending the boom, the range of the machine and the height of the discharge are increased. The arrow consists of two parts connected by bolts, the lower of which is broadened to the heel of the arrow and pivotally fixed in the eyes of the turntable. The length of the boom can be increased due to additional inserts between the upper and lower parts of the boom. At lengthening of an arrow apply a ladle and the smaller capacity. During the work of the dragline, the angle of the boom is usually set in the range from 30 to 40.
Tip # 1: Choose a bucket type based on soil conditions.
Operators should also verify that the selected bucket does not exceed the working capacity of the machine. For contractors, there are two basic types of bucket: heavy buckets and harsh buckets. Heavy buckets are the most common type of excavator bucket because they work well in a variety of soil conditions, such as clay, gravel, sand, silt and shale. Buckets are made of high quality wear-resistant material, durable side cutters for added strength and protection, and lower wear-resistant gaskets.
84.Single Bucket universal excavator. Running equipment. Control systems.

One-bucket universal e. - this is uh. cycling with one bucket or another working body, carrying out, in addition to excavation, loading, piling and other works using one of the types of replacement work equipment. According to the type of propellers, the following equipment is distinguished: tracked, pneumatic, walking, rail, floating, air cushion, etc. The tracked and pneumowered are the most common on construction vehicles. Tracked drive: slight pressure on the ground, overcoming large slopes, good permeability, etc .; limitations.: large mass, high cost, low speed, etc. Pneumatic motion: high transport speeds, pressure control on the base, etc .; limitations.: high pressure on the ground, limited off-road capability, etc. The control system refers to a set of elements intended for switching on and off the mechanisms of the machines, as well as for controlling the power plant. Hydraulic control systems are pumpless (pressure is created by the muscular strength of the operator) and pumping. Advantages: compactness and small size of the control panel, working cylinders and engines, the ability to transfer forces to remote points. Disadvantages: the sharpness of the inclusion of mechanisms, difficulties in the operation of machines in hot and cold climates, an increased class of accuracy in the manufacture of hydraulic equipment. Pneumatic differs from the hydraulic softer inclusion mechanisms. Disadvantages: the need for careful care at "-" temperatures, bulkiness. The single-bucket excavator consists of the following main parts: undercarriage equipment, turntable with mechanisms, control cabin, power plant and work equipment. In most cases, they are used for the development of rocks and soils. The excavator perfectly does work on the production of pits, device embankments, excavations, channels, dams, etc. It differs in carrying capacity and execution of works in a short time. The excavator has a turntable, which relies on the chassis frame through rollers of a turntable. The same system can be installed on different interchangeable chassis equipment, depending on the purpose and conditions of the machine. The movement of the working bodies and the entire excavator is transmitted from the power plant (diesel) through the transmission to the cargo and boom winches, mechanisms of rotation, pressure and movement of this technology. From the cargo winch system of ropes, tap blocks movement is transmitted to the working body, which is suspended on the boom of transport or strengthened to it. The design of the drive and control systems must ensure: - the tightness of the elements of the hydraulic drive systems - according to GOST 20245. The flow of the working fluid through the fixed and rotary interfaces is not allowed. Oil removal in movable joints (on the surface of hydraulic cylinder rods, in rotating joints, etc.) during work should not exceed the standards established by standards and specifications for hydraulic drive elements *; - prevent leakage of working fluid from the hydraulic tank when replacing working equipment and technical equipment maintenance of filters; - limiting the speed of lowering the boom *; - preventing the lowering under the action of gravity of the boom or arm when the hydraulic cylinders are turned on to lift these working elements is equipped I * -. the possibility of free movement of the boom and the swing when towing a dredge-type EPO (towing journalled bucket in tow car) * According to the control system distinguish excavators rychazhnomehanicheskim, pneumatic, hydraulic, electric and hybrid (electro-pneumatic, electro-hydraulic) control. Lever-mechanical control provide for low-power excavators. Due to a large number deficiencies this type of control has recently been replaced by pneumatic or hydraulic on most machines. Pneumatic control is installed on low-power excavators with a bucket capacity of 0.5-2.0 m 3. Hydraulic and electric control is used with the appropriate types of drive.
Heavy buckets are best suited for excavator operators who work with abrasive materials for heavy or heavy digging and loading. Buckets are made of wear-resistant material for additional protection and strength when digging in loose rock or quarry and quarries. The side cutters of the cones, the bottom of the housing, the side wear plates and the protective covers for welding consist of a wear resistant material. In addition, reinforced crochets help to strengthen the couplings on the buckets to speed up the work.
Tip # 2: Choose a bucket style to suit your digging needs.
Additional abrasion resistant components, made in rough buckets, include front edge, front wear pads and a webbing belt. According to Smith, there are three main types of bucket for use with excavators. They are trenches, ditches and angled inclined buckets.
Lecture number 1. Machines for excavation. Excavators are single-bucket.
Any construction process begins with the production of earthworks, because with. development of the soil, moving it or loading it on vehicles. So, for the construction of the foundations or foundations of any building or structure, trenches of the required size and depth are torn off, and for laying the external networks of pipelines - trenches. Sometimes, for the construction of structures such as dams, dams or roads, arrange mounds, and with the rolling of the soil. All of them are essentially earthworks, which for the duration of their service may be temporary and permanent. Temporary (pits, trenches) are arranged only for the period of construction of buildings, structures, networks of pipelines, and then filled with soil, and permanent (dams, dams, channels) are designed for a long service life.
Trenchers can easily dig narrow deep trenches, maintaining excellent breakthrough strength and contributing to fast cycle times for the excavator. Buckets are made of wear-resistant material with reduced weight and offer high-strength side wear plates and bottom wear tapes for added strength.
Submersible buckets have a similar profile for standard buckets, but have a wider and deeper profile for smooth operation in sand and clay. In addition, buckets provide optimum versatility when loading material, sorting, backfilling, cleaning ditches to improve drainage and working on slopes.
Earthworks by their specific weight in the total volume of construction works are the most massive and time consuming, and therefore it is not possible to cope with them manually. When performing them, mechanized methods of work are extremely necessary through the use of special machines.
Standard characteristics of gutter buckets include a lifting eye for lifting, threaded side cutters and a reversible cutting edge that leaves the work area smooth when work is completed. Angled inclined buckets are versatile and cost-effective when used in finishing, sorting and cleaning works. The buckets can be rotated 45 degrees in any direction of the center and are equipped with an adjustable tipping speed with additional flow control valves.
Tip # 3: Add accessories to adjust buckets
“When using angled inclined buckets, operators can easily assess or level the area without changing the frequency of their excavator, making them more efficient,” says Smith. The angles of inclination have many other functions, including. Heavy components for greater durability and power. Anti-freeze protection through the protective cover and protective covers. Universal hydraulic connections for easy attachment or detachment of hydraulic lines. Excavators can be operated to lift, carry and place pipes with a bucket lifting eye.
Machines for excavation by appointment are divided into:
1. earthmoving designed to perform a single operation - the separation of soil from the array. Such machines include single-bucket excavators (cyclical) and multi-bucket (continuous). Single-bucket excavators, which perform about 40% of the total volume of earth-moving work, have the greatest application.
This is common among utility contractors working on wet or dry utility projects and placing the pipe in an open trench. The operator should always refer to the load diagram of the excavator to understand the capabilities of the machine for excessive and handling needs.
Depending on the model and use of the excavator, the inclined power connector can be rotated 90 degrees left or right, providing flexibility up to 180 degrees. Increased snapping flexibility can help operators save valuable time because they may not need to frequently move an excavator while working or stop changing attachments to perform certain tasks, says Smith. "This is especially useful when working under or around objects such as an underground pipe."
2. earthmoving which not only separate the soil from the array, but also move it. The main earth-moving machines are the bulldozer and the scraper, which in one cycle develop the soil, move it, unload it into the embankment and return to the face in the empty state.
How are units classified
This application can be most useful for those who work in general excavations, underground utilities, sorting and erosion systems. Another key to maximum performance from an excavator is an investment in a quality investment change system, which is optional on most manufacturers' machines. According to Smith, investing in a quality connectivity system, such as a fast adapter, can increase the flexibility of your application and increase utilization.
Bulldozersdesigned for the development and movement of soil at a distance of 100 m, the construction of embankments up to 2 m high, the development of excavations, backfilling of trenches after laying utilities, planning of construction sites, cleaning of roads and roads .), slope layouts. On the basis of bulldozers, rippers are used that have attached or trailed working bodies in the form of a tooth or several teeth for layer-by-layer destruction and loosening of heavy and frozen soils up to 1.5 m in depth.
Work equipment and its drive
Depending on the soil conditions and material density, the utility contractor may need a digging bucket in one place, a trencher in another, or at a bucket angle to the next, he says. “Quick connectors make it easier and faster to replace buckets and other attachments in the workplace.”
Operators also with more likely use a bucket of the right size if they can quickly switch between the buckets to best fit the width of the trench. Side and bottom wear plates, protective side panels and side cutters are other bucket accessories that help reduce bucket wear by allowing the machine to work as long as possible to protect these investments.
Scrapers - the most high-performance earthmoving machinery; used in the passage of pits and surface layout. Currently used trailed (with a bucket volume of 3, 7 and 8 m) scraper. The use of trailed and semi-trailed scraper is most effective when transporting soil at a distance of up to 1000 m, and of self-propelled ones up to 3000 m. without boulders, with an admixture of pebbles and rubble no more than 10%).
Tip # 4: Inspect Wear Details and Replace Parts.
Maintaining an excavator bucket is just as important as regular schedules. maintenance the excavator itself and should not be overlooked. Smith recommends daily checking of the bucket teeth, cutting edges and bucket heels for noticeable wear or breakage. The bucket teeth should be replaced before they wear out and the bucket adapter is exposed. Also, if necessary, inspect worn housings for component wear and replace them.
“Forging has a lot of replaceable wear items, so it’s crucial that when operators complete a general inspection, they replace these items in order to extend the bucket’s service life,” says Smith. "If the bucket shell is worn out without repair, equipment owners should replace the bucket."
3. special intended for soil compaction (rollers, tamping, vibrating compactors)
Indeed, as is well known, the durability of earthworks largely depends on the quality of soil compaction, which is performed during planning works, erection of embankments, backfilling trenches and foundations. In order to obtain the highest density of the laid soil, the lowest filtration capacity and reduce subsequent sediment, the soil is laid and compacted in compliance with certain technological requirements.
Construction department staff and construction inspectors. This guide describes what a fast coupling is, discusses general failure modes, in particular with semi-automatic clamps, and directs inspectors to take action in response to certain site scenarios.
Working equipment of the single-bucket excavator
The purpose of this guide is to consider key issues that inspectors would like to consider during the relevant checks, and provide guidance on when enforcement may be appropriate. Rapid traction on an excavator is a locking device that allows you to attach attachments to the installation bucket and quickly change. An excavator operator can change a bucket on his excavator up to 30 times a day to maximize machine performance.
Depending on the physical and mechanical properties of the soil, two types of sealing effects can be used: static and dynamic.
Static machines designed for layer-by-layer compaction of the soil under the action of its own weight. These include:
- self-propelled rollers with smooth rollers - for final compaction of dirt roads and platforms, gravel, crushed stone, black and asphalt concrete pavements of roads;
However, there may be many dangerous cases that may not be reported when the bucket is unintentionally disconnected from the hitch, but without injuries, because at that time no one is down. Latch on hydraulic devices moving in jerky motion; Any obvious missing or broken parts; or hydraulic pipes located close to the hitch, severely damaged. Inspectors should establish whether the hitch is permanently attached to the excavator and make sure that the hitch is part of a thorough inspection as part of the machine or accessory, depending on the answer.
- trailed cam rollers - for layer-by-layer preliminary consolidation of cohesive soils;
- trailed, semi-trailed and self-propelled rollers on pneumatic tires - for layer-by-layer compaction of soil, gravel and crushed-stone materials, as well as asphalt-concrete mixtures.
Dynamic machines designed for layer-by-layer compaction of the soil under the action of the resulting force or mass of a falling load. These include:
Appendix 1 for recommended compliance actions and Appendix 2 for photographs on what to expect. A standard bucket is attached to the bucket with two pins. The disadvantage is less flexibility since only special buckets can be used. In addition, substantial investment in special buckets and attachments.
General arrangement of shovels
Non-manual systems are known as semi-automatic and automatic. The manual system requires the operator to change the bucket, for example, by winding a screw thread to open and close the latch, or with a rod to open the spring-loaded latch. This pin usually works by locking the latch in the closed position; this is often referred to as a “safety bar” and it is not a load bearing part of the hitch. The safety pin cannot be inserted unless the latch is in the fully closed position. Automatic systems can be fully controlled from the cab and usually have an independent locking system that functions automatically and which does not rely on hydraulic pressure to hold the latch in the closed position. Automatic systems should have a method in which the operator can check that the hitch is locked from the cab - for example, the locking pins can protrude from the hitch side when the latch is in the unlocked state. Large nozzles, such as tampers, may prevent the closure from being checked out of the cab, in which case the driver must come out of his cab to check the locked state. If they are replaced, it is important that the controls are compatible with the new device or replaced at the same time.
- self-propelled and towed vibratory rollers - to compact both loose and cohesive soils to a depth of 0.6-1.2 m. In addition, self-propelled rollers are used to compact asphalt concrete and small gravel pavements, driveways, and repair roads;
- vibrating plates- for consolidation of loose bulk soils of gravel-crushed-stone materials with a layer up to 0.6 m with small volumes and in cramped conditions;
- tamping machine - for compaction of heavy cohesive soils to a depth of up to 1.2 m in the construction of the subgrade, construction sites, approaches to bridges, etc.
4. for piling (vibratory pile drivers, diesel hammers).
Earthmoving machinery
The most common type of earthmoving machinery are single-bucket construction excavators. They serve to develop the soil and move it to the dump or for loading into vehicles. They develop soils of I ... IV groups and loosened frozen or rocky soils. In addition, excavators are used for piling, loading and unloading, installation and other works, using various types of interchangeable working equipment.
Get the full textSingle bucket excavators are cyclic machines. The workflow includes the operations of soil acquisition, rotation of a loaded bucket, to the place of unloading, unloading of soil into a vehicle or into a dump and installing the bucket and its initial position. The combination of these operations - the duty cycle.
Shovel excavators are classified by purpose, design of the undercarriage, type and suspension of working equipment, type of working bodies and other features.
To destination shovel excavators are divided into: construction, construction and quarrying, quarrying, overburden and tunnel. Construction and construction and career excavators are universal and are used to perform various works in construction (excerpts of pits and trenches, the development of quarries for building materials, loading and other works). Quarry excavators are used for mining in open pit mining; overburden - to remove the top layer of soil or rock in the preparation of quarries for development; tunnel - to work underground in the construction of underground structures and mining.
Single-shovel excavators may have different running gear types: tracked, pneumowheel, walking, rail type, special and combined. For construction excavators the most characteristic is a tracked and pneumatic wheeled undercarriage.
Running gear tracked type, it is intended for movement of the excavator within the construction site. It consists of a frame and two tracked trolleys connected to it. When relocating from object to object tracked excavators transported on a special trailer with the help of an auto trailer.
Pneumatic chassis equipment provides greater mobility: when relocating from object to object, the excavator can move under its own power or on a rigid hitch behind a tractor (the drive of the driving wheels and the hydraulic cylinder of turning the front wheels should be disabled). Since the rigidity of the pneumatic chassis equipment is low, it is imperative to use outboard supports for unloading the wheel to increase the support contour.
To destination shovel excavators are divided into universal and special.
Universal Excavators are equipped with several types of replaceable working equipment, and special ones are equipped with only one type of such equipment.
Replaceable working single-bucket excavator equipment is designed for various earthworks. A straight shovel is used to develop the ground located above the level of the excavator parking, in the process of digging the bucket moves upward from the excavator.
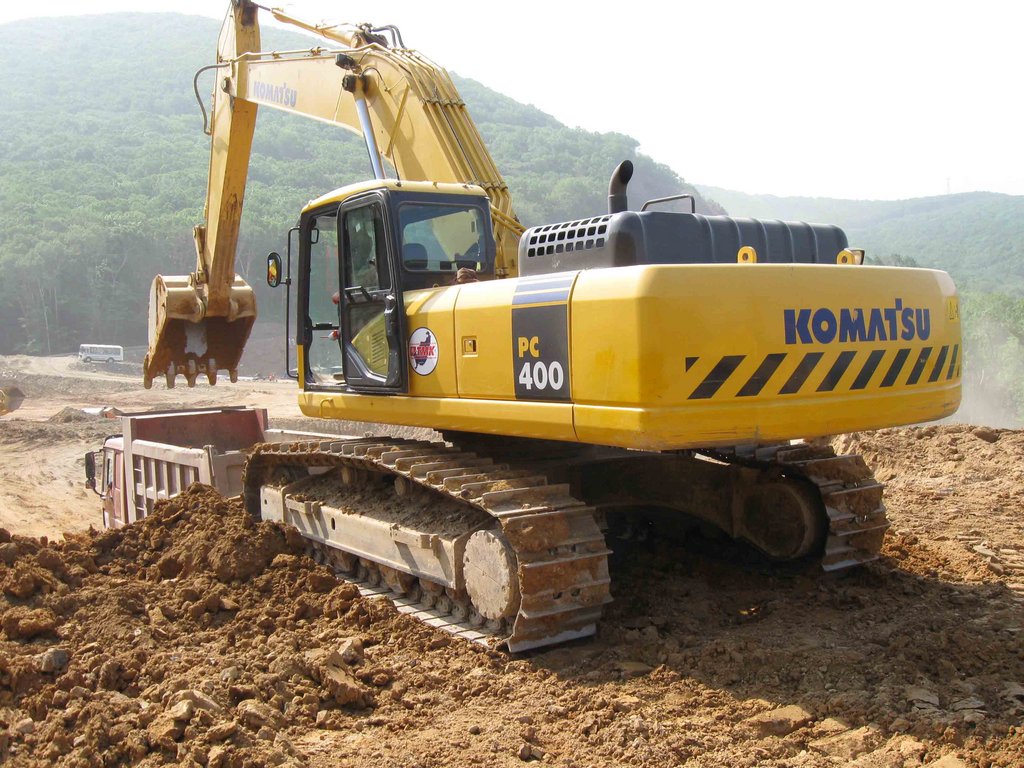
Straight shovel (Fig. 1) hydraulic excavators of the 4th to 6th size groups are widely used and on mechanically driven excavators. She develops soils of I - III categories in the temperature range from -40 to +40 ° С
http://pandia.ru/text/78/236/images/image002_19.jpg "width =" 354 "height =" 227 src = "\u003e
Fig.2. Backhoe hydraulic excavator
1 - undercarriage; 2 - turntable; 3 - power plant; 4 - exhaust pipe; 5 - cab; 6 - arrow; 7, 9, 11 - hydraulic cylinders of a handle, a ladle and an arrow; 8 - a handle; 10 - bucket.
Get the full textBackhoe boom is welded from alloy steel sheet. It is pivotally fixed in the lugs of the turntable, to which are also attached the hydraulic cylinders 11 of the boom lift. The rods of the hydraulic cylinders are pivotally connected to the boom, when extending the rods, the angle of the boom changes relative to the platform.
The handle is pivotally suspended at the head of the boom. In its rear part is pivotally fixed the rod of the hydraulic cylinder 7 of the rotation of the handle. On the other hand, the hydraulic cylinder is connected to the boom. Extending or retracting the hydraulic cylinder rod ensures that the handle rotates relative to the boom clockwise or counterclockwise. In the front part of the handle, the bucket 10 is pivotally mounted, which can be freely rotated by means of a hydraulic cylinder, 9. To increase the angle of rotation of the bucket, the hydraulic cylinder is connected with it by a special articulated multi-link.
The return shovel is provided with interchangeable buckets of various shapes and capacities. Reverse shovel buckets most often make a welded structure without opening bottom. Upper belt bucket has a gain. In the area of the cutting edge of the front wall, pockets are welded to install the teeth, the number of which depends on the width of the bucket and the type of work for which they are intended. Often, the teeth are installed on the side walls, mainly when developing the soil in trenches. These teeth cut the walls of the trench, eliminating jamming of the bucket in it. The front wall in the lower part has a perforation to remove water in the development of waterlogged soils.
When mounted on excavators of a composite boom, the main and extending parts of the boom are interconnected pivotally, but to prevent them from turning relative to each other, additional traction is established between them. It has several fixed positions, which allows, if necessary, to change the angle between the main in the extending parts of the boom.
Develop the ground by turning the handle relative to the boom or turning the bucket relative to the handle.
Backhoe shovel with mechanical (cable) drive (Fig. 3) is slightly different from the back shovel of a hydraulically driven excavator.
shovel "
1 - running gear; 2 - turntable; 3 - racks; 4, 6 - ropes; 5 - block racks; 7 - the handle; 8 - jet thrust; 9 - backhoe bucket; 10 - traction rope.
The bucket 9 (Fig. 3) is fixed to the handle 7, which is achieved by installing the reactive rods 8 between the rear wall of the bucket and the handle. The working movements of the bucket are provided by changing the length of the traction 10 and lifting 6 tackle.
Dragline (Fig. 4) is designed for the development of soil mainly below the level of the parking of the excavator. Due to the elongated lattice boom, the dragline can work on a large digging radius; therefore, it is used for extracting large trenches, digging canals in irrigation construction and performing loading and unloading operations on bulk materials. This is the only type of working equipment that is mounted exclusively on power-driven excavators.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/236/images/image005_9.jpg "width =" 444 "height =" 306 src = "\u003e
Fig.5. Working equipment grab
1 - the basic part of the boom; 2 - thrust; 3 - hydraulic cylinder handle; 4 - arrow head; 5 - the handle; 6 - swivel head; 7 - frame; 8 - slider; 9 - thrust; 10 - bucket jaw; 11 - bucket teeth; 12 - axes.
For the attachment of the grapple use the base 1 and the head part 4 of the boom, connected by a brace 2, and the handle 5 of the reverse shovel. The grab bucket consists of two jaws 10 with teeth 11 and two rods 9. The bucket suspension mechanism includes a frame 7, a swivel head 6, a hydraulic cylinder located inside the frame, and a slider 8. The width of the bucket jaws depends on the conditions of use. Grab bucket, depending on the conditions of rotation in the plan can be attached to the handle in three ways: not turning, part-turning and full turning. For any kind of connection, the bucket can swing in the longitudinal and transverse directions.
When digging, the initial position of the claws of the clamshell bucket is open. The necessary pressure is created by the hydraulic cylinders 3 of the handle control. The jaws are closed by a hydraulic cylinder located inside the frame. The swivel head rotates the bucket in the horizontal plane by 180, which increases the operational capabilities of the equipment.
Get the full textWhen extracting deep (up to 30 m) wells, grab equipment is used on a pressure rod, designed for excavators of the 5th and 6th size groups.
When equipping with a mechanically driven excavator grab, an elongated lattice boom is mounted on it (Fig. 6). The bucket jaws are closed with a pull rope, and the height is changed by a lifting rope.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/236/images/image007_8.jpg "width =" 502 "height =" 252 src = "\u003e
Fig. 7. Replaceable working equipment of single-bucket excavators:
a-straight shovel; b-reverse shovel; V-dragline, g - grab; d - pile driver; e - crane; W - strug; e - soil ripper
Additionally, drilling, pile driving, crane and other types of equipment can be installed.
By type of suspension working equipment (Fig. 8) distinguish excavators with flexible elements (mainly ropes) to hold and actuate the working equipment ( flexible suspension) and with rigid elements - mainly hydraulic cylinders ( stiffer suspension).
http://pandia.ru/text/78/236/images/image009_21.gif "width =" 179 "height =" 154 src = "\u003e
Fig.9. The basic part of the shovel excavator and the main types of interchangeable working equipment
1 - counterweight; 2 - power plant; 3 - cab; 4, 7 - exhaust pipe; 5 - turntable; 6 - slewing bearing; 8 - running gear
The choice of the type of excavators, its model and type of working equipment is made on the basis of soil and climatic conditions, the volume and timing of the work, the parameters of earthworks, the distance of soil transportation and a number of other factors.
The main provisions when choosing an excavator are also: the choice of a rational scheme of work; selection of rational technological parameters of the face; rational use of interacting machines (excavators and dump trucks).
The type of working equipment is specified depending on the nature of the work (Table 1.1).
Table 1.1.
Scopes of the replaceable working equipment of one-bucket excavators
Off-road "href =" / text / category / bezdorozhmze / "rel =" bookmark "\u003e off-road and on dispersed objects.
Lecture number 2. Multi-bucket (trench) excavators. Bulldozers.
Multi-bucket or, as they are also called, trench excavators are earth-moving machines that perform all the operations of the technological cycle (developing the soil, transporting it to the surface and unloading it into a dump or vehicle) at the same time.
They are self-propelled earth-moving machines of continuous action, which, in their translational motion, tear open a longitudinal excavation behind them — a trench of a certain depth and width. Unlike single-bucket trenches constantly move during operation and separate the soil from the array using a group of buckets or scrapers continuously moving along a closed contour and at the same time evacuating it from the trench to the dump or to vehicles using the dump device. Thus, the performance of trench excavators, constantly moving during operation and separating the soil from the array using a group of buckets or scrapers continuously moving along a closed contour, is 2-2.5 times higher than that of single-bucket machines, with higher quality of work and smaller power consumption per 1 m3 of the developed soil. Moreover, trench excavators are able to effectively develop both non-frozen and frozen soils. Types and parameters of trench excavators are determined by GOST. The main parameter is taken to be the depth of torn-off trenches.
Get the full textTogether with other types of machines and auxiliary equipment, continuous excavators form technological complexes designed to perform various types of work during the construction of oil and gas pipelines, irrigation and drainage canals, installation of drainage systems, closed pressure conduits, and non-metallic mining and processing. building materials, construction of underground cable lines and power lines, other communications.
Trench excavators are classified according to the following main features:
- as a working body - chain (ETC) and rotary (ETR);
- according to the method of connecting the working equipment with the base tractor - with attached and semitrailer working equipment;
- according to the type of drive unit of the base tractor - on caterpillar and pneumowheel
- by type of drive - with mechanical, hydraulic, electric and combined drive.
The working body of chain excavators (Fig. 1) is a single-row or double-row freely sagging endless chain 5, envelope the inclined frame 7 and carrying buckets or scrapers 6.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/236/images/image012_6.jpg "width =" 387 "height =" 279 src = "\u003e
Figure 2. Diagram of a rotary trench excavator
The width of detachable trenches of a rectangular profile depends on the width of the bucket or scraper and the location of the cutting elements on them.
Interchangeable bodies with different widths and number of buckets (scrapers) for digging trenches with different profile parameters can be hung on the same basic tractor. To obtain a trapezoidal profile, the working bodies of the chain and rotary trench excavator are equipped with active and passive slope formers.
Active offenders of double-chain trench excavators (Figure 1, a) are obliquely located chains 8 with transverse incisors that reciprocate.
Passive rake of rotary machines made in the form of two inclined replaceable knives 13 (Fig. 2, a), rigidly fixed on the sides of the rotor frame. Skimmers are used when working in non-frozen soils with low bearing capacity.
For the development of frozen soils, chain excavators will be equipped with special interchangeable tools. When developing frozen soils, buckets of rotary excavators are equipped with special replaceable teeth reinforced with carbide wear-resistant plates. The digging of frozen soils is carried out at lower speeds of the tractor and the working body, so the performance of the excavator is reduced by 3-5 times.
During operation, the chain or rotor moves in the plane of movement of the tractor. The soil is separated from the array and the working body is filled by the message of the chain or rotor of two combined digging movements: the main one is translational relative to the frame (for the chain) or rotary around its axis (for the rotor) and the feed movement is translational in the direction of the machine movement. The main movement contributes to the separation of the soil layer and is directed along the tangent to the digging trajectory. The feed motion regulates the thickness of the soil layer to be separated and is directed perpendicularly (normal) to the tangent. The ratio of the speeds of these movements determines the trajectory of movement of the cutting elements of the working body in the longitudinal-vertical plane, which is an inclined straight line in chain excavators (Figure 1, b) and trachoid in rotary (Figure 2, c).
The chip thickness separated by the chain working body is almost constant along the entire height of the face. Rotary working body separates chips of variable thickness, reaching a maximum value at the level of the axis of rotation of the rotor. The speed of movement of the working body and the feed rate (movement of the machine) is selected so that, regardless of the depth of the trenches, 100% bucket filling is ensured. The working speed of excavators when digging trenches is infinitely adjustable over a wide range depending on the working conditions, physical and mechanical properties of soils and is 5-800 m / h for chain machines and 10-500 m / h for rotary machines. The speed of movement of the working body is largely determined by the method of unloading the buckets of rotary excavators and dynamic loads acting on the chain, the chain. The speed of the working body of chain machines does not exceed 2.4 m / s. The working bodies of modern trench excavators have several speeds, and lower speeds are used when digging trenches in heavy thawed and frozen soils. On both types of machines used gravitational method of unloading under the action of its own weight of the soil.
Unloading of the soil separated from the massif and lifted from the trench is performed on double-chain excavators on the lateral dump conveyor belt 3 (Figure 1, a) when turning the buckets b or scrapers relative to the drive sprockets of 4 chains. Evacuation of the soil raised by scrapers to the surface on both sides of the trench in single-chain excavators is carried out by two screws 9 (Fig. 1, c) of a screw dump conveyor driven by the working body chain or a scraper conveyor. In rotary excavators (Figure 2, a), the soil from the buckets 11 is unloaded when they reach the upper extreme position above the transverse dump conveyor belt 7 located inside the rotor 12. The front bottom shield 6 prevents the soil from the buckets from pouring into the internal cavity of the rotor when they are raised. Belt conveyors of chain and rotor excavators throw soil in the right or left side parallel to the trench in the dump or in vehicles (Fig. 1, a) and (Fig. 2, c). Usually conveyors have a curvilinear shape, which, in combination with a rather high belt speed (3.5 ... 5 m / s), provides the necessary lifting height and soil drop.
Get the full textThe depth of the severed trench at the chain and rotary excavator is regulated by a hydraulic lifting mechanism, which also transfers the working member from transport position in working and vice versa. The working body of the chain excavator is connected to the hydraulic cylinders 1 (Fig. 1, c) of the lifting mechanism by the lever system 2 and is buried by them in the ground, held in a predetermined position and recessed from the ground forcibly.
The working body of the rotary excavator is suspended on plate chains 4 and 5 (Figure 2, a) of the lifting mechanism and is buried in the ground to a predetermined level of the floor by its own force of gravity, and is held in a predetermined position and recessed by hydraulic cylinders 2 and 3. both ends of the working body allow the rotor to be buried and removed from the trench when the excavator is stationary and to work in cramped urban conditions, characterized by the presence of a dense network of roads communications, etc. The back of the working body of a rotary excavator when digging is located and hanging or resting on a pneumatic wheel. A stripping device 10 is installed behind the rotor for stripping the bottom of the trench from crumbling soil.
As regards designation, alpha-numeric indexing is adopted for continuous excavators. The letter part of the index characterizes the type of working body: ETR is a rotary type working body; ETC - the working body of the chain type. The first two digits reflect the digging depth, dm, the third - the serial number of the model; for excavators rotary boom the first three digits - the capacity of the bucket, l, the fourth - the serial number of the model; for cross-diggers, the first two digits are the bucket capacity, l, and the third is the model number. When upgrading, after the numbers are added letters in the order of the Russian alphabet.
For example, the ETR-252A index means: a trench rotary excavator with a digging depth of up to 25 dm, the second model, the first modernization.
The main directions of further improvement of continuous-action excavators is to increase their performance (productivity and reliability), expanding the versatility and scope.
Performance as one of the most important operational characteristics can be improved by increasing the unit capacity of power plants for driving working equipment and improving the development work processes in soil transportation.
Over the past five years, continuous excavator capacity has increased by an average of 20%, and for certain categories (canal diggers) - by 30-40%.
Improving workflows involves a complex effect on the ground by the working bodies of the intensifying action, the use of the inertial method of unloading the sleeves, the use of the effect of the collapse of the soil. The adoption of these measures leads not only to an increase in productivity, but also to a decrease in specific indicators of application.
The reliability of continuous excavators is enhanced by the use of modern components and materials, more advanced design solutions, as well as a high level of their unification.
Expanding the versatility and scope of continuous excavators is achieved by using various types of interchangeable working equipment (for example, for the development of frozen soils, fragments of wide or narrow trenches, etc.).
In the design and operation of continuous excavators, technical performance for each soil category and technical performance averaged over soil categories are distinguished.
The technical capacity of continuous excavators for the soils of one group, Fri, m3 / h is
vx - working speed of the excavator, m3 / h;
F is the cross-sectional area of the notch, m2.
In determining the technical performance of averaged over categories of soils, take into account the proportion of soil of each category in the overall development of machines and performance for each category.
Bulldozers.
Bulldozers are mounted on a basic tracked or pneumowheel tractor (two-axle wheeled tractor), which includes a blade with knives, a pushing device in the form of bars or a frame and a blade control system. Modern bulldozers are structurally similar machines, basic tractors and attachments which are widely unified.
The most common bulldozers with a non-rotary blade, with a rotary blade, bulldozers-rippers, as well as bulldozers, loaders.
Bulldozers with rotary dumps are hard (Fig. 1, a) and hinged (Fig. 1, b) push bars.
http://pandia.ru/text/78/236/images/image014_5.jpg "width =" 433 "height =" 276 src = "\u003e
The first type of bulldozer is equipped with a blade 1, to which two pusher bars 7 are rigidly welded, covering the outside base tractor 8. The bars are pivotally mounted on the crossbeam 6, bolted to the tractor frame. A subframe 5 is also attached to it in front, to which one double-acting hydraulic cylinder 3 is hinged through the carrier frame 2. Two high-pressure hoses 4 are connected to the hydraulic cylinder, which connect it to the hydraulic system of the tractor. It consists of a hydraulic pump, hydraulic distributor, hydraulic tank and hydraulic lines. By applying the oil pressure developed by the hydraulic pump into one cavity of the hydraulic cylinder, the dozer blade is raised, into the other - it is lowered. The blade in the cutting area is equipped with removable knives 9.
The second type of bulldozer includes rectangular pushing bars 7, which are hinged on one side by means of cart hinges 18 and connected to tractor trolleys 16, and on the other side - universal hinges with a blade 1.
To preserve a certain position and cut the ground with minimal energy, the blade on one side is held by the hydraulic slider 19, on the other - by a rigid draft. Gidraskos connected to the hydraulic system of the tractor and carries the tilt of the blade in the transverse plane. The bulldozer is equipped with two hydraulic cylinders 3 lifting - lowering, which are also connected with the hydraulic drive of the tractor.
The lifting and lowering cylinders with the 3 cylinders are installed in the lower 7, working II, transport III and intermediate positions.
A tractor, tractor or special chassis can be used as a base vehicle. The engine through the clutch 11 or the torque converter drives the gearbox 13 and the rear axle 14. The sprockets 15 transmit rotation from the engine to the tracks 17, which move the whole car forward or backward.