Tractors in the USSR. The very first tractor in the world
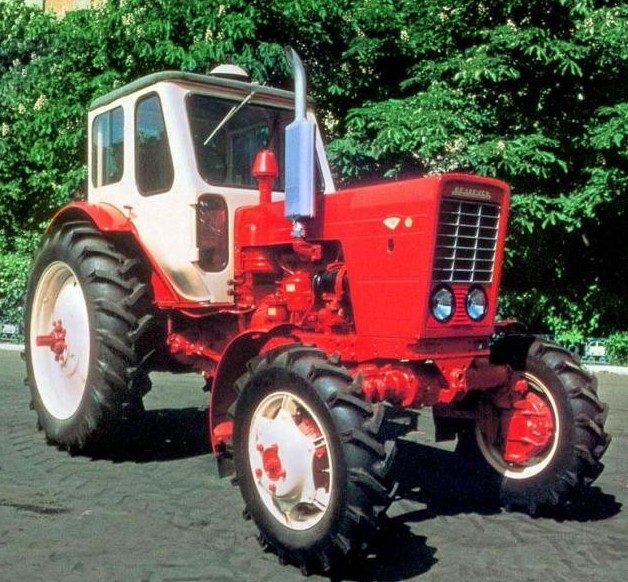
The day of November 4, 1950 was marked in the annals of labor exploits of Belarusian tractor-builders as the day of the commencement of the serial production of tractors KD-35.
Tractor «KD-35»
The first-born of Minsk tractor-builders enjoyed great and well-deserved success among the field workers. Tractors KD-35 were equipped with 4-cylinder diesel engines with a power of 37 hp. the engine was very economical. So, for one hectare of plowing under average conditions, he spent 13 kg of fuel. The fuel tank of the tractor contained fuel for 10 hours of trouble-free operation. Experimental models of the machine for 10 hours plowed up to 6 hectares of land.
The tractor was produced not for long, only 9 months, until August 1951. For this time 406 cars came off the assembly line. Production of diesel engines and start-up engines for the KD-35 at the plant did not stop. They were delivered to the Lipetsk Tractor Plant. Later this engine was used on the wheel universal tractor, over which the factory designers had been working since 1948.
MTZ-1 and MTZ-2

The universal wheeled tractor "Belarus" was intended for work with hinged, semi-mounted and trailed agricultural machines. The construction of the tractor was carried out in two modifications: MTZ-2 for inter-row processing of low-stemmed crops with a matching trace of the front and rear wheels and MTZ-1 for processing high-stemmed crops with closely spaced front wheels. The work of the tractor was provided on wheels of two options: rubber bottles of low pressure and wheels with a rigid steel rim with spurs. The tractor had an independent power take-off drive, a hydraulic system for lifting attachments, and was equipped with a removable adjustable trailer attachment.
The day of July 18, 1949 became significant for all tractor factories. The first Belarusian wheeled tractor of the factory design came out of the gates of the experimental shop. The prototype of a wheeled tractor later became the basis for the creation of the MTZ-2 serial vehicle.
In 1949, 7 prototypes were produced, which were subjected to long factory tests.
The historical date for the collective of the plant was 1953, when the assembly line ended on October 14 mTZ tractors-1 and MTZ-2, created by factory designers. These machines determined all further specialization of the plant on the production of wheeled universal-tractors.
KT-12 and KT-12A
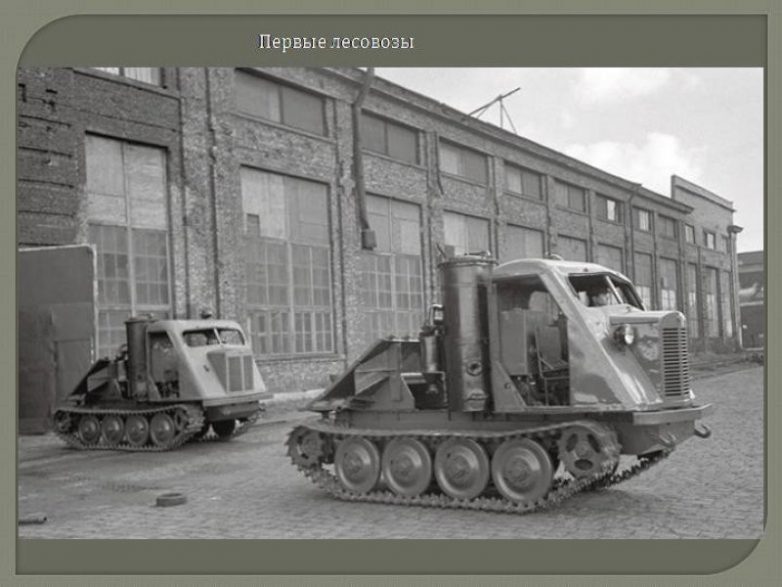

In the spring of 1951, the MTZ team received a very important government task - to master the production of skidders, the great need for which was experienced by the logging industry.
Gas generator KT-12 is a special tracked vehicle designed for skidding. He appeared in the USSR in the first post-war years. There were no analogues to him in any country in the world. Previously skidding was carried out by horse-drawn transport (on horses), by manual or mechanical winches. The KT-12 tractor was designed by designers of the Kirov plant in Leningrad in cooperation with scientists from the Leningrad Forestry Academy. The KT-12 tractor was produced at the Kirov plant until 1951. Now it was necessary to establish its production at the Minsk Tractor Plant. To resolve all organizational issues, only three months were set aside. So for a short history of its existence, MTZ had to master the second (after KD-35) car, and besides its own design.
On August 15, 1951, the first shipment of skidding machines KT-12 came off the main assembly line of the tractor-assembly shop. In the production process, the tractor was upgraded, aimed at improving the performance of the machine. Within a short time, factory designers, having changed a number of units and parts, increased the warranty period of the machine by 1.5 times.
TDT-40

In the early 1950s, the Ministry of Forestry of the USSR stated that KT-12A with its gas-generator plant did not meet the increased requirements.
Given the shortcomings of the tractor, the ministry decided to abandon this machine altogether and raised the question of creating a new, more reliable logging tractor with a capacity of 60 hp instead.
Analyzing the situation, the designers and management of MTZ recognized the advisability of creating a more powerful skidder, but they also expressed the opinion that one powerful class of the tractor for all zones in all logging operations would be uneconomical. It was necessary to design a skidder tractor of medium power, which can be created on the basis of KT-12A, installing a diesel engine of the wheeled tractor "Belarus" on it.
In 1954, developed the design of this tractor, assigning him the brand TDT-40. The tractor was intended for hauling the whips directly from the cutting area. In addition to skidding, he was indispensable in forestry, on all kinds of transport operations in off-road conditions. According to the results of operational tests in 1955, the interdepartmental commission ascertained that the TDT-40 tractor is very necessary for the Ministry of Forestry of the USSR and it is expedient to set up its production in a short time. According to the decision of the Ministry of Tractor and Agricultural Machine Building of the USSR, in May 1956 MTZ started serial production of diesel tractors TDT-40. By the end of the year, their number had reached 3430. In the same year, design work was completed and the first experimental D-50 diesel engines for a prospective tractor were manufactured. The new engine exceeded the power of its predecessor by 10 hp, was smaller in size and 350 kg lighter.
TDT-54 and TDT-60
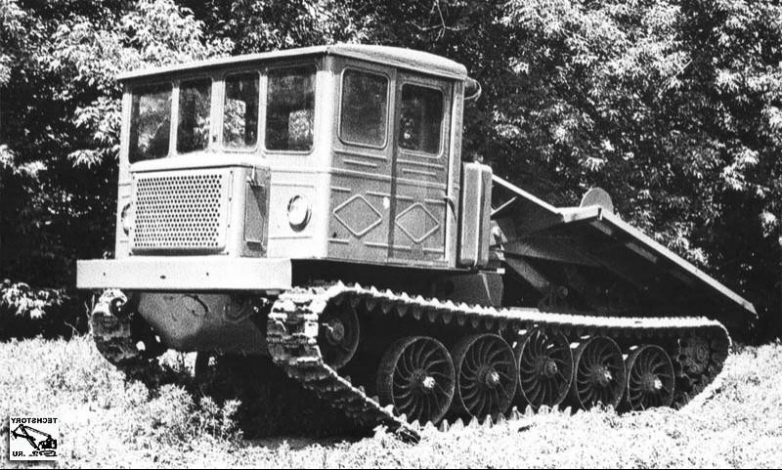

To work in the forests of the Urals, Siberia and the Far East, more powerful logging tractors were required than TDT-40. The project of this tractor was commissioned by the Ministry of Automotive and Tractor Industry to be developed by designers of Minsk of a tractor factory together with the Research Institute of Automotive and Tractor Institute (NATI) on technical requirements of the Ministry of Forestry of the USSR. Initially, the tractor was given the brand TDT-54. To improve performance, the D-54 diesel engine with a capacity of 54 hp was used. tractor DT-54 of the Kharkov Tractor Plant.
After the skidder tractor TDT-54 received the "good" of the state commission for mass production, a detailed analysis of each node was made. As a result, it was decided to modernize most of its nodes. In addition, the diesel D-54 is boosted to 60 hp. and as a result the tractor received a new name TDT-60. Four of its prototypes in 1956 passed all state control tests in production conditions in the Vakhtansky Lespromkhoz of the Gorky Region.
Simultaneous production of two completely different in design and designation of tractors MTZ-2 and TDT-40 put the plant in a difficult position. The plant did not have the opportunity to simultaneously develop two different production lines: the MTZ-2 tractor, which is extremely necessary for agriculture, and the TDT-40 tractor, in which the Ministry of Timber Industry of the USSR was interested.
Technical and economic calculations showed that the Minsk plant should specialize in the production of wheeled universal-tilled agricultural tractors.
The management of the plant made a proposal to the ministry to stop the MTT production of the tractor TDT-40, passing it to the plant in Karelia, and the developed TDT-60 model to the Altai Tractor Plant. Decree of the Government of the USSR of January 30, 1956 for the production of tractors TDT-40, the Ministry of Tractor and Agricultural Machinery of the USSR was transferred to the Onega Machine-Building Plant in Petrozavodsk. Before that, he was in charge of the Ministry of Forestry of the USSR. In 1957, without stopping the production of TDT-40 at MTZ, the tractor began to be developed at the Onega Tractor Plant. Until 1958 MTZ produced 12977 tractors TDT-40. In 1957, the TDT-60 tractor was put into serial production at the Altai Tractor Plant. This concludes the history of skidders at MTW, where for 7 years they were produced in parallel with the wheeled tractors.
MTZ-5
Time passed, and with it requirements for the MTZ-2 tractor were growing. He had a low transport speed (13 km / h), insufficient number of gears. The tractor began to lag behind in terms of fuel efficiency and material consumption. It was necessary to increase the reliability and life of the machine. Summarizing the experience of operating tractors MTZ-2, taking into account the state and level of tractor construction, the team of designers of the plant in 1955-1956. carried out work on the fundamental modernization of the machine. This allowed not only to eliminate existing shortcomings, but also expand the scope of the machine, improve technical and economic indicators. So there were new models of the tractor "Belarus": MTZ-5 (model of 1956). MTZ-5M and MTZ-5L (samples of 1957). MTZ-5, having great versatility, had independent power take-off drive, more powerful and economical engine, hydraulic hinged system with remote cylinders.
MTZ-5S
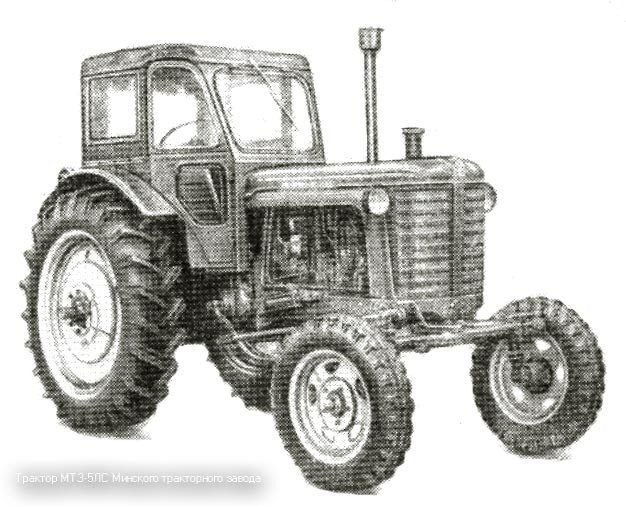

In 1959, after the completed design improvements, the production of MTZ-5LS and MTZ-5MS tractors began. The letter "C" in the designation meant "high-speed". Engine power was increased to 48 hp. (instead of 45) by increasing the speed to 1600 rpm (instead of 1500). The range of operating speeds was set within 5-10 km / h. The number of gears in the gearbox increased from four to five. In other respects, there were no fundamental differences from tractors MTZ-5L and MTZ-5M. Production high-speed machines began in 1959.
MTZ-7
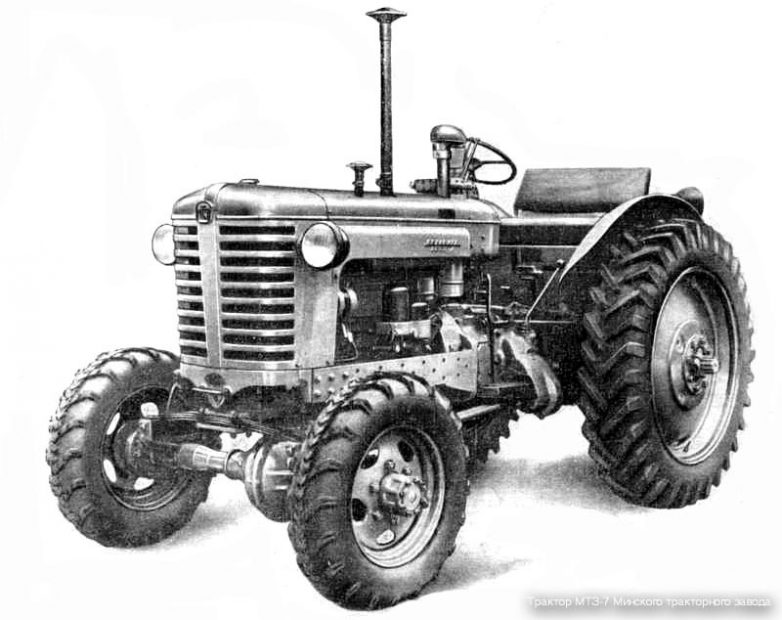

In 1958, the design was improved, prototypes were manufactured, tests were carried out and drawings for tractor MTZ-7 of cross-country terrain with four driving wheels were issued for preparation of production. The first design of the tractor was developed with the use of the front drive axle from the military passenger car GAZ-67, did not have the adjustable width of the track of the front wheels, and therefore did not provide for the performance of tilled work. Due to the insufficient strength of the GAZ-67 bridge, the tractor did not withstand the tests. The problem was solved after the tractor was fitted with the GAZ-63 driving axle. Production of a cab for Belarus tractors was started. The design of the removable cab allowed its use on the tractor completely closed and in the form of an awning. With the use of such a cabin, the working conditions of the tractor operator have significantly improved.
MTZ-7M
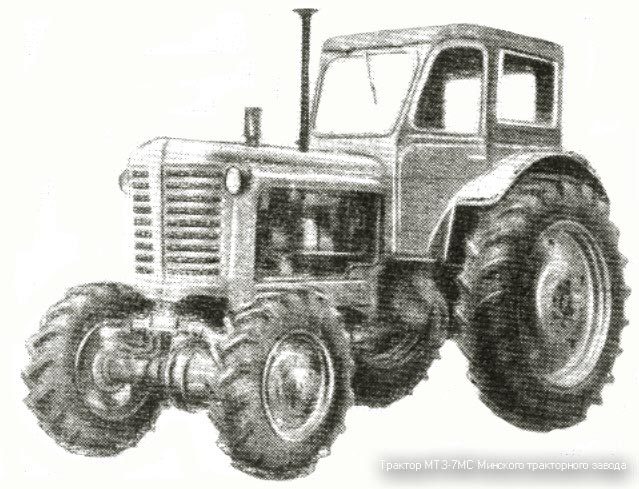

In 1959 MTZ-7M, MTZ-7MS and MTZ-7LS tractors were put into series production, though for a short while, the main goal was to get more information on how good the tractors with the four driving wheels in different climatic and soil conditions. In the same year, the plant produced 169 tractors, and in 1960 - 1277.
A total of 279 MTZ-7 tractors were produced. Their production was discontinued in 1961.
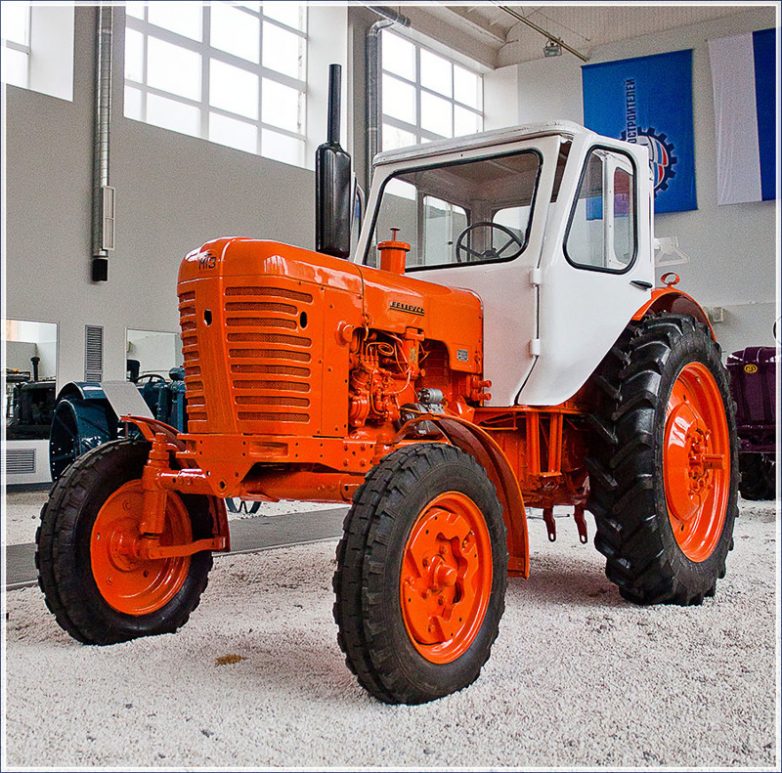
MTZ-50

Until 1959, MTZ had the capacity to produce only 18,000 wheeled tractors such as MTZ-2, 6000 tracked tractors TDT-40 and 40,000 D-40 engines.
There was also a serial production of tractors MTZ-5, MTZ-5M, MTZ-5L, work was carried out on their modernization, and in 1956 the designer basically designed a new diesel engine for the future tractor MTZ-50. The creation of a new prospective tractor was of great interest not only at the plant, but also in the country. The technical design of the tractor was completed in 1957 and approved in the Head Scientific Tractor Institute.
In 1958, the experimental workshop produced several prototypes of the tractor. Based on the test results, the Scientific and Technical Council of the "Soyuzselhoztekhnika" recommended a universal wheeled tractor of class 1.4 "Belarus" MTZ-50 to batch production. The MTZ-50 tractor was equipped with a diesel engine of 55 hp, the weight of the car was reduced by more than 400 kg. In the tractor transmission, a 9-speed gearbox was installed, providing a range of speeds ranging from 1.65 to 25 km / h.
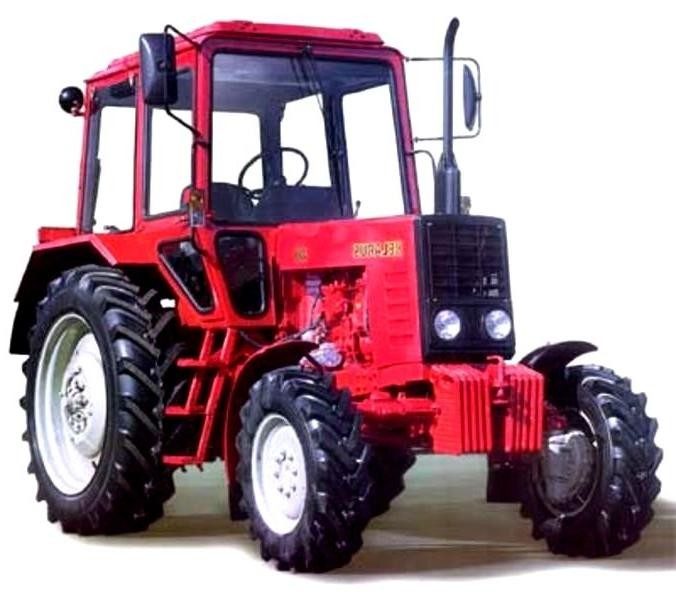
MTZ-52

In 1959, based on the results of state tests, the design of the MTZ-50 tractor was finalized, the necessary documentation was issued and put into production preparation. On the basis of the tractor MTZ-50, a modification of the high-cross-country tractor with four driving wheels was developed - MTZ-52. due to lower losses on slippage, the fuel efficiency of the MTZ-52 tractor on all operating limits is higher than that of the MTZ-50 tractor.
November 14, 1959 the Council of Ministers of the USSR issued a resolution "On the organization of specialized production of wheeled tractors, motorcycles and engines to them at the enterprises of the BSSR." One of the points of the document stated:
2. To require the Council of Ministers of the BSSR to ensure:
c) the production of tractors "Belarus" MTZ-50 starting from 1961 and tractors MTZ-52 starting from 1962 with the completion in 1965 of the production of tractors of these brands to 75,000 units per year.
The Council of the National Economy of the BSSR, by its decision of December 19, 1961, decided:
3. For the non-stop transition to the new model of the tractor, to provide for the gradual introduction of the MTZ-50 tractor, for which: - to approve the tractor MTZ-50 PL for the production at the MTZ for 1961-1962 on the chassis of the MTZ-50 tractor with the serial engine D-48 PL, boosted to a power of 50 hp. - production of tractors MTZ-50 with engine D-50 to begin with the IV quarter of 1962.
1960 year. The plant is under reconstruction. In the shops new equipment was installed, the obsolete equipment was replaced. The MTZ-50 tractor was revised, the necessary documentation was produced and put into production preparation. On the basis of the MTZ-50 tractor, a team of designers of the plant developed a modification of a high-cross-country tractor with four driving wheels MTZ-52. This machine has supplemented the basic model, expanded the field of its application in agricultural and transport operations, especially in conditions of high soil moisture.
MTZ-50X

In 1963, design development was completed and prototypes of the MTZ-50 cotton-growing tractor were produced. The tractor is designed for cultivating and harvesting cotton in a four-row machine system with a spacing of 90 cm. The MTZ-50X tractor was fundamentally different from the MTZ-50 tractor with a front axle design - it had one steering wheel. The end gear unit with additional gears was also modified. All necessary tests of the tractor were completed in 1966, after which preparations for its serial production by the factory services began. Production of the MTZ-50X tractor lasted eight years: from 1969 to 1977. Then the production was transferred to the Tashkent Tractor Plant.
On the basis of the MTZ-50 tractor three caterpillar modifications were created, and the nodal unification with the MTZ-50 tractor was more than 62%. Crawler modifications were unified by 95-98%. In 1967, a version of the T-54B tracked tractor was launched in two versions: T-54B-C1 with a track width of 950 mm for cultivating vineyards with a spacing of 1.8 m and more and a T-54B-C2 with a gauge of 85- mm for the cultivation of vineyards with row spacing 1.5 m.
In 1968, the production of the T-54L tractor began.
MTZ-80

In 1966, the Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR No. 606 on the creation of a universal tractor with a capacity of 75-80 hp was issued. traction class 1.4. such a tractor designers created by upgrading the tractor MTZ-50, giving it the brand MTZ-80/82. In the construction of this tractor, in addition to increasing the power of the serial engine, a significant number of improvements have been made.
In 1972, the state tests of the MTZ-80 / 80L tractor (with electric start and start-up engine) were completed. Tests showed that the number of machines and implements mounted with the tractor increased to 230 items. High speed (up to 35 km / h) made it possible to use the tractor in transport operations more rationally.
In 1974, the plant started serial production of MTZ-80. The tractor was designed as a base, taking into account the development on it of a new family of unified, energy-saturated tractors, both wheeled and caterpillar. The main differences between MTZ-80 tractor and MTZ-50 tractor were the following:
A reduction gearbox was installed in the gearbox, doubling the number of gears - 18 front and 4 reverse gears;
In the clutch coupling damping springs were introduced, the design of the flywheel was changed - it became flat, which improved the ventilation of the entire clutch compartment and the cleaning of the cavity from the wear products of friction surfaces;
Introduced a speed reducer - gear reducer, providing an expansion of the speed range of the tractor. Its application allowed the tractor to move at speeds up to 1.3 km / h;
Has undergone a change and automatic locking differential rear axle. Now the lock could be carried out on the tractor;
The change in the design of the rear PTO drive made it possible to obtain two rotational speeds instead of one;
Modernized and hydro hinged system. It is equipped with a hydraulic tow hitch (FGV), power and position regulator. The lifting capacity of the system is increased to 2000 kg (instead of 1500) by increasing the pressure in the system from 130 to 160 kg / cm2;
The Minsk Motor Plant was engaged in the modernization of the engine. The engine had two modifications with start-up from the electric starter. The speed of the crankshaft was raised to 2200 rpm.
MTZ-82

MTZ-82 is almost identical to the 80th, but it has a full drive, as well as MTZ-52. The operational experience of MTZ-80 in various regions of the country revealed the need to create modifications of this machine, intended for a certain complex of agricultural and other works. The most popular modifications of the MTZ-82 tractor were: rice-growing MTZ-82R, low-traction MTZ-82N, steep-deflected MTZ-82K.
MTZ-100, MTZ-102

MTZ-100, MTZ-102 are identical to MTZ-80 and MTZ-82 tractors, but they are equipped with a more powerful diesel engine with a turbo-supercharging. Now, in my opinion, they are removed from production and replaced with more modern models.
During its inception, the Young Country of Soviets paid close attention to the development of tractor construction. After all, the agriculture of a still not strengthened state needed an accelerated rate of mechanization. But their own factories, which would have produced tractors of the USSR, had not been built yet.
In 1920, VI Lenin, realizing the urgent need to increase the productivity of rural labor, signed a decree "On a single tractor farm." And two years later the production of tractors was started in the USSR. The first units were low-power and technically imperfect. However, thanks to the constant adoption of measures aimed at the development of this direction, a decade later, in the issues of the construction of profile production, a real breakthrough came.
First-born of Russia
Our country has always been rich in talents. She was famous for her inventors. There were some among them who worked in the field of creating agricultural machinery.
The question of the mechanization of agriculture was raised in the 18th century. agronomist IM Komov. By the middle of the 19th century. DA Zagoyaksky and VP Guryev developed steam tractors intended for plowing. The first such unit on a caterpillar track was assembled and tested in 1888 by FA Blinov.
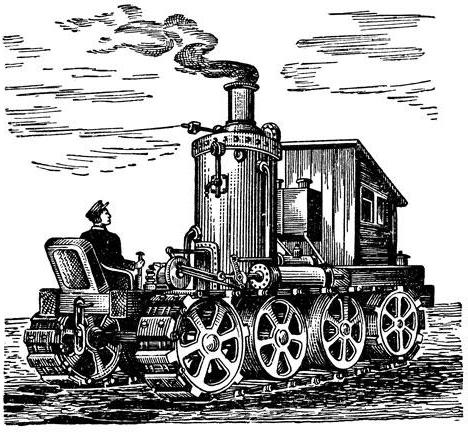

However, the official date of the appearance of the Russian tractor construction is considered to be 1896. It was then at the fair in Nizhny Novgorod that the assembled public was shown the world's first steam tractor on caterpillar tracks.
By the beginning of the 20th century. designer JV Mamin, invented a compression-free engine that worked on heavy fuel. He was great for working vehicles. The first tractor, in which an 18-kilowatt internal combustion engine was installed, was assembled in 1911. This unit was named very patriotically - "Russian". After the upgrade, a 33 kW motor appeared on this tractor. This gave him more power. The small-scale production of such tractors was mastered at the Balaklava plant. This equipment was manufactured privately in Kolomna and Bryansk, Kharkov and Rostov, Kichkasse and Barvenkov, as well as in some other settlements. However, the total number of tractors produced in Russia was so small that it could not have a significant effect on the state of affairs in agriculture. By 1913 there were 165 tractors in the country. However, the Russian Empire actively imported agricultural machinery. Already by 1917, 1500 were imported to the country.
"Kolomenets-1"
The principle of creating a single tractor farm, which was laid by Lenin, could be realized not only through the production of "iron horses", but also by the adoption of a set of measures that contributed to the organization of a testing and research base, as well as solutions for organization and repair, training of masters and instructors.
The first tractors of the USSR were produced in 1922 at the Kolomna plant. The head of this project was ED Lvov. He is considered the founder of the Russian school of tractor construction.
The first unit was named "Kolomenets-1". Without any doubt, it was a real symbol of the beginning a new era in the country's agriculture.
Zaporozhets
These are also the first tractors of the USSR. Their release took place in 1922 at the enterprise "Red Progress" in Kichkasse. However, this model proved to be imperfect. She had only one driving wheel - the rear wheel. In addition, the Zaporozhets tractors were equipped with a low-power 8.8 kW engine, which was able to accelerate the "iron horse" to just 3.4 km / h. This tractor had one forward gear, and the power on the hook was 4.4 kW. Despite such low characteristics, this vehicle was still able to greatly facilitate the work of collective farmers.
"Dwarf"
Mamin, the inventor, did not abandon his affairs either. He went down in history by issuing tractors of Russia and the USSR. After the improvement of his own pre-revolutionary design Mamin became the head of the project to create tractors of the family "Dwarf".
Their release began in 1924. Thus, agriculture received three-wheeled tractors "Karlik-1", equipped with one transmission. Their speed developed to 3-4 km / h. The tractors "Karlik-2" were also produced, equipped with a reverse.
Kommunar
At a time when the designers of the USSR were working on the creation of new, more sophisticated models, the government of the country organized the release of agricultural machinery under the license of foreign firms. Thus, in 1923 the Kharkov plant produced caterpillar tractors of the USSR, which were the heirs of the German units "Ganomag Z-50". As a rule, they were used for the needs of the army in the transportation of artillery pieces. These tractors served the country until 1945.
Fordzon Putilovets
All USSR tractors produced by the country in the early twenties of the last century were made either in small batches or in single samples. This did not satisfy the needs of agriculture. The first tractor in the USSR, which was launched into mass production, was produced in Leningrad in 1924. The workers of the Krasny Putilovets plant took up the case. These were the first wheeled tractors of the USSR, which massively descended from the conveyor.
As a model, Soviet designers took Fordson's American Ford model, which had been manufactured since 1917. These were the first tractors of the USSR (see photo below), which, thanks to their design, were of low cost. In addition, these units in their characteristics exceeded "Kolomenets" and "Zaporozhets".
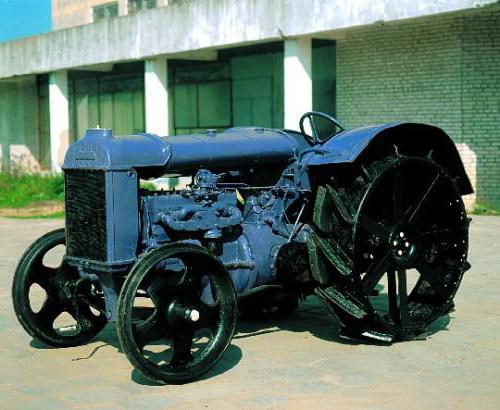

Models "Fordson-Putilovets" were equipped with a carbureted kerosene engine in 14.7 kW and developed a maximum speed of 10.8 km / h. Their power on the hook was 6.6 kW. In these tractors designers have provided a three-speed transmission.
This model was produced until 1933. During this period, about 36-49 thousand units came off the assembly line. Of course, the overwhelming majority of these tractors were sent immediately to the fields of the collective farms. However, the old tractors of the USSR have also proved themselves in construction, which lacked motorized traction equipment. On the basis of the "Fordzon-Putilovets" a crane was installed, which was used to carry out loading and unloading operations. Also these tractors acted as tractors for trailed rippers.
"Universal"
In 1934 a new model of tractors was launched at the Krasny Putilovets plant. In place of the first massive "Fordson" came "Universal". As a basis of its design was taken model of the tractor "Farmol", which was produced by the American firm "International". In terms of its parameters, it was slightly superior to its predecessor. Its kerosene carburetor engine had a power of 16 kW, the operating weight was 2 tons, and the speed reached 8 km / h. The tractor "Universal" went off the assembly line of the Leningrad plant until 1940. After that, its production was moved to Vladimir. Here, at the tractor plant, these units were produced from 1944 to 1955.
Construction of new production facilities
Over time, it became obvious that in order to provide the collective farms with the necessary agricultural machinery, special plants must be built. In them production capacities should be combined with research and design bureaus. The initiator of such a project was F. E. Dzerzhinsky. It was planned to equip the new enterprises with the most advanced equipment. This would allow the mass production of reliable and cheap models on caterpillar and wheel traction.
The history of the tractors of the USSR as objects of large-scale production began in Stalingrad. After that, the capacities of the Leningrad and Kharkov plants were significantly expanded. The largest enterprises appeared in Chelyabinsk, Barnaul, Minsk and other cities of the country.
Stalingrad factory
Stalingrad did not accidentally become a city in which from scratch the country built the first production facilities intended for the production of tractors. The city had a good strategic position, being at the intersection of the supply routes of the Urals metal, Baku oil and Donbass coal. In addition, there was a whole army of skilled labor in Stalingrad. By the way, according to this indicator the city has overtaken Taganrog, Kharkov, Voronezh, Zaporozhye and Rostov.
The decision to build a tractor plant in Stalingrad was taken by the government in 1925. And already five years later the famous wheeled units STZ-1 came off the production line. And after that, the factory produced a variety of models of wheel and caterpillar type. These are such tractors of the USSR as:
- wheeled SCTZ 15/30 (1930);
- caterpillar STZ-3 (1937);
- caterpillar SHTZ-NAITI (1937);
- caterpillar DT-54 (1949);
- caterpillar DT-75 (1963);
- caterpillar DT-175 (1986).
In 2005 Volgograd Tractor Plant (formerly STZ) was declared bankrupt. VGTZ became the legal successor of the enterprise.
DT-54
Crawler tractors of the USSR (see photo below) have received the widest distribution. They were represented by a variety of models, in number significantly exceeding wheeled.
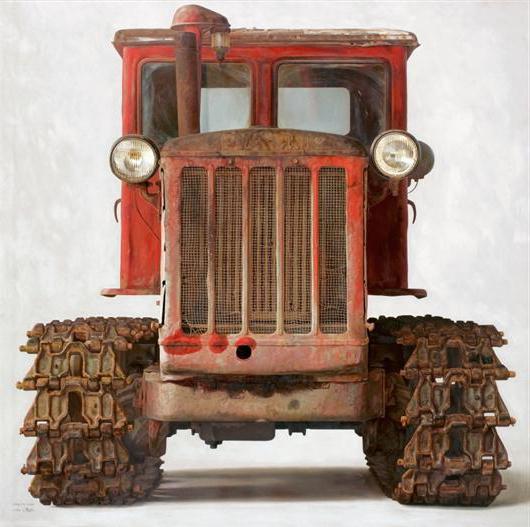 A remarkable example of agricultural technology is the DT-54 tractor. It was issued in the period from 1949 to 1979. This model came off the conveyors of Stalingrad and Kharkov, as well as the Altai plant. Tractor was filmed in many films. The most famous of them are "Kalina red", "It was in Penkovka", "Ivan Brovkin on virgin land". These tractors of the USSR as a monument can be found in dozens of localities.
A remarkable example of agricultural technology is the DT-54 tractor. It was issued in the period from 1949 to 1979. This model came off the conveyors of Stalingrad and Kharkov, as well as the Altai plant. Tractor was filmed in many films. The most famous of them are "Kalina red", "It was in Penkovka", "Ivan Brovkin on virgin land". These tractors of the USSR as a monument can be found in dozens of localities.
In the model DT-54 there is a four-stroke four-cylinder in-line liquid-cooling engine, which is rigidly mounted on the frame. Engine power of the unit is 54 liters. from. In its design, there is a three-way five-speed gearbox, connected by a cardan with the main clutch. The working speed of the tractor is in the range from 3.59 to 7.9 km / h. Its pulling force is 1000-2850 kg.
Tractor factory in Kharkov
In 1930, the construction of an HTZ began in the country, which was named after Sergo Ordzhonikidze. Production facilities were located fifteen kilometers east of Kharkov. The construction of this giant was carried out in just 15 months. Tractors of the USSR began to descend from the assembly line of the enterprise already on 01/09/1931. These were models borrowed from the Stalingrad plant - SKTZ 15/30.
However, the main task of the enterprise was the creation of a new domestic tractor Caterpillar, which has a capacity of 50 liters. from. The decision of this issue was worked on by designers under the leadership of PI Andrusenko. They developed a diesel engine, which would be able to equip all caterpillar tractors of the USSR.
In 1937, the plant began the production of a series of a new model, created on the basis of the SCPP-NATI. It installed a more productive and at the same time the most economical motor, working on diesel fuel.
After the war began, the company had to be evacuated to Barnaul. Later, the Altai Tractor Plant was established here. In 1944, after Kharkov was liberated, the production earned on the previous site. The series again included the legendary SCTs-NAITI.
The main models of tractors of the USSR, produced at the Kharkov plant:
- wheeled SCTZ 15/30 (1930);
- caterpillar SHTZ-NAITI ITA (1937);
- wheeled HTZ-7 (1949);
- caterpillar CTZ DT-54 (1955);
- tracked T-75 (1960);
- tracked T-74 (1962);
- tracked T-125 (1962).
In the 70s the plant underwent a radical reconstruction, without stopping the main production. After that, the production of wheeled three-toners T-150K and caterpillar T-150 was mastered. The first of them, on tests conducted in 1979 in the USA, showed the best characteristics among the world famous analogues. This proved that the tractors of the USSR were in no way inferior to foreign models.
At the end of the 1980s, KhTZ-180 and KhTZ-200 were manufactured at KhTW. They became 50% more productive than previous models and 20% more economical.
T-150
Tractors produced in the USSR were distinguished for their reliability. The same characteristic was possessed by high-speed universal units T-150 and T-150K. They have earned a good reputation because of their wide field of application. In addition to agriculture, they were used in road construction and transport. And until now you can meet these models, working in the fields, in conditions of difficult off-road and cargo transportation.
On the T-150 and T-150K there is a 6-cylinder turbocharged diesel engine, which has a V-shaped configuration and liquid cooling. The power of such an engine reaches 150 liters. from. The maximum speed is 31 km / h.
Tractor factory in Minsk
MTZ was founded on 29.05.1946. Until now, this plant is considered to be the most successful enterprise that has preserved production capacities from the times of the USSR, producing vehicles under the brand name "Belarus".
Until the moment the USSR ceased to exist, MTW produced almost 3 million units of wheeled and caterpillar vehicles. Among them are such brands as:
- tracked KD-35 (1950);
- tracked KT-12 (1951);
- wheel MTZ-1 and MTZ-2 (1954);
- caterpillar TDT-40 (1956);
- wheeled MTZ-5 (1956);
- wheeled MTZ-7 (1957).
In 1960, a large-scale reconstruction was begun at the Minsk plant. Simultaneously with the placement of new equipment, designers designed promising models. These were MTZ-50 tractors, as well as a more powerful unit with a hollow drive MTZ-52. Their serial production was adjusted, respectively, in 1961 and 1964.
![]()
Beginning in 1967, the plant began producing T-54B tracked modifications with various fillings. An unusual tractor MTZ was also produced at the enterprise.
The USSR needed cotton technology. In this connection the MTZ-50X modification was developed. It was characterized by a pair of front wheels, as well as increased clearance. Such models have been produced since 1969. The plant also supplied steep-angle MTZ-82K.
The next stage of the plant's activity was the development of the MTZ-80 line. Its mass production was established in 1974. After that special modifications of MTZ-82N and MTZ-82R were developed.
In the mid-1980s, the Minsk Tractor Plant mastered a technique with a capacity of more than one hundred horsepower. These are models such as MTZ-102, MTZ-142. At the same time, the low-power mini-equipment came off the assembly line of the enterprise, in the design of which an engine from 5 to 22 liters was envisaged. from.
Tractor factory in Chelyabinsk
This enterprise has made its significant contribution to the matter of equipping agriculture with the necessary equipment for it. And during the war the production of "self-propelled guns" and tanks was set up.
The construction of the ChTZ was started in an open field, located far from the main thoroughfares. When designing the plant, whose first production facilities were commissioned in 1930, the experience of similar US enterprises was taken into account.
01.06.1933 the first caterpillar tractor "Stalinets-60" came off the assembly line of ChTZ. In 1936, more than 61,000 of them were produced. To date, these tractors are considered obsolete. But in the 30s, by their characteristics, they were almost twice as high as those produced by STZ and KhTW.
Since 1937, more economical C-65 models have been produced at ChTZ. A year later, this tractor received the highest award - "Grand Prix" at an exhibition in Paris. You can see C-65 in the cinema. It was used in the filming of the famous movie "Tractor".
In 1946, the plant underwent a radical reconstruction. Simultaneously with the modernization of equipment, the release of the S-80 began. In 1948, after the final restructuring of the enterprise, ChTZ produced 20 to 25 pieces of equipment per day. In 1955, the design bureau of the plant began work on the creation of a more powerful tractor model S-100. At the same time, the development of new options that would improve the life of the S-80 did not stop.
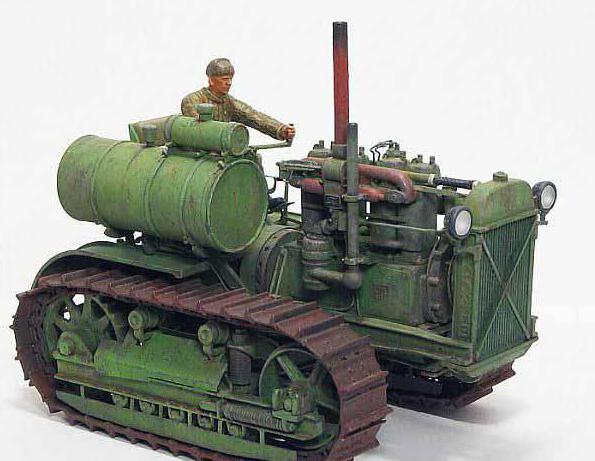 The models of tractors produced by ChTZ in the period of the USSR are represented by the following caterpillars:
The models of tractors produced by ChTZ in the period of the USSR are represented by the following caterpillars:
- C-60 (1933);
- C-65 (1937);
- C-80 (1946);
- C-100 (1956);
- DET-250 (1957);
- T-100M (1963);
- T-130 (1969);
- T-800 (1983);
- T-170 (1988);
- DET 250M2 (19789);
- T-10 (1990).
Other companies
Of course, the article lists not all the factories that produced tractors of the USSR and continue their activities after its disintegration. These are such enterprises as:
- Altai (Barnaul);
- Onega (Petrozavodsk);
- Uzbek (Tashkent);
- Kirov (St. Petersburg);
- Pavlodar (Kazakhstan).
There are tractor factories in Moscow and in Bryansk, Lipetsk and Kolomna, as well as in other cities.
Since 1991, a new era has begun in the production of this technology. If before this period all the tractor enterprises belonged to the same ministry, at the moment many of them began to be on the territory of new states. In addition, most of the plants went into private hands. I want to believe that the history of tractor construction in Russia will continue to have a worthy continuation.
March 27, 1878 Russian peasant F.Blinov * filed an application for a patent for the "wagon with endless racks" invented by him (the world's first caterpillar tractor).
The first caterpillar tractor was built in Russia by a native of the village of Nikolskoye Volsky Uyezd in Saratov province by peasant Fyodor Abramovich Blinov, and on September 20, 1879, he already received patent ("Privilege") to the "wagon with endless rails for transportation of goods by road and country roads ".
The opening part read:
« Privilege, issued from the Department of Commerce in 1879 to peasant Fyodor Blinov, on a special device wagon with endless rails for the carriage of goods along highway and country roads…»

The Blinov tractor had a steam engine and a two-track steam system. All units were mounted on a frame. The vertical boiler was located in the central part of the frame. Crude oil was used as fuel. Two tanks: for fuel and water, were fixed to the front of the frame. The power unit consisted of two slow-moving steam engines, providing a direct and reversible course when switching the rocker mechanism. The original Blinova double track track system consisted of two caterpillar belts, a pair of driving belts and a pair of steering wheels, as well as two wheels located between them, which function as support rollers and supporting rollers. The axles of all wheels had a rigid connection with the frame.
The tractor was serviced by two people: the driver controlled the course from the booth, and the operator served the boiler and steam cylinders. The driver's seat was located behind the boiler.
Inventor: William Howard
A country: England
Time of invention: 1850
A tractor is a universal machine designed to move and operate a variety of agricultural mechanisms attached to it. From this it is clear that the functions of the tractor are twofold: first, it works as a tractor, and secondly, as a drive, which allows it to be used in a variety of agricultural works.
The advantages of a tractor are obvious - speed, time saving, productivity. Therefore, its appearance amounted to a revolution in agriculture, perhaps the most important since its inception. From that time, mechanical traction gradually began to displace the muscular strength of animals from agricultural production. 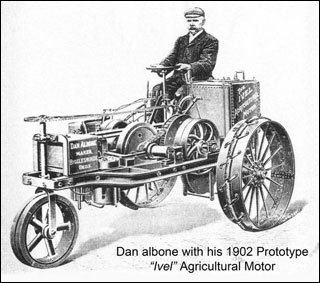 The first tractors were steam. As early as 1850, the English inventor William Howard used a steam car (locomobile) for plowing. The invention became widespread, and steam plows were widely used in the second half of the XIX century in some European countries (especially in England, where they numbered more than 2 thousand).
The first tractors were steam. As early as 1850, the English inventor William Howard used a steam car (locomobile) for plowing. The invention became widespread, and steam plows were widely used in the second half of the XIX century in some European countries (especially in England, where they numbered more than 2 thousand).
The first tractors with internal combustion engines, designed by engineers Charles V. Hart and Charles Parr, were assembled in the United States in 1901. Their appearance was greeted with enthusiasm, and the American farmers placed great hopes on them. But the disappointment quickly ensued, because the tractors, because of their huge weight, were more destructive to the soil than they helped to process it. In addition, they were too large for the average farm. During their use, many design flaws were discovered. 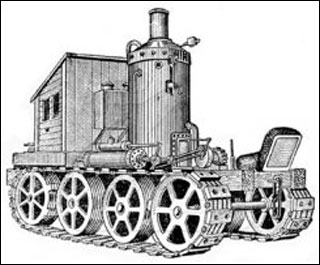 Tractors often broke down, repairing them required a lot of time and high costs.
Tractors often broke down, repairing them required a lot of time and high costs.
However, gradually these machines were improved. In 1907, quite efficient tractors arrived on the market. Their weight, size and power have decreased, but reliability has increased, which made the use of the tractor comfortable on average in terms of the size of the farm. A network of repair shops was set up, and the production of spare parts was set up, due to which the negative attitude of farmers to this machine was overcome in a few years, and the growth of the tractor industry began in America. In 1920, about 200,000 tractors of various designs were sold in the USA. In 1912, Holt first began the production of tracked tractors.
 Soon the tractor took about 80-90% of all arable work on the farm. In addition, the tractor engine was used to drive various agricultural machines (for this purpose it was supplied with a special pulley). Threshers, mowers, sawmills, churns, straw choppers and other auxiliary mechanisms could be connected to it. Tractor also took on about half of the work related to harvesting. In the future, thanks to the creation of various trailers, the scope of the tractor has expanded several times.
Soon the tractor took about 80-90% of all arable work on the farm. In addition, the tractor engine was used to drive various agricultural machines (for this purpose it was supplied with a special pulley). Threshers, mowers, sawmills, churns, straw choppers and other auxiliary mechanisms could be connected to it. Tractor also took on about half of the work related to harvesting. In the future, thanks to the creation of various trailers, the scope of the tractor has expanded several times.
In Russia, the first application for a "crew with moving ruts", that is, a caterpillar drive, was made in 1837 by the Russian 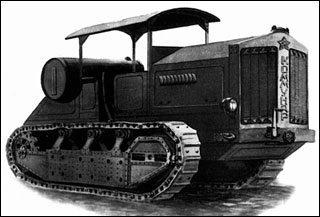 a peasant, later a staff captain of the Russian army, Dmitry Zagryazhsky. Here is how he described his invention: "Near each ordinary wheel, on which the carriage rolls, an iron chain is drawn, pulled by hexagonal wheels in front of the ordinary one. The sides of the hexagonal wheels are equal to the links of the chain; these chains replace to some extent the railway, representing the wheel is always a smooth and firm surface "(from the privilege granted in March 1837).
a peasant, later a staff captain of the Russian army, Dmitry Zagryazhsky. Here is how he described his invention: "Near each ordinary wheel, on which the carriage rolls, an iron chain is drawn, pulled by hexagonal wheels in front of the ordinary one. The sides of the hexagonal wheels are equal to the links of the chain; these chains replace to some extent the railway, representing the wheel is always a smooth and firm surface "(from the privilege granted in March 1837).
The first Russian steam caterpillar tractor was built by a native of the village of Nikolskoye Volsky Uyezd in Saratov province by peasant Fyodor Abramovich Blinov, in 1879 he received a patent ("privilege") on  "A car with endless rails for the carriage of goods along highway and country roads". The construction of the prototype was completed by Blinov in 1888. The finished steam engine of small dimensions did not yet exist, and Fyodor Abramovich himself built it from sheet iron and pipes burned near Balakovo. Then he made the same second machine. They both did forty revolutions per minute. Each of them was managed separately.
"A car with endless rails for the carriage of goods along highway and country roads". The construction of the prototype was completed by Blinov in 1888. The finished steam engine of small dimensions did not yet exist, and Fyodor Abramovich himself built it from sheet iron and pipes burned near Balakovo. Then he made the same second machine. They both did forty revolutions per minute. Each of them was managed separately.
The speed of the tractor's movement corresponded to the speed of the bulls' movement - three miles per hour. Thus, the device was powered by two steam engines (one for each "caterpillar") with a capacity of 10-12 hp each. F. Blinov demonstrated it in 1889 in Saratov and in 1897 at the Nizhny Novgorod Fair. However, this tractor did not become popular either in industry or in agriculture, and further the prototype of tractors in Russia it did not go.
 In Russia, the importance of tractors for the country was assessed only by the Soviet government after 1917, allocating money for the construction of tractors in difficult years for the country's intervention. Beginning in 1918, at the direction of VI. Lenin is preparing production for the production of tractors. In 1919 the inventor Ya.V. Mom created a tractor "Gnome" with an oil engine capacity of 11.8 kW.
In Russia, the importance of tractors for the country was assessed only by the Soviet government after 1917, allocating money for the construction of tractors in difficult years for the country's intervention. Beginning in 1918, at the direction of VI. Lenin is preparing production for the production of tractors. In 1919 the inventor Ya.V. Mom created a tractor "Gnome" with an oil engine capacity of 11.8 kW.
The production of tractors was so important that the Decree of the Council of People's Commissars of April 1, 1921 on recognition of agricultural machinery as a matter of extraordinary state importance was issued. In 1922 tractors "Kolomenets-1" designed by E.D. Of Lviv. In 1922-1923 the Zaporozhets tractor was created under the supervision of the engineer LA Unger. In 1924, the tractor Kommunar (a copy of the German tractor Hanomag WD Z 50) was launched at the Kharkov locomotive plant.
In 1924, the production of tractors "Karlik" designed by Ya.V. Mom's with the engine  capacity of 8.8 kW (12 hp), in two versions: the Karlik-1 tractor (three-wheeled, with one forward transmission, with a speed of 3-4 km / h) and the Karlik-2 (four-wheeled, with one transmission and a reverse). From 1924 to 1932, the Leningrad plant "Krasny Putilovets" mastered and produced about 50 thousand tractors "Fordzon-Putilovets", and then since 1934 this factory began to produce a tractor "Universal" with a kerosene engine and metal wheels. "Universal" was the first domestic tractor exported abroad.
capacity of 8.8 kW (12 hp), in two versions: the Karlik-1 tractor (three-wheeled, with one forward transmission, with a speed of 3-4 km / h) and the Karlik-2 (four-wheeled, with one transmission and a reverse). From 1924 to 1932, the Leningrad plant "Krasny Putilovets" mastered and produced about 50 thousand tractors "Fordzon-Putilovets", and then since 1934 this factory began to produce a tractor "Universal" with a kerosene engine and metal wheels. "Universal" was the first domestic tractor exported abroad.
The first soviet tractors "Gnome", "Kolomenets-1", "Dwarf", "Zaporozhets", "Kommunar" were issued in relatively small batches, but they taught a lot, raised the first tractor builders and rightfully entered the history of domestic tractor construction. Further development of the country required the construction of large specialized tractor plants.
 Using the currency received from the sale of grain, with the help of American and European engineers and the supply of equipment of several hundred foreign companies, the Stalingrad Tractor Plant was built in 1930 (produced tractors STZ-15/30), the Kharkov Tractor Plant in 1931 (produced khTZ tractors, similar to tractors of STZ), Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant in 1933, which produced caterpillar tractors S-60.
Using the currency received from the sale of grain, with the help of American and European engineers and the supply of equipment of several hundred foreign companies, the Stalingrad Tractor Plant was built in 1930 (produced tractors STZ-15/30), the Kharkov Tractor Plant in 1931 (produced khTZ tractors, similar to tractors of STZ), Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant in 1933, which produced caterpillar tractors S-60.
In the ten prewar years, the domestic industry produced about 700,000 tractors for agriculture. The total output of domestic tractors was 40% of their world production. Thanks to these successes in the planned development of the economy, the backward, fragmented agriculture of pre-revolutionary Russia has become a major mechanized one.
During the Great Patriotic War, the Altai Tractor Plant was built, and in the postwar years - factories in Minsk, Vladimir, Lipetsk, Chisinau, Tashkent, Pavlodar.
In the early 30-ies for the mechanization of labor-intensive work on cultivating tilled crops, the Universal tractor was developed. The tractor "Farmol" of the American company "International Harvester" was used as a basis for the design. The modifications were made to the design of the prototype: components and materials of domestic production were used, a new calculation method and technology of gearing were applied. A front two-wheeled bridge of original design was designed for processing low-growth tilled crops .
In the early 30-ies for the mechanization of labor-intensive work on cultivating tilled crops, the Universal tractor was developed. The tractor "Farmol" of the American company "International Harvester" was used as a basis for the design. The modifications were made to the design of the prototype: components and materials of domestic production were used, a new calculation method and technology of gearing were applied. A front two-wheeled bridge of original design was designed for processing low-growth tilled crops The tractor had an enlarged clearance, narrow wheels and a track corresponding to the size of most rows taken for row crops The power unit is a kerosene carburetor engine.As a supplementary equipment, a crane lift for mounted cultivators and other implements could be installed on the tractor, and since 1950, for the first time in the USSR, tractors were equipped with hydraulic hoists for mounted agricultural implements. The tractor "Universal" is similar to the tractor СХТЗ-15/30.
For the first time in the world, the domestic designers developed two modifications of the tractor Universal: U-1 with the front wheels adjoining - adapted for inter-row processing of high-growth crops (irrigated cotton, sunflower, maize); U-2 with front wheels arranged - suitable for inter-row processing of sugar beet and other low-growth tilled crops. In the 1940s, two more modifications were made to the tractor, "Universal: U-3 - for inter-row processing of rain-fed cotton, U-4 for the installation of cotton harvesters." This model was used for the first time in the USSR to install wheels with non-pneumatic tires. "Universal" in the domestic tractor construction was launched a new direction - the production of row tractors.
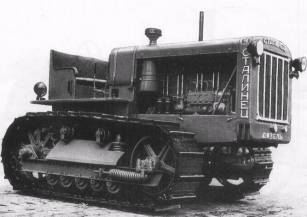
Model C-60 was created as a powerful tractor with high traction and cross-country ability. The prototype was chosen one of the best in the world of caterpillar tractors "Caterpillar-60". For the production of C-60 in 1932 was commissioned Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant-giant with the mass production of mass production. The frame of the tractor-semi-frame is formed by the transmission case and the engine subframe. On the tractor was installed a soft seat for the tractor driver and assistant. Engine - carburetor four-stroke four-cylinder in-line, fuel - naphtha. The clutch is a two-disk clutch. Suspension - semi-rigid. Caterpillar - compound with stamped links and shoes made of special rolled metal. The tractor had a power take-off shaft and a pulley. C-60 was widely used not only in agriculture, but also in construction, and was also used for army needs. In the production process, the C-60 was significantly upgraded: the carburetor engine was replaced by a slightly larger diesel engine. The first domestic diesel tractor of mass production was produced under the brand S-65. The non-compressor diesel with a pre-chamber mixture was started with a gasoline-powered starting engine with electric ignition. To install the diesel tractor chassis has also been upgraded: the transmission ratio and the length of the tracks have been changed. In addition to the basic model of the C-65, two modifications were made: SG-65 - gas-generating and C-2 - transport.
In the mid-1930s, it became necessary to create a mass caterpillar agricultural tractor. Taking into account the needs of the army and other branches of the national economy in caterpillar tractors, tractors at the Stalingrad Tractor Plant, together with NATI, unified agricultural and transport modifications of the caterpillar tractor were developed. The first mass-produced tractor of the original domestic design was developed taking into account the best achievements of the world and domestic tractor construction. SCHTZ-NATI had a frame structure with a riveted frame consisting of two spars and four crossbars. Elastic suspension on four balanced carriages with coiled spring springs. The cabin is half-closed. The engine and power train are mounted on the frame in three points. The power unit is a four-cylinder kerosene carburetor with water cooling. The gearbox is a three-way gear, the caterpillar is made of links cast from high-manganese steel. For a whole decade, the SHTZ-NATI remained the most common caterpillar tractor, only in 1949 it was replaced by the DT-54, which, by arrangement, power transmission scheme, running system and skeleton, retained continuity with the SCHPN-NATI and differed from it with a diesel engine, a closed cabin and the location of the fuel tank from the rear.

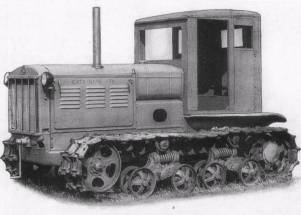
Development of the construction of a medium-duty caterpillar tractor began in the late 1930s. The war interrupted these works. In 1943, the government, anticipating the great need for tractors after the war, decided to resume work on the development of new tractors and the construction of new tractor plants. In accordance with this, at the height of the war in NATI, the development of the design of a new medium-sized tractor began, and prototypes were created and tested. In parallel with the design of the tractor, in Lipetsk was started construction of a plant for its production. The designers of the construction of the Lipetsk Tractor Plant joined the development of the tractor. At the same time, a diesel engine was developed at the NATI for a medium-duty tractor. On July 1, 1944, the Lipetsk Tractor Plant began the production of Kirovets-35 tractors with a carburetor engine, and in 1947 switched to the production of a KD-35 tractor with a diesel engine, Rama KD-35 - riveted, suspension - semi-rigid, stars, spring - sheet. In the process of production, the tractors were equipped with closed cabins. A four-cylinder diesel with a vortex-chambered mixture and an all-regulator has a low fuel consumption and high reliability. For a long time the engine was upgraded many times. Modifications of this engine were used on wheeled and caterpillar tractors of various types, on road construction machines, power stations and other stationary installations. In 1950, at the Lipetsk Tractor Plant, the modification of the KD-35 tractor KDP-35 tractor began, which differed from the prototype with an enlarged clearance, a wider track and a smaller track width.

The T-38 tractor is the result of the modernization of the KDP-35 tractor, which has increased the strength of the running system as a result of the use of roller bearings and rubber-metal end seals in rollers and guide wheels. The use of centralized lubrication of rollers from a common oil tank has significantly reduced the time required for lubrication. Torsion suspension of the trolley carriages made it possible to increase the smoothness of the stroke, especially when working across rows. As a result of the rotation of the lower gearboxes of the final gears, the arrangement of the center of gravity was improved, which increased the stability of the tractor when working with mounted implements.
When upgrading, the engine power was increased due to an increase in the speed of the crankshaft. The upgraded version received the T-38M brand. Tractor T-38M was used mainly in beet production. Working in narrow rows of sugar beet crops with wide-spread hinged and trailed machines, and when harvesting - with a three-row combine, it provided high efficiency and economy.

To increase the economy and reliability of the main arable tractor on the basis of SCHTZ-NATI a new tractor was created, in which the carburetor engine was replaced by a diesel engine of the same dimension. This tractor received the DT-54 brand. The four-cylinder non-compressor diesel tractor DT-54 had a vortex-chambered mixture. The vortex chamber, cast in the block head, was not machined. The volume of fuel supplied to the cylinders was regulated by a centrifugal all-regulator with a corrector. The diesel engine was started by a starting engine. The decompressor is dual-wired. The power train and skeleton of the DT-54 tractor basically did not differ from the STIP-NATI. In the running system, in contrast to the SXTZ-NATI in the DT-54 support rollers, end metal self-seal seals were used. Due to the high continuity of the construction of the DT-54 tractor with the SCHTZ-NATI, the transition to the production of the new model was carried out at factories without stopping production, only with a small decrease in output in the first year. When upgrading to the DT-54 was installed a closed cabin. After installation, for the first time in the world for crawler tractors, a hydraulic mounted tractor, the tractor was manufactured under the DT-54A brand. On the basis of this tractor at the Volgograd, and then in the Altai Tractor Plants, the swamp-type modification DT-55A was produced. High traction and cross-country ability, as well as low cost, provided the DT-54 in the 50-60s with the greatest popularity among domestic tractors in agriculture.

The first small-sized domestic tractor of mass production is KhTZ-7. This is one of the first tractor in the domestic tractor construction, on which pneumatic low pressure tires and a hydraulic hinged system were installed. HTZ-7 had a classic layout, frameless skeleton and was adapted to work both forward and reverse. For backward movement, the tractor was able to change the position of the driver's seat and reverse control. The design of the tractor made it possible to adjust it for work both in the aisles of row crops with increased road gleam, and in the gardens with a reduced height of the tractor. All the necessary adjustment for this could be done in the field. The tractor was equipped with a two-cylinder petrol carburetor engine. Final drives could be turned over, which allowed changing the height of the tractor by 207 mm and ground clearance. The tractor had a power take-off shaft and a pulley. DT-14, created on the basis of KhTZ-7, differed from it mainly by installing a more powerful single-cylinder diesel with water cooling. In the process of modernization of the DT-14, an electric engine start was set up on it and a unified, separate, modular hinged system was installed.
DT-20 is the further development of the DT-14 design with a more powerful engine of a larger working volume. The tractor had increased speeds. In connection with the increase in speed, a third brake pedal was introduced to jointly act on both brakes, as well as the foot accelerator. Like HTZ-7 and DT-14, four adjustments provided different sizes of the base and clearance, as well as the ability to work in reverse.
The engine and power transmission of the self-propelled chassis are integrated into one unit, installed at the rear of the car behind the seat. The two-branched frame is free from chassis mechanisms and is intended for placement on it of hinged agricultural machines or a dumper platform. Attached machines are placed between the axes of the front and rear wheels of self-propelled chassis, which allows work in the aisles with small protective zones and provides a good visibility of the working bodies. On the self-propelled chassis DSSH-14 was installed unified with diesel tractor DT-14 engine. The chassis is equipped with a hydraulic hinged system, two remote hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic low pressure tires. The main power take-off shaft - with a semi-independent drive, three power take-off shafts - with a synchronous drive. For the work with planting material, a speed reducer is used. ДВСШ-16 - modernization of the self-propelled chassis DShS-14, which differs from the prototype by a double-cylinder diesel engine of air cooling of high power with electric start-up. It is also possible to install a drive pulley.
Self-propelled chassis T-16 - the development of the design DVSH-16. A distinctive feature - gearbox providing speed reversal. For stationary operation, a pulley with drive from the main power take-off shaft is provided. As a result of the modernization of the T-16, the engine's power was increased and its design was improved. The chassis was manufactured under the T-16M brand, it was equipped with a two-cylinder air-cooled diesel engine with direct injection (piston chamber). The gearbox provides higher speeds on all gears. The carrying capacity of the platform is increased and the wheels of the increased size are installed. A frame with awning, sidewalls and doors is provided.
In the 1950s, the construction of row tractors was significantly improved. In these years, the series introduced pneumatic tires, hydraulic hinged system, diesel, adjustable track, top speed increased from 8 to 18 km / h. Pneumatic tires and hydraulic system for the first time in the USSR began to install on tractors "Universal", and all of the above innovations were introduced on the DT-24. The DT-24 tractor is designed to work in a 2- 4 row system. Three models of tractors were produced: DT-24-1 for processing high-growth tilled crops; DT-24-2 - for inter-row processing of high-growth tilled crops and DT-24-3 - for processing cotton crops. On all models of tractors ДТ 24 there is a two-cylinder, non-compressor, vortex-chamber diesel engine, which is started manually with a gasoline trigger by means of a handle. The starting device is equipped with a carburetor and magneto. The upgraded DT-24 was manufactured under the T-28 brand with a more powerful engine (mainly due to increased fuel supply). To clean the oil in the engine lubrication system, a centrifuge with a hydraulic drive is installed. On the tractor there is a unified separate-aggregate hydraulic system.
The first cotton-growing tractors of the Vladimir Tractor Plant were based on the Universal tractor, then as modifications of the DT-24 tractor. Tractors Т-28Х, Т-28Х2, Т-28ХЗ, Т-28Х4 were produced on the basis of the chassis of the T-28 tractor. The T-28XZ tractor with two driving rear wheels and one front steering wheel, thanks to the additional on-board gears at the rear wheels, has a high ground clearance. Four-cylinder diesel - with an unshared combustion chamber and air-cooled. The tractor is equipped with a rear power take-off shaft with a dependent and independent drive, a side power take-off shaft with a synchronous drive. The upgraded T-28XZ tractor was manufactured under the T-28X4 brand, had a high-power engine, a high agro-technical clearance of 825 mm, and a rear wheel gauge adjusted with a hydraulic cylinder. In the course of further modernization, the engine power of the T-28X4 tractor was increased to 60 hp. and the speeds of movement are increased. The tractor was manufactured under the T-28H4M brand.
In the first in the domestic tractor-building MTZ-2 was designed as a medium-sized wheeled tractor for row work in the 4-6-row system. The tractor is equipped with pneumatic low-pressure tires and a hydraulic hinged system. The MTZ-2 tractor is a classic configuration and a semi-frame design with a four-cylinder diesel engine, which differs from the engine mounted on the KD-35, a lightweight radiator and a crankcase. The tractor is equipped with a power drive shaft with a dependent drive, a pulley for driving stationary machines and a speed reducer with: two interchangeable sets of gears, the track of the front and rear wheels is adjustable and wide.
In the production process the MTZ-2 tractor underwent modernization: an engine with a capacity of 40 hp was installed.
The MTZ-2 tractor became the first model of the mass wheel universal tractor of the Minsk Tractor Plant.
The YUMZ-6L / 6M tractor was developed on the basis of MTZ-5. The engine can be delivered in two trim levels: with an electric starter (UMZ-6M) or with a starting motor (UMZ-6L). The modernized tractor YUMZ-6L / 6M is manufactured under the YUMZ-6AKL / 6AKM brand, it is equipped with a speed reducer (optional), an independent power take-off shaft, a power steering with an adjustable steering column angle, a hydraulically operated split-aggregate system with an automatic coupler . On request, the tractor is equipped with additional equipment: wheels for rowing work in narrow rows, semi-tracked; preheater and others.
Tractor T-40-traditional layout and semi-frame construction, its versatility is provided by the ability to adjust the ride height and track. The tractor has a four-cylinder, air-cooled engine. The engine has a combustion chamber of an undivided type. The double-acting clutch provides independent power take-off drive. Transmission 7-speed, with the reverse of all gears. Power steering. The closed all-metal cabin is equipped with a fan and a windshield wiper. PTO shafts with independent and synchronous drives for the mechanisms of aggregated machines. On the basis of the T-40, a modification of the T 40A with four driving wheels has been developed. The front drive axle with two freewheel clutches is automatically engaged at a certain amount of skidding of the rear wheels. The portal design of the front axle allowed to preserve the quality of the universal tractor. In the process of production, the T-40 and T-40A tractors were modernized and began to be produced under the T-40M and T-40AM brand, whose engine power is increased to 50 A from the new-design tractor cab. The rigid frame for driver safety provides better visibility.
The MTZ-50 tractor is a further development of the MTZ tractors' standard size of the classic layout. It is equipped with a high-power engine, power steering, sprung front axle, hydraulic linkage weight increase, differential lock mechanism, closed cab. On request, the tractor is equipped with a pneumatic brake system for transport trailers, a manual brake drive. MTZ-52 with four driving wheels - modification MTZ-50, completely preserved the versatility of the basic model due to the same with it the ground clearance and adjustable track of the front wheels. The front wheel drive with an automatic freewheel clutch is activated when the rear wheels are slackened. On the basis of MTZ-50 a family of unified modifications for different purposes was created: with all driving wheels; cotton-growing, steep, semi-caterpillar, caterpillar-vineyard and beet-growing. Common for all wheeled and caterpillar modifications are the main components of the MTZ-50 tractor: engine, clutch, gearbox, hydraulic system, electrical equipment, power take-off shafts, etc. The degree of unification with the base model is 80-97.5% for wheeled and semi-tracked and 50-65% for crawler tractors. In the production process, MTZ-50 and MTZ-52 tractors underwent a phased modernization. So, since 1980 new frame cabinets of the improved appearance began to be installed and tractors began to be produced under the MTZ-550 and MTZ-552 brands, and with the increase in engine power up to 60 hp. - MTZ-560 and MTZ-562. To meet the needs of the market, low-profile tractors MTZ-530/532 with a capacity of 65 hp were created and started to be manufactured on the basis of MTZ-560 and MTZ-562 tractors. and their garden modification "Belarus-680".
The T-75 tractor was created as a result of the modernization of the DT-54A: the engine of increased power, the frame was strengthened by the installation of the front bar and braces, the number of forward gears was increased, the starting motor with the electric starter, the two-seater cabin of the closed type with heating and ventilation. The structures of the rear axle and running system T-75 and DT-54 are basically similar. T-74 - modernization of the T-75 tractor, differs, mainly, by installing the engine of a new more advanced design. To maintain the former location of the center of gravity of the tractor using a lighter engine, a bumper is installed on the front bar.
Tractor T4 is designed as a plow tractor for work in the steppe regions of Siberia and in the zones of irrigated and irrigated agriculture in Central Asia, characterized by an increased specific resistivity of the soil. A single-stage planetary steering mechanism ensures a reduction in track, while improving the conditions for the assembly of the tractor with agricultural machines. The restaurant is equipped with a separate-aggregate hydro-mounted system, as well as a power take-off shaft. Closed metal cabin with soft adjustable seats and ventilation and heating system. The upgraded T-4 tractor is produced under the T-4 brand with a high-power engine, a semi-rigid suspension on one transverse balance spring, and a preheating pre-heater is installed before the engine is heated.
The construction scheme of the tractor DT-75, in comparison with the tractors SCHTZ-NATI and DT-54, has not changed, but the main units have been improved: the engine, the power train and the cab. The construction of the tractor is adapted to the assembly with mounted agricultural machines, mainly due to the installation of the hydraulic attachment system and the reduction of the overall width of the tractor. Four-cylinder diesel engines of the Kharkov motor plant Serp i Molot (DT75, DT-75V, DT-75N) and the Altai motor plant (DT-75M, DT-75MV, LT-75ML, DT-75D) with water cooling and starting a motor with an electric starter. The main clutch is a dry, two-disc, permanently closed type. Rear axle with two single-stage planetary turning mechanisms, with brakes of sun gears and two stop brakes. Separate-aggregate hydro-mounted system with attachment of agricultural implements to 2-hour 3-point circuits was installed. Cab of closed type, metal with heating and ventilation. Tractors are supplied in various configurations, a swamp-type tractor is created and produced on their basis. For a number of years, the shuttle-reverse steep-roll tractor was also produced.
The design of the T-25 tractor was developed with the modernization of the T-20, the traditional layout was retained and a two-cylinder air-cooled engine was installed. The wide universality due to the adjustable rings and agrotechnical clearance, the reversibility of the main gears is preserved. There are three changes in the tractor height: basic, low and high. An 8-speed gearbox is installed, as well as a dependent and synchronous power take-off shaft. Start the engine from the electric starter, and the incandescent light. The modernized tractor T-25 is manufactured under the T-25A brand. Depending on the equipment, a cab can be installed on the tractor, the safety net canopy. Cabin - all-metal single, with safety cage, heater, ventilation system, with windshield wiper.
The MTZ-80 tractor is designed for the modernization of MTZ-50. Unification of the details of these tractors is 70%. The tractor is equipped with a liquid-cooled diesel engine of increased power. An additional gearbox is added to the gearbox, doubling the number of gears. Reversing differential with automatic locking, rear power take-off shaft is made by two-speed. The universal pneumatic system serves for the drive of the trailer brakes and tire inflation. The hydraulic system is supplemented with mechanisms of power and position control of the depth of the stroke.
The tractor is equipped with tires of increased size. Sealed with a rigid frame, the cabin is equipped with a single seat, electric wiper, heating and ventilation system.
The MTZ-82 tractor MTZ-80 modification is equipped with a leading portal front axle for increased cross-country capability, a safety clutch and a mechanism for deflecting the freewheel interaxle are used in the front axle drive. The MTZ-80 tractor and its modifications have been continuously improved: a more comfortable cab has been installed, a gearbox with switching without a power flow gap, a hydrostatic power steering, brakes with brake discs increased to 205 mm in diameter. A gradual improvement in the appearance of new types of hoods, modern cab elements, a more ergonomic cabin interior with simultaneous increase in power and a reduction in fuel consumption became the basis for the appearance of the upgraded models MTZ-890/892, MTZ-900/902 and MTZ-950/952. On the basis of MTZ-80/82 tractors special modifications have been created and produced: MTZ-80X-cotton; MTZ-82N - low-pass, MTZ-82R - rice, caterpillar, etc.
The T-70S tractor was developed during modernization of the T-54S with the use of MTZ-80 tractor units: engine, clutch, transmission, electrical equipment and hydraulic systems. The T-70S tractor has increased energy saturation and a wide range of speeds. Equipped with a two-speed power take-off shaft with independent and synchronous drives. Suspension of the tractor is semi-rigid, with front and rear suspension of the frame torsion bars. The cabin is sprung with a rigid frame, equipped with an evaporative-type air cooler.
The construction of MTZ-102/100 tractors was created as a result of a thorough modernization of the MTZ-80/82, a box was used with a gear change without a power flow gap, the engine power was increased as a result of the application, turbo-supercharging, the steering was equipped with a hydrovolume drive, the load capacity of the hinged devices, installed tires of greater carrying capacity, which together with the increased traction mass provide working traction up to 2 tons. The working position of the mounted implements is regulated by a high-altitude, power, position on-line and mixed methods. Tractors MTZ-102/100 are constantly being modernized. Samples with more modern forms of the hood and elements of the cabin with an improved interior are produced under the brand MTZ-1025.
The T-150K tractor has four driving wheels of equal size, the turn is carried out also due to the articulated frame. The vertical hinge of the frame serves to turn the tractor, horizontal - to adapt the wheels to the terrain. Transmission 12 -speed, 3-band. Brakes - wheeled shoe with pneumatic booster, pneumatic drive system of trailer brakes. The power take-off shaft is independent, 2-speed, rear. By order of the customer, the tractor is equipped with a diesel engine with a starting engine or an electric starter, a gearbox with a hydraulic gear change without a power flow gap, a speed reducer for working with artophelploscopes or a transmission with creeping speeds for working with earth-moving machines. Twin wheels and dozer equipment with a swivel blade can also be installed.
The tractor DT-175S is developed on the basis of DT-75 tractors with preservation of the classic layout. A special feature of the design is the presence in the transmission of a torque converter, which automatically regulates the speed of the tractor's forward motion. The hydrotransformer complex, blocked. The transmission is mechanical. The main gear, the planetary gear and the tractor's brakes DT-175S are similar in design to those installed on the DT-75 tractors. The tractor is equipped with a six-cylinder V-engine with gas turbine supercharging and intermediate cooling of air. The tractor's power take-off shaft is two-speed dependent. The tractor is equipped with a separate-aggregate hydraulic system, a rear linkage mechanism with automatic coupling and a towing device. The two-seater all-metal sealed cabin is fixed to the tractor frame on a sprung base and shifted to the right of the tractor axle.
The design of the TZOA-80 tractor was developed as a result of the modernization of the T-25A with the preservation of the traditional layout. A new two-cylinder air cooling diesel engine of increased capacity has been installed to increase the throughput and traction qualities - a portal-type leading front axle with automatic inclusion with increased overshoot of the rear wheels, a double-flow clutch, an independent power take-off shaft and disc brakes, a hydrostatic-type steering system, carrying capacity, single cabin (removable, sealed, soundproofed with ventilation, heating, sprung seat). On request, the tractor can be equipped with a universal regulator of plowing depth, a drive pulley, an automatic coupler, a mechanized digging of the hinged system.
The tractors KhTZ-120 and KhTZ-121 are designed on the basis of the T-150K tractor (unification factor of 40%), they have four driving wheels of equal size and front steerable wheels. The gearbox with gear change gears, 12-speed - at the KhTZ-120, and 1b-speed with the shifting of gears without a break in the power flow with the help of hydropodic couplings - at the KhTZ-121. The steering gear is hydrostatic. The front axle is a balancer with swivel wheels. A single-frame frame-safe cabin with a central tractor driver's seat. For operation (power take-off, the engine has a second mode providing operating power of 145 hp (106 kW) .On the customer's request, the tractor is equipped with a front power take-off shaft, a front mounted system, a set of twin wheels with narrow tires 9.5-42 for work with row beams, as well as prefabricated discs for mounting wheels on a track of 2800 mm.
The construction of the tractor LTZ-55A was developed as a result of a deep modernization of the T-40AM tractor: a sealed noise-proofed cab with a ventilation and heating system with a large glazing surface was installed. comfortable adjustable in height and weight of the driver's seat. A more convenient arrangement of controls and a new design distinguishes the tractor LTZ-55A from its predecessor. The gearbox provides a reversal of all gears, the steering column is adjustable, the engine load is controlled by an electronic alarm.
Design features tractors provide high technical reliability, simplicity and convenience in service, work in any geographical areas with minimal operating costs. Tractors LTZ-60AV h LTZ-60AG) differ from LTZ-55A by installing engines with water cooling capacity of 60 hp. Rybinsk Motors JSC (LTZ-BОАВ) and the Minsk Motor Plant (ЛТЗ-60АБ), a hydrostatic steering drive with a cylinder built into the trapezium, and a water heating system.
The tractor has a traditional layout, a two-cylinder air-cooled diesel engine with direct fuel injection, a mechanical reversing gearbox, to increase the throughput - the differential lock. The tractor cabin is a single-frame safe frame type sealed heat and noise insulated with heating and ventilation. The steering column is adjustable in height and angle.
The MTZ-1221 tractor was designed as a result of a thorough modernization of the MTZ-102. The increase in power is achieved by the use of a 6-cylinder engine of the same dimension, the rear drive axle is reinforced by the installation of additional planetary final transmissions. The front drive axle is upgraded for heavy duty applications. The working position of the implements is regulated by force, positional and mixed methods. The lifting capacity of the hinged system has been increased up to 3000 kg, front tires - 14,9-24, rear ones - 18,4-З8. The tractor pulling force and the size of the attached implement ensure efficient assembly of a class of tractors with a set of agricultural machines. A number of measures have been taken to improve the working conditions of the tractor operator.
At present, tractors LTZ-133 of the integrated circuit are produced in small series. On the tractor LTZ-155, all driving and steering wheels of the same size are installed. The engine is pushed forward on the front axle, and the cabin has a central location. At the same time, the tractor's mass distribution in static is 60% on the front axle and 40% on the rear axle. The space behind the cab, above the rear axle, is used to accommodate technological equipment. The frame of the tractor is semi-frame. Original steering control of all steerable wheels. Synchronous drive of the front and rear wheels is realized through the interaxial gear differential with electrically controlled locking and the self-locking differential of the front axle. Braking of the front wheels is carried out simultaneously with the rear wheels. The control station in the cabin is made quick-convertible. A variety of the range of equipment available on request (front attachment, front, rear top and side power take-off shafts, narrow twin wheels, speed reducer, towing devices) allows expanding the scope of the tractor.
The VT-100 tractor differs from the DT-75N, on the basis of which it is created, increased energy saturation, the use of a two-level engine for operation in the traction and drive modes, the presence of a 5-speed gearbox with gears of constant engagement, a 2-speed power take-off shaft, comfortable working conditions driver, etc. The installation of a reverse gear and a speedometer allowed to significantly increase the number of working transmissions. The cab of the tractor with increased comfort and modern interior is equipped with an evaporative-type air cooler. On request, a reversible control station is installed on the tractor.
Tractor T-170M1.03-53 is developed on the basis of industrial tractor T-170M. In contrast to the basic model, the T-170M1.03-53 engine is equipped with an increased power engine, a rear agricultural hinged system and a frame from the T-170B swamp-type tractor, as well as 6-track crawler carriages, 600-mm-wide tracks, , a 2-speed power take-off shaft is installed. On the front, the tractor is equipped with a ballast counterweight or bulldozer blade, which increases the longitudinal stability and improves the position of the pressure center during field work and transport operations with attachments.
The tractor is equipped with a three-cylinder D-130 air-cooled diesel engine and a front drive axle, a low cabin (the tractor's height is 2350 mm) allows it to be used for mechanization of work on livestock farms and hothouse farms throughout the year. On the tractor, progressive solutions are realized: transmission with synchronized gearbox, front portal type gantry with automatic switching on with increased skidding of the rear wheels; disc brakes; hydrostatic power steering; independent three-speed (540, 750 and 1000 rpm) power take-off shaft with switching to synchronous; cabin with a rigid frame, increased vibration and noise insulation and improved working conditions; hydro-mounted system of increased payload. Various configurations for the order are envisaged, including equipment with safety cage with awning instead of cab, automatic coupler.
The goal of the development is the creation for agriculture of a mobile traction-energy facility of Class 1.4 of the classical layout, maximally unified with an LTZ-155 tractor of the integrated circuit, Class 2.0. The tractor is equipped with a lot of progressive tractors borrowed from the tractor LTZ-155 constructive elements: single-disk clutch, gearbox with helical gears of constant engagement, 4-diapadon, with shifting of 4 gears within ranges, on order - synchronized; rear driving axle; PTO shafts; attachments. Other advanced technical solutions: hydrostatic power steering with built-in trapezium hydraulic cylinder and separate oil bath; stop disc wheel brakes with hydraulic servo, locked with a central brake and front axle drive; combined oil bath of the transmission and hydraulic system. By request, the tractor can be converted to work on the reverse; equipped with narrow dual tires of the rear wheels, traction-coupling devices of various types, front attachment, rear upper and front two-speed power take-off shaft, a driver. The prototype of the tractor is factory tested
The design of the tractor is designed to create a universal tractor of high technical level on the basis of units and assemblies of the YUMZ-6K tractor manufactured in Russian Federation, including engine and clutch, body parts and transmission elements, hydraulic hitch assemblies, etc. MVM-NATI-80 is a classic tractor with all driving wheels. Compared with the analogue tractor UMZ-6K, it has a more powerful turbocharged engine, hydrostatic power steering, unified seat. Installed on the inn, the front drive axle of the original design allows you to increase the angle of rotation of the front wheels, up to 500, while maintaining agro-technical requirements for maneuverability and agrotechnical clearance, with the tires enlarged with increased tire size (11,2-28). For the tractor a new top structure with an inclined hood is developed to improve the visibility of the front working area, as well as a new cab with better workplace organization and a universal information system with a real-speed radar sensor. At present, a prototype of the tractor is manufactured and its evaluation tests are carried out.
The VT-130K tractor was developed on the basis of DT-75N and VT-100 using their engine, transmission case, a number of gears, frame, working equipment, cab elements. The tractor has a new layout with all the leading and steerable wheels of equal diameter. The front wheels are sprung. The engine, transmission, cab and working equipment. For the VT-130K tractor a gearbox with gears of constant engagement and hydraulically controlled friction clutches is developed. The gearbox has a built-in friction mechanism for the power take-off shaft, as well as switching it to independent or synchronous modes. For the tractor a cylindrical gear differential with forced locking is developed, as well as disc dry brakes with installation on the semi-axles. The drive to the rear wheels through the cylindrical planetary gearbox, and the drive to the front wheels is separated by the beams from the rear axle through the bevel gearboxes, overtaking clamped couplings and final planetary gears. The tractor is controlled by turning the front wheel guides with the help of two power cylinders and additionally turning by means of braking the lagging board. Suspension of the front wheels is individual with coil springs. The VT-130K tractor is at the stage of state acceptance tests, as well as operational tests of the pilot lot.
The layout of the tractor is traditional. Six-cylinder liquid-cooled diesel with. turbocharging and intercooling of air with a four-valve head. The transmission is mechanical, full-range, with on-the-fly shifting by means of hydraulic couplings without breaking the power flow in the entire speed range. The mechanism of rotation with hydropodic friction clutches and disk brakes working in oil. In the running system on each side there are six support rollers with a plastic individual suspension with torsion spring elements. Caterpillars of the forging engagement are two-track, the tension of the tracks is hydraulic. A version of the caterpillar with rubber-metal hinges is provided. A single sealed heat and noise insulated cabin is equipped with means for normalizing the microclimate during the summer and winter periods, with a safety cage. The T-250 tractor passed acceptance tests and in 1994 was recommended for production.
A fundamentally new arrangement of the tractor with a triangular crawler bypass provides, in comparison with the traditional, a decrease in the operating weight, a reduction in the harmful effect on the soil, an optimal arrangement of the center of mass and the possibility of aggregation with heavy mounted machines and implements. A constant power motor with a large torque reserve, a transmission with all gear shifts on the move, a stepless turning mechanism and a comfortable noise- and vibration-proof cab. Rubber-reinforced asphalt caterpillars significantly expand the scope of use of the tractor. Instead of rubber caterpillars, steel with rubber-metal hinges can be installed, and instead of a stepless turning mechanism, a traditional slewing mechanism with wet-type side clutches is used. Experimental tractor samples are laser-polsvye and operational tests.