Nutrition and digestion of the spider spider. Spider spider - distinctive features
Subtype Helicerata (Chelicerata)
The body of chelicerae consists of the cephalothorax, from which six pairs of appendages depart: chelicera , designed to fix food, pedipalps , serving for the sense of touch, chewing food, as well as a copulatory organ and four pairs of walking legs. Representatives of the subtype are known from the Cambrian (terrestrial forms - from the Devonian) and combine in four classes: Sablefish, Rakoskorpions, Sea spiders and the Arachnids.
In order to prevent further spread of the Jacob mites, the mowing areas should be cut before flowering. With Jacob's pollen the contaminated property should be removed from the useful surface, not composting. Pruning should be incinerated or, alternatively, in a biogas plant.
- C can not be fed a ragweed infected areas.
- Cut out individual plants at an early stage before flowering.
In general, the reserves of the rural areas of Vice-Ben and the exchange of seeds are likely to take place in both directions. Thus, they remain a constant suitable habitat for the ragwalker in Jacob - fly-ready seeds found in poor, dry soil of the right conditions for germination. For which a sufficient number of seeds in the soil can "sleep" and always germinate. Nevertheless, the closure of the turf is hardly possible. Since only mechanical removal of plants is in the protected area in the issue of uprooting or mowing - you have to deal with the subsequent damage.
Class Arachnids (Agachchnida)
Arachnids are the most prosperous group of chelicera animals, numbering 60,000 species. It refers to spiders, scorpions and false-scorpions, saltweed, haymaking, mites and other animals. Science, which studies arachnids, is called arachnology (from the Greek. arachne - the spider; so called, according to one of the myths, a weaver, whom Athena turned into an enraged spider).
How to recognize a ragwort?
The haircut before the flowering time of the peasant Yakov did not come because of the flowering of later species of orchids well in question. This also applies to use as a green fertilizer - effective seeds can not be distributed. This is where the Hitch. In addition, hybrids are observed in-types, resulting in more or less poisonous plants.
When do we move from Jacob to the ragwort?
Most likely, these two species can be distinguished by the shape of the leaves. The next two figures and tables are taken from the publication. If the pastures near the affected areas, including the Young fish feed, we should also here that Jacob Cross remove 100%. If the area is covered thoroughly by the Jacob's cripple, we also need to be active and mow down the area before flowering. With low invasion, away from agricultural land, it is necessary to consider whether the intervention is suitable for. If cuttings are fed, we must remove Jacob's 100% ragwort. . Periods of additional care measures will be available.
Representatives of arachnids are eight-legged terrestrial arthropods, in which the body is divided into cephalothorax and abdomen , connected by a thin constriction or merged. Arachnids do not have antennae. On the cephalothorax there are six pairs of limbs - chelicera, nimbus and four pairs of walking legs. There are no legs on the abdomen. They have respiratory organs lungs and trachea . The eyes of arachnids are simple. Arachnids are dioecious animals.
Human settlements are generally in low places, bathing areas, estuaries or cakes, cane sugar and rice fields. Its size can exceed one meter forty, being females longer and heavier than males. It is easy to understand by his projects in the form of handsets or C, aligned with yellow or cream on the sides of his body. It is not expected that he will see at a distance, that prudently, the spot of the cross on his head, which gives him his name. On each side of the head and between the nostril and the eye there are two forms, called loreal pits, small heat-sensitive organs that capture infrared radiation, which allows you to accurately find warm-blooded prey and hunt when the day falls, the time in which it abounds favorite prey, and also more than compensates for his poor vision.
The length of the body of various representatives of this class is from 0.1 mm to 17 cm. They are widely distributed around the globe. Most of them are terrestrial animals. Among ticks and spiders there are secondary forms.
External structure and way of life of spiders
Spider-crosses (named so for a cross-shaped figure on the dorsal side of the body) can be found in the forest, garden, park, on the window frames of suburban and rural houses. For most of the time, the spider sits at the center of its hobby network with a sticky thread - spider webs .
It feeds mainly on the basis of rodents, but does not despise the fat-tukus or birds. Still fearing man, it would be a mistake to consider her as his enemy, because in his ecosystem this is an important controller of a population of extremely prolific species that, without these natural interventions, can cause significant damage to vegetation in general and especially to agriculture. The remaining records come from the bites of non-venomous snakes. Although in our country there is a third dangerous kind of poison, corals, they tend to avoid contact with people, and in our country there are no accidents.
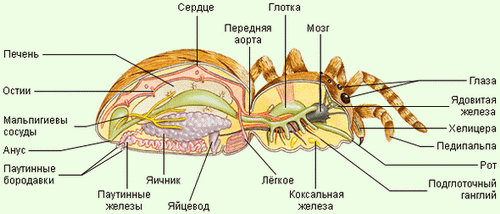
The body of the spider consists of two parts: a small elongated cephalothorax and a larger spherical abdomen. The abdomen is separated from the cephalothorax by a narrow constriction . At the anterior end of the cephalothorax there are four pairs of eyes on top, and below the hook-shaped hard jaws - chelicera . The spider grabs its victim. There is a channel inside the chelicer. According to him, poison from the poison glands located at the base of the chelicer enters the body of the victim. Near the chelicerae there are short, sensitive organs of touch - sensibles (pedipalps) . Four pairs walking legs located on the sides of the cephalothorax. The body is covered with light, strong and rather elastic chitinous cuticle . Like crayfish, spiders periodically shed, dropping the chitinous cover. At this time they grow.
The greatest frequency of accidents is observed in the summer months and beyond this season during periods of high temperature and humidity, which are recorded separately in the rest of the year. These latter accidents are characterized by the fact that they are more serious, since in the state of animal's hibernation, which resorts to minimizing all their vital actions in order to withstand the winter, when it is strict enough, the amount of poison is larger and of different characteristics. In our country, it can be said that it extends almost throughout the territory, with the exception of urban areas and areas of influence associated with the metropolis of Montevideo.
At the lower end of the abdomen are three pairs spiderweb warts , which produce the web, are modified abdominal legs.
Building a Network Hunter
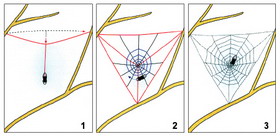 The most beautiful, wheeled tent (hunting nets) are built by females of the spider-spiders of the family of cross-arms. First the spider climbs to a high place, usually near an open space (path), and secrets a very light thread, which is picked up by the breeze, and accidentally hitting an adjacent branch or other support, wraps around it. The spider moves on this thread to a new point, along the way reinforcing the web with an additional secret. In the same way, two or three threads are made, which constitute a closed frame, inside which the network itself will be located. Then thread-radii, connecting in the center, are pulled. After this, starting from the center, the spider moves to the periphery in a spiral. The spiral thread of the web is covered with droplets of sticky secretion. From the network to the spider, the signal thread stretches. The female waits for the signal string to oscillate. Then the spider rushes to the prey, bites it, injects the poison with the upper jaws and leaves, waits.
The most beautiful, wheeled tent (hunting nets) are built by females of the spider-spiders of the family of cross-arms. First the spider climbs to a high place, usually near an open space (path), and secrets a very light thread, which is picked up by the breeze, and accidentally hitting an adjacent branch or other support, wraps around it. The spider moves on this thread to a new point, along the way reinforcing the web with an additional secret. In the same way, two or three threads are made, which constitute a closed frame, inside which the network itself will be located. Then thread-radii, connecting in the center, are pulled. After this, starting from the center, the spider moves to the periphery in a spiral. The spiral thread of the web is covered with droplets of sticky secretion. From the network to the spider, the signal thread stretches. The female waits for the signal string to oscillate. Then the spider rushes to the prey, bites it, injects the poison with the upper jaws and leaves, waits.
The female gives birth to three to twenty-five viborezones about twenty-five centimeters in length between March and Maya. The vision of these animals is not bad and in fact is sensory, which causes anxiety during food or a protective event, with. eg. A feature of the Ophites with thermoreceptor pits is that all the information about the wavelength is analyzed together in the brain tecton. It feeds on birds and small mammals, which in our fauna are mainly represented by rodents, for which you also belong to Tukko-Tuko.
The internal structure of the spider-crosspiece
In the spider, like in other crustaceans, the body cavity has a mixed nature - in the course of development it occurs when the primary and secondary cavities of the body are joined.
Digestive system. A spider-spider can not eat solid food. Catching prey, for example some insect, with the help of cobwebs, he kills him poison and lets in his body digestive juices . After a while, the contents of the caught insect become diluted, and the spider sucks it out. From the victim there is only an empty chitinous shell. This way of digestion is called extraintestinal .
Of the four species of poisonous snakes in our country, two that lead to accidents are the cruiser and the yara. The number of annual accidents ranges from 50 to more than 70, and the Ministry of Public Health distributes a specific serum against poison against the poison of these 2 species throughout the country. Two other species do not cause accidents due to: the non-aggressive character of the corals and because the rattlesnake is endangered, and also usually "warns" of its presence by shaking the rattlesnake that, if it meets a person, it usually costs life.
The spider's digestive system consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestine. In the midgut, long blind outgrowths increase its volume and suction surface. Undigested residues are taken out through the anus.
Respiratory system. The respiratory organs in the spider are lungs and trachea. Lungs or pulmonary sacs are located at the bottom of the abdomen, in the anterior part. These lungs developed from the gills of distant ancestors of spiders that lived in water. The spider-cross has two pairs of unbranched trachea - long tubes, which have special spiral chitinous thickenings inside. They are located in the back of the abdomen.
Although the venom has a more dangerous poison, in both cases it is necessary to take antinuclear serum in the event of an accident. The composition of the poison is the same throughout the year, in the colder months it can be more concentrated, because the animal does not spend it on feeding, and the glands do not stop producing, albeit at a lower rate.
Its distribution throughout our territory excludes stony areas, especially high ones. Melitta Menegel is accused of a biotere of overgrown animals - a serpentarium. This is calculated by researchers from Germany, Sweden and Switzerland. Amazing amount!
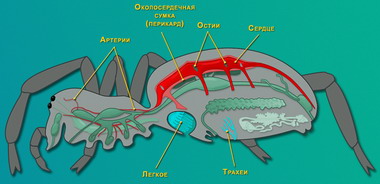 Circulatory system in spiders unclosed
. The heart has the form of a long tube located on the dorsal side of the abdomen. From the heart go away blood vessels. Like the crustaceans, in the spiders in the body circulates the hemolymph.
Circulatory system in spiders unclosed
. The heart has the form of a long tube located on the dorsal side of the abdomen. From the heart go away blood vessels. Like the crustaceans, in the spiders in the body circulates the hemolymph.
Excretory system is represented by two long tubes - malpighian vessels . At one end Malpighian vessels blindly terminate in the body of a spider, others open into the posterior part of the intestine. Through the walls of the malpighian vessels, the metabolic products are removed, which are then released to the outside. In the intestine, water is absorbed. Thus spiders save water, so they can live in dry places.
Spiders surpass people in consuming meat. According to the information published in the journal Nature Science, every year mankind consumes about 400 million tons of meat and fish. But how to measure how many spiders there are in a year? Researchers did not rely on the daily diet of spiders, but they counted the quantities using two methods: first they calculated the total population of spiders in seven different territories. The population is equivalent to 25 million tons of spider's mass.
Then they calculated the average number of victims of spiders per square meter. Great variety, great ecological significance. In total, there are more than a thousand species of spiders. But most of the time you do not see them, because they are camouflage artists. They are also nocturnal animals. Most people prefer them this way.
Nervous system The spider consists of a cephalic node and numerous nerves running away from it.
 Reproduction. Fertilization in spiders is internal. The pairing of the crosses takes place at the end of the summer. The male transfers spermatozoa into the genital aperture of the female with the help of special outgrowths located on the front legs. Vision of spiders is weak, with the help of 8 simple eyes they see badly. The male needs to be very careful that the female does not take it for prey. Immediately after mating, the spider hastily retires, as the behavior of the female can dramatically change, and the sluggish males are often killed and eaten.
Reproduction. Fertilization in spiders is internal. The pairing of the crosses takes place at the end of the summer. The male transfers spermatozoa into the genital aperture of the female with the help of special outgrowths located on the front legs. Vision of spiders is weak, with the help of 8 simple eyes they see badly. The male needs to be very careful that the female does not take it for prey. Immediately after mating, the spider hastily retires, as the behavior of the female can dramatically change, and the sluggish males are often killed and eaten.
However, this result demonstrates the ecological significance of spiders as an insect eater. "Together with other insects, such as ants or birds, they contribute to a significant reduction in insect density," says Martin Niffeler, author of the study, which adds that "spiders are important for natural balance."
First of all, it can be seen in the forests or in the countryside: here spiders kill more insects than other places. Spiders are fighting with a lot of parasites in these areas. However, they are not significant enemies of pests that affect the yield. The explanation is that crop fields are often "modified systems". Also in desert areas or tundra, the destruction of insects is minimal.
By the autumn, the female lays several hundred eggs in cocoon from the web. Hides it under the bark, under the rocks. By the winter dies. In spring, spiders crawl out of the cocoon, climb up branches and fly with gusts of wind on the cobwebs, settle. Complex behavior of the spider: the construction of trap networks, flight adaptations, dwellings - this instincts i.e. The norms of behavior peculiar to each species, which are inherited.
We must respect the spiders. First, because they make up the majority, and secondly, because they perform very important tasks for ecological balance. If the mere fact of thinking about spiders gives you goose bumps, you should know that the chances of being bitten by you are less than you imagine.
I have been practicing spiders for almost 20 years, and I was never bitten. You really need to work to be bitten by a spider because they do not want to bite, "says Chris Buddle, an arganologist at McGill University in Montreal. And spiders tend to avoid people, and usually they have no reason to bite people, because they are not "bloodsuckers" and do not eat people, says Buddle, who says: they are much more afraid of us than us.
Arachnids are mostly terrestrial arthropods. They breathe with the help of the lungs or trachea. Their body is divided into the cephalothorax and abdomen, or it is fused. Externally, arachnids can be distinguished from other arthropods by the following features: they do not have antennae, two pairs of oral organs and four pairs of walking legs. The complex behavior of spiders (the construction of trap networks, cocoons) is based on instincts.
Buddha noted that when a person is bitten by a spider, when a spider reaches the gloves, shoes or clothes that are used. And yet most of them are not toxic to humans. The specialist says that spiders feed on small invertebrates as insects, so their poison is not aimed at large animals, such as humans.
In fact, many are not even able to pierce human flesh. The Buddha said that he watched as the arachnids "moved their fangs to the skin again and again," but in vain. Only a dozen of the approximately 000 species of spiders in the world can cause serious harm to average healthy adults. Although there are very dangerous - for example, an angled spider or a black widow, even despite this, records show that the bites of these spiders are very rare, emphasizes Badl.
Representatives of arachnids are eight-legged terrestrial arthropods, in which the body is divided into two sections - the cephalothorax and abdomen, connected by a thin constriction or merged. Arachnids do not have antennae. On the cephalothorax there are six pairs of limbs - two front pairs (oral organs) that serve to grasp and grind food, and four pairs of walking legs. There are no legs on the abdomen. Respiratory organs in them are the lungs and trachea. The eyes of arachnids are simple. Arachnids are dioecious animals. The class of the Arachnids includes more than 60 thousand species. The length of the body of various representatives of this class is from 0.1 mm to 17 cm. They are widely distributed around the globe. Most of them are terrestrial animals. Among ticks and spiders there are secondary forms.
But now the deaths from spider bites are rare due to antidotes. Spiders can kill "annoying insects," which are more likely to bite people than spiders, Buddle adds. "In the vast majority of cases, spiders are our friends," he added.
The true causes of the so-called "spider bites"
The vast majority of brands identified as "spider bites" are caused by something else. Vetter said that the study shows that of those who seek treatment for this reason, only 3, 8% were actually bitten by spiders, and 85, 7% suffered from various infections.
The biology of arachnids can be considered by the example of a spider-cross.
External structure and way of life. A spider-cross (called so for a cross-shaped figure on the dorsal side of the body) can be found in the forest, garden, park, on the window frames of village houses and dachas. For most of the time, the spider sits at the center of its hobby network with a sticky thread - cobwebs.
How to recognize a terrible angular spider
In addition, in addition to various viral and bacterial infections, other factors that can cause symptoms similar to spider attacks are fleas or bugs, allergies, poisonous oak and poison ivy. If you are traveling to a cabin that you have not visited for a long time or even at home, you should be aware of the possible appearance of angled spiders, species that hide in dark places and are difficult to access. Although they allow you to control the population of other small insects, its bite can become fatal.
The body of the spider consists of two parts: a small elongated cephalothorax and a larger spherical abdomen (Figure 90). The abdomen is separated from the cephalothorax by a narrow constriction. At the anterior end of the cephalothorax there are four pairs of eyes from above, and from below a pair of hook-shaped hard jaws is the chelicer. The spider grabs its victim. There is a channel inside the chelicer. Through the canal, the poison from the poison glands located at their base enters the victim's body. Near chelicera are short, sensitive sensory organs covered with sensory hairs-the senses of the senses. Four pairs of walking legs are located on the sides of the cephalothorax. The body is covered with a light, durable and quite elastic chitinous cover. Like crayfish, spiders periodically shed, dropping the chitinous cover. At this time they grow.
Fig. 90. The external structure of the spider: 1 - the sensory; 2-foot; 3 - the eye; 4 - cephalothorax; 5 - abdomen
At the lower end of the abdomen, there are three pairs of cobweb warts that produce a cobweb (Figure 91) - these are modified abdominal legs.
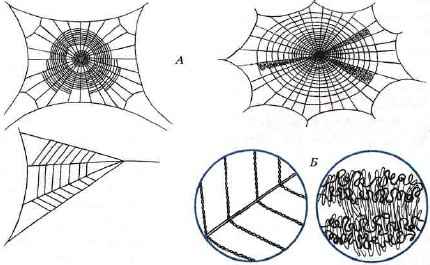
Fig. 91. Spider webs of various types of spiders (A) and the structure (with increasing) of a spider's thread (B)
Spilled out of spider webs, the fluid instantly hardens in the air and turns into a strong spiderweb thread. Different parts of cobweb warts distinguish cobwebs of different types. Spider webs vary in thickness, strength, and tackiness. Different types of spider webs are used to build a hitching net: at its base are stronger and not sticky threads, and concentric threads are thinner and more sticky. Spiders use cobwebs to strengthen the walls of their shelters and to make cocoons for eggs.
Digestive system The spider consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestine (Figure 92). In the midgut, long blind outgrowths increase its volume and suction surface. Undigested residues are taken out through the anus. A spider-spider can not eat solid food. Catching prey, for example some insect, with the help of cobwebs, he kills him with poison and lets in his body digestive juices. Under their influence, the contents of the caught insect become diluted, and the spider sucks it out. From the victim there is only an empty chitinous shell. This method of digestion is called extraintestinal.
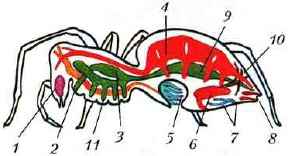
Fig. 92. Internal structure of the spider-cross: 1 - poisonous gland; 2 - the mouth and esophagus; 3 - stomach; 4 - heart; 5 - pulmonary bag; 6 "- the sexual gland, 7 - the trachea, 8 - the arachnoid gland, 9 - the gut, 10 - Malpighian vessels, 11 - the outgrowth of the intestine
Respiratory system. The respiratory organs of the spider are lungs and trachea. Lungs, or pulmonary sacs, are located from below, in front of the abdomen. These lungs developed from the gills of distant ancestors of spiders that lived in water. The spider-spider has two pairs of unbranched trachea - long tubes carrying oxygen to the organs and tissues. They are located in the back of the abdomen.
Circulatory system spiders are not closed. The heart has the form of a long tube located on the dorsal side of the abdomen. From the heart go away blood vessels.
In the spider, as in the case of crustaceans, the body cavity has a mixed nature - in the course of development it occurs when the primary and secondary cavities of the chela are joined. The hemolymph circulates in the body.
Excretory system is represented by two long tubes - Malpighian vessels.
At one end Malpighian vessels blindly terminate in the body of a spider, others open into the posterior part of the intestine. Harmful products of vital activity leave the walls of mal-piegive vessels, which are then discharged outside. In the intestine, water is absorbed. Thus spiders save water, so they can live in dry places.
Nervous system The spider consists of a cephalic nerve node and numerous nerves that leave it.
Reproduction. Fertilization in spiders is internal. The male transfers spermatozoa into the genital aperture of the female with the help of special outgrowths located on the front legs. The female, after some time after fertilization, lays eggs, braids them with a web and forms a cocoon (Figure 93).
Fig. 93. A female spider with a cocoon (A) and the settling of spiders (B)
Small spiders develop from eggs. In the fall, they release spider webs, and on them, like parachutes, are carried by the wind for long distances - spiders settle.
A variety of arachnids. In addition to the spider-crosspiece, another 20,000 species are also assigned to the Pauky squadron (Figure 94). A significant number of spiders build spider webs. Y different spider webs differ in form. Thus, in a house spider inhabiting a person's habitation, a snare net resembles a funnel, in a poisonous, mortally dangerous for human karakurt, the snooping net resembles a rare hut. Among spiders there are also those who do not build hawking networks. For example, spiders-sidewalks sit in ambush on flowers and wait for small insects arriving there. These spiders are usually brightly colored. Spiders-hoppers are able to jump and thus catch insects.

Fig. 94. Various spiders: 1 - spider-cross; 2 - Karakurt; 3 - the spider-regiment; 4 - spider-crab; 5 - tarantula
Spiders-wolves roam all over the place, searching for prey. And some spiders sit in the holes in the ambush and attack the insects crawling nearby. They belong to a large spider, inhabiting the south of Russia - the tarantula. The bites of this spider for man are painful, but not fatal. To the Hay-mowers belong very long-legged arachnids (about 3500 species) (Fig. 95, 2). The cephalothorax is not clearly separated from the abdomen, the chelicerae are weak (therefore, the haymakers feed on small prey), the eyes are arranged in the form of a "turret" on top of the cephalothorax. Hay mowers are capable of self-mutilation: when a predator grabs a haystack by the leg, he throws this limb away, and runs away. And the severed leg continues to bend and unbend - "mow".
Scorpions are well represented in the subtropics and deserts by small animals 4-6 cm long (Figures 95, 3). In the tropics live large scorpions up to 15 cm in length. The body of the scorpion, like a spider, consists of the cephalothorax and abdomen. The abdomen has a fixed and wide front part and a narrow, long movable posterior part. At the end of the abdomen there is a swelling (there is a poisonous gland) with a sharp crochet. They scorpion kills its prey and protects itself from enemies. For a person, the injection of a large scorpion with a poisonous sting is very painful, can lead to death. Helicers and tentacles in scorpions have the shape of a claw. However, the chelicer claws are small, and the claws of the tentacle are very large and resemble claws of crayfish and crabs. A total of about 750 species of scorpions.
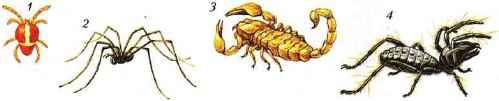
Fig. 95. Various representatives of arachnids: 1 - mite; 2 - haymaker; 3 - scorpion; 4 - phalanx
Ticks. Mites have more than 20 thousand species. Their body length usually does not exceed 1 mm, very rarely - up to 5 mm (Figures 95, 1 and 96).
Unlike other arachnids, the body is not divided into the cephalothorax and abdomen. In mites that feed on solid food (microscopic fungi, algae, etc.), the jaws are gnawing type, while in those who eat liquid food they form a prickly-sucking proboscis. Ticks mite in the soil, among the fallen leaves, on plants, in water and even in human homes. They feed on rotting plant remains, small fungi, algae, invertebrates, suck plant juices, in the living quarters of the people microscopic mites feed on dry organic remains contained in dust.

Fig. 96. Iksodes tick
The value of arachnids. Arachnids play a big role in nature. Known among them are herbivores and predators that eat other animals. Arachnids, in turn, are fed by many animals: predatory insects, birds, animals. Soil pliers participate in soil formation. Some mites are carriers of severe diseases of animals and humans.
Arachnids are the first terrestrial arthropods that have mastered almost all habitat conditions. Their body consists of the cephalothorax and abdomen. They are well adapted to life in the land-air environment: they have dense chitinous coverlets, they possess pulmonary and tracheal breathing; save water, play an important role in biocenosis, are important for humans.
Exercises for the material
- Name the signs of the external structure of arachnids, distinguishing them from other representatives of arthropods
- On the example of a spider-cross, tell us about the ways of obtaining and digesting food. How are these processes related to the internal organization of the animal?
- Give a description of the structure and activity of the basic systems of organs, confirming the more complex organization of arachnids in comparison with annelids.
- What is the importance of arachnids (spiders, mites, scorpions) in nature and human life?