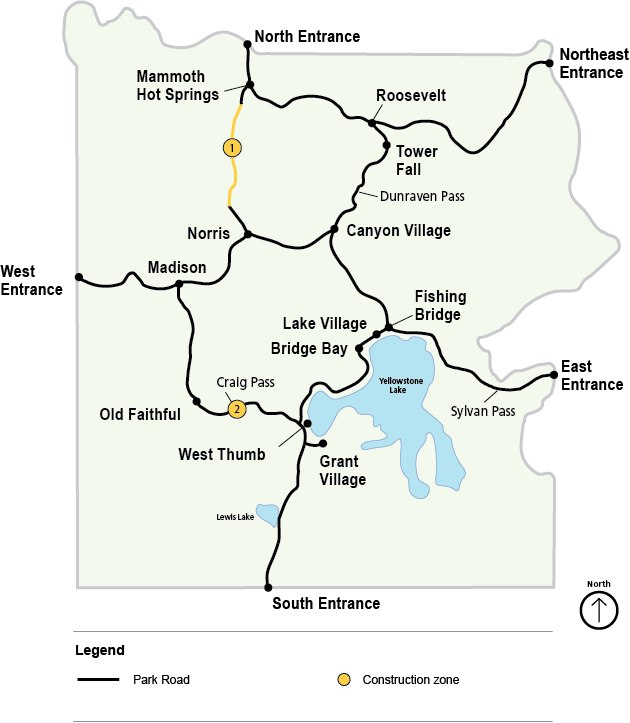
The Yellowstone volcano is a real threat to the Earth
Supervolcans are the most destructive force on our planet. The capacity of their eruptions is tens of times greater than that of ordinary volcanoes. While they are dormant for hundreds of thousands of years, the magma is locked in huge tanks inside their vents. But one day it pours on the surface of the earth with an apocalyptic force capable of destroying whole continents. Such sleeping "monsters" on Earth are a few and one of them - Caldera.
News from Yellowstone:
"The terrible date of the eruption of the super-volcano Yellowstone is approaching, but it is not being divulged so as not to cause panic ..."
Recently, the US TRC NAT GEO WILD has increasingly begun to show popular science films, during which many people get cold in their veins, and nervous viewers simply swear to turn off the TV. What is so terrible show our transatlantic neighbors? What news from Yellowstone impress Americans so much? And they demonstrate an incredibly faithfully modeled tape with detailed comments that connects the end of life, and the planet Earth itself with the eruption of a super volcano, whose wild nature awakens now in the Yellowstone reserve in the north of the central US.
The American continent in anticipation of the disaster in Yellowstone.
Our blue planet, so small and defenseless touching the ice in the dark space, inhabited by diverse animal world, consisting of flowering, fertile land, forests, rivers, lakes and morey- live and be happy! - has incredibly huge resources for the periodic destruction of all life on its surface. And wildlife resources are as follows: tornadoes, hurricanes, typhoons, earthquakes, giant tsunamis. Dangerous places on Earth, of course, are everywhere. In 2004, more than 500,000 people died, and South-East Asia was almost destroyed, and in 2011 such a terrible fate could befall Japan. But today's misfortune comes from waking up super volcanoes. One of which is the Yellowstone volcano.
The main difference between super volcanoes is the huge size and extraordinary eruption force, which is tens of thousands of times greater than the eruption of ordinary volcanoes. One of the biggest super volcanoes is in North America in Yellowstone Park. The volcano in Yellowstone National Park is of particular concern.
The Yellowstone bomb is ready for the explosion.
Yes, yes, a natural disaster is brewing in the most fertile corner of this richest natural resource country in the world. Yellowstone National Park, known for its forests, grizzly bears and hot springs, is in fact a bomb that will explode in the near future. If this happens, the entire North American continent may die. And the rest of the world will not seem a little, and some planetologists generally believe that all life on Earth will end. Of course, not at once, but in a couple of years exactly, makes your prediction NAT GEO WILD. About this a little later.
Caldera Yellowstone. How it all began?
And it all started, it's just wonderful and interesting. In 2002, several geysers with hot healing water were simultaneously killed in the reserve. Local travel companies immediately promoted the advertisement of a new phenomenon in the Yellowstone caldera.
However, strange things soon began to happen. The US government tightened the regime of visiting the Yellowstone Reserve in 2004, and some areas of the park were declared closed to tourists. But the most interesting is that scientists, seismologists and volcanologists, who are irresistibly attracted by the wild nature of the caldera, have become frequent here with the trips.
Scientists have previously worked in the Yellowstone caldera, because the entire territory of the reserve with its unique nature is nothing but a huge patch on the crater of an extinguished ancient super volcano. From here, in fact, and hot geysers. On the way from the bowels to the surface of the earth, their water is heated by the magma gurgling directly under the earth's crust. Local sources were still known when the European colonialists took Yellowstone to the local Indian tribes, and here you have three new ones at once! And why would that be?
Scientists slowly sounded the alarm. After thoroughly examining the entire territory of the park and in particular the mouth of the sleeping giant volcano, in 2007 they created a Scientific Council with wide emergency powers under the US president. Along with the leading geophysicists and seismologists, the Council included the Minister of Defense, the Director of the NSA, the CIA, the FBI. And also the chairman of the National Security Council!
The monthly meetings of this organ closed to all are headed personally by President Bush (today, by the way, Mr. Obama is doing it).
ATTENTION! ATTENTION! The catastrophe in Yellowstone is expected in 2012-2016!
You probably already guessed what the essence of all anxieties is. The oldest and, as to this day, experts believed, a completely safe "grandfather-volcano" - a paradise for all living things - suddenly showed signs of activity. Thirty-three-meter hot springs that had killed overnight became the first harbingers of the approaching planetary tragedy. Why, I wonder, the planetary?
Yes, because the explosion of the awakening volcano monster emission of magma, ash, dust, gases and other instantly reach a height of 50 kilometers (stratosphere), and within two days of the release of spread to a territory twice the area the whole territory of the Americas, still creeps to Greenland, Antarctica and, of course, Europe. About a week later, the "death cloud" will reach Pakistan-India on the one hand and the Australian continent on the other. The world will be taken into the ring, where not the slightest sunbeam penetrates! What does it mean?
Without sunlight, the entire flora will perish, oxygen will disappear, without air and plant food, the entire fauna of the planet, of course, and people, too, will die out at about the same period.
And what do scientists say about the Yellowstone volcano?
Based on information about the eruptions of the Yellowstone volcano, they developed an algorithm for its vital activity. The result was shocking. That the intervals between volcanic eruptions are constantly shrinking, scientists have been known before. However, given the astronomical duration of these gaps, this information had no practical significance for the population of the Earth. In fact, Yellowstone erupted 2 million years ago, then 1.3 million years, and the last eruption - 630,000 years ago. What from that?
The US Geological Society expected the awakening of the wildlife of Yellowstone not earlier than 20,000 years ago. But based on the latest data, computer programs produced an unexpected result - the next disaster is expected in 2075. However, after a short time, it became clear that events were developing with frightening speed. The result was adjusted again. The terrible date of the eruption of the Yellowstone volcano approached, but in order not to cause panic, it is not disclosed.
The further scenario of the Earth's death.
Thousands of cubic kilometers of lava erupt from the super volcano. The amount of this is enough to cover the entire surface of the United States of America with a layer of 15 centimeters. The eruption of Yellowstone will have a force that is 2500 times greater than the strength of the last eruption of the Sicilian Etna.
A couple of weeks after the sun disappears in the dust clouds, the air temperature on the surface of the Earth will fall in various parts of the world from minus 15 degrees to minus 50 degrees and below. The average temperature on the entire surface of the Earth is only minus 25 degrees Celsius.
Winter will last at least a year and a half. This is quite enough to change the natural balance on the planet forever.
Those few of the people who still survive in the giant cataclysm will have to move from the frozen surface to deep caves, and scientists raise their questions about getting water and food ...
Before mankind there is a most complex question: how to escape from the grandiose eruption of the super-volcano Yellowstone or at least reduce the consequences of the monster's destructive activity?
Perhaps in the near future we will learn about the data that characterize the current state of the super volcano in Yellowstone Park, because the imminent danger of catastrophe threatens all of humanity. It is known that many countries, including Russia, have already sent their observers to Yellowstone in order to be aware of the state of affairs in the hotbed of tension.
According to the magazine Focus, United Kingdom, the site "Our Planet
AND ALL NEWS (July, 2014):
Because of the underground heat, asphalt melts in Yellowstone
On July 10, the Yellowstone National Park Service issued a warning about the closure of one of the roads. Because of the extreme heat from nearby thermal areas, the asphalt began to melt on the Firehole Lake Drive.

The press release states that the extreme heat from the surrounding thermal pads made to bubble and melt the road surface, damaging the asphalt and creating hazardous driving conditions on the popular and scenic park road in the district of Lower Geyser Basin.
The Independent told about NASA warning about the threat of a super volcano eruption
NASA experts believe that the eruption of the super-volcano will lead to more terrible consequences than the fall of the asteroid
US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA's) warns about the threat of the eruption of the Yellowstone supervolcano (volcano, whose eruption reaches eight points on a scale of volcanic eruptions and can cause climate change on the "Y" planete.-). About it informs The Independent. More, incl.
Under the surface of the earth in Yellowstone lies a huge reservoir with a red-hot magma that will one day explode if not taken
Yellowstone Volcano is located in the state of Wyoming. Its eruption can lead to a "volcanic winter". To prevent this from happening, scientists want to "cool the volcano" by driving water through a hole in it, and then using the resulting steam to produce electricity.
The experts believe , that for today on the Earth there are about twenty super volcanoes that can wake up at any moment. At the same time, they note that the eruption of such volcanoes will lead to a "volcanic winter", as a result of which millions of people may die.
The most dangerous among all the super-volcanoes scientists believe Yellowstone, which is in the US state of Wyoming. Its caldera has a size of 55 kilometers by 72.
Now, NASA specialists are developing a plan to prevent the eruption of the Yellowstone volcano. In particular, the option is considered with increasing the volume of water for its "cooling".
Later it turned out that NASA was talking about the threat of an eruption of a super volcano since the middle of the last summer month - a warning, in particular, is mentioned in material BBC on August 18:
Scientists NASA came up with how to save mankind from the super-volcano
Nature and cataclysms
If the catastrophic eruption of the Yellowstone Super Volcano is inevitable, then the plan of American scientists is perhaps the only way to save humanity from destruction.
Under the Yellowstone National Park in the northwest of the United States lies a volcanic caldera - a huge bubble of hot magma.
It was her underground energy that created a lot of geysers and hot springs, which attract tourists. However, this caldera (it is also potential super-volcano) is the greatest natural threat to the existence of all mankind.
And as some NASA scientists say, the threat is even more terrible than a collision with a giant asteroid or comet.
A team of NASA researchers provided a report to the BBC that was not previously published in open sources. He - just about what can happen to our planet in the event of another eruption of the super volcano and how to avoid it.
"I was a member of the advisory board NASA to protect the planet from asteroids and comets, - said Brian Wilcox, who works in a NASA laboratory at the California Institute of Technology -. And during the study of the earth protection capabilities from the fall of celestial bodies, I have concluded that the eruption super volcano is much more dangerous for humanity. "

Astronauts from space have a stunning view of volcanic eruptions
On Earth, there are about 20 known super volcanoes, and truly catastrophic eruptions occur on average every 100,000 years.
One of the most serious consequences of such an eruption can be called a massive famine, since volcanic winter (ash for a long time will close the sun) will not allow humanity to provide the necessary amount of food. (During the eruption in the territory of modern Wyoming 600,000 years ago, the super volcano, located on the site of the current Yellowstone Park, thrown into the atmosphere more than 1000 cubic kilometers of lava and ash. - Ed.)
According to estimates made by the UN in 2012, people will have enough food for 74 days.
When NASA scientists began to investigate the problem, they came to the conclusion that the easiest and logical thing would be to cool the super volcano somehow.
A huge volcanic caldera - in this case Yellowstone - is essentially a giant thermal generator, the equivalent of six industrial power plants.
Currently, about 60-70% of the heat of Yellowstone rises to the surface and leaves in the atmosphere with water (it seeps to the magma through cracks).
The rest accumulates in magma, which gradually dissolves the surrounding rocks. When the underground heat reaches a certain limit, an explosive eruption will inevitably begin.
But if you let go to the surface of more than now, the amount of thermal energy, the eruption will not happen.
According to NASA's calculations, it's enough to increase this amount by 35%, and Yellowstone will no longer be a danger. That's just how to do it?
One option is to increase the volume of water entering magma. But if to speak in practice, it will be extremely difficult to convince the country's authorities to sanction this.
"Building a giant aqueduct in a mountainous area will be both technically and very expensive at the same time, and people are unlikely to like that water will be spent on it," Wilcox said.
"Across the world, there is an acute shortage of water - and here is such a powerful infrastructure project, in which it is used only to cool some super-volcano ... This will cause at least serious controversy."
Therefore, NASA developed a completely different plan.

If the eruption of the super volcano happens, it will be many, many times more powerful than the eruption of this volcano in Indonesia
Scientists believe that the most suitable solution is to drill wells with a depth of 10 km and pour water into magma at high pressure.
Returning to the surface of the water will have a temperature of about 350 degrees Celsius, gradually cooling the volcano, hiding beneath the surface of the earth.
And although the implementation of this project will cost about $ 3.46 billion, it has one very attractive feature that will help convince politicians that investments are worth it.
Wilcox explains that Yellowstone can be used as a geothermal power plant, which will generate incredibly cheap electricity - about $ 0.10 per kWh.
Yes, drilling will require serious investments, but it will pay off quickly. The region will receive a source of cheap electricity for many years to come - for tens of thousands of years!
"Well, of course, you will thereby save mankind from the imminent threat of a catastrophic eruption of the super volcano," Wilcox emphasizes.
However, drilling in the super volcano area has its risks. Namely, it can provoke the very eruption that scientists are trying to prevent.
"The most important thing is not to make things worse," Wilcox says, "when you drill on the surface of the magma, the risk is high." Drilling can make the top layer, the "cover" of the magma boiler fragile, and this lid will tear, or it will crack. "
"You can also provoke the release of explosive gases in the upper part of the underground reservoir with magma."

The eruption of Etna (view from space). Further north next to Naples is the large volcanic region of Campi Flegrei (Phlegrean fields)
Therefore, scientists suggest drilling beyond the Yellowstone National Park and getting to the magma reservoir from below.
"So you prevent the temperature rise in the upper part of the boiler with magma, which is exactly what constitutes the main danger," explains Wilcox.
But even if the NASA scientists project is accepted for implementation, its authors will not see its completion, and even during life it is unlikely to find out whether it is successful or not.
Cooling down Yellowstone one meter per year is a matter of tens of thousands of years, after which only a cold rock will remain in its place.
And even if we take into account that the Yellowstone magma does not need to be cooled to a solid state in order to remove the threat to mankind, it's all the same - before hundreds of years or even thousands of years we do not understand how successful the project of American scientists is.
Despite this, such long-term planning is perhaps the only way to prevent a catastrophe.
"If such a project begins to be implemented, all we get from it at first is cheap electricity," Wilcox said.

Wander over the cauldron with a hot magma - this pleasure attracts many tourists
Such a plan can in principle be applied to any active supervolcan on our planet, and NASA scientists hope that their ideas will turn into practical scientific discussions about how to ward off the threat of a catastrophic eruption.
"When people first became acquainted with the idea of protecting the planet from the impact of an asteroid, the reaction was about the same as today's threat from a super volcano," Wilcox emphasizes. "We are such a tiny, people said." How can we eliminate the threat of a collision of the Earth with an asteroid? "
"However, it turned out that if you invent something that only slightly pushes an asteroid, it makes him eventually fly by the Earth and the solution to the problem is easier than we thought."
"In any case, we need to unite the intellectual forces of scientists around the world, and we need to start as soon as possible." Yellowstone erupts about 600,000 years ago, and that's exactly what happened since the last catastrophic eruption, so we need to keep this in mind. "
David Cox, BBC Future
"Kommersant" / "BBC", August 18 - September 10, 2017
Yellowstone National Park and its famous resident - the eponymous supervolcano - relatively often on the front pages of newspapers and in news reports worldwide channels, and it is quite justified: in the past there have been many earthquakes in the region and geophysical maps clearly show how the region changes its shape .
All this creates a tense atmosphere, however, one should pay attention to the scientists' forecasts - the threat of a super volcano eruption this year is one chance out of 730 thousand, besides, the nearest eruption of Yellowstone will simply be a slow flow of lava.
Risk

Nevertheless, there is still a risk of a major eruption. Severe eruption The Yellowstone super volcano can easily lead to catastrophic consequences for the whole world and the US in particular.

The explosion will completely erase the USA from the face of the earth, and also destroy most of the agriculture of the whole world. This will not only cause economic collapse, but will also destroy millions of people.
Forecasts

According to the BBC, a study of the Space Agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory has confirmed that the threat of a super volcanic eruption is considered the most likely cause of the "doomsday", along with nuclear explosions.
In the future, predictive methods will accurately predict when such super-volcanoes as Yellowstone will erupt, but at the moment forecasts can not give accurate or even approximate dates. Therefore, according to many, the best thing we can do is to prepare for the worst.
What to do?

NASA researchers, apparently, do not agree with such sentiments. They decided to approach the threat of a super volcano eruption from the other side and answer the question of how to avoid it.
To potentially reduce the risk of eruption, a team of NASA scientists came up with a rather bold plan: they are going to drill a magma chamber and cool the magma.

It turns out that magma erupts only when it reaches a certain high temperature and is sufficiently "liquid". While the magma is in a more solid state, it moves very slowly and heavily.
According to the report, by cooling the magma in the hearth by about 35%, we can completely prevent the eruption threat.
Is it possible?

In this case, drilling a vast focus of magma supervolcan proved to be the only reasonable solution. Icelandic scientists are actively drilling the rocks over the magma volcanoes of Icelandic volcanoes to obtain clean, geothermal energy, so why not do the same in Yellowstone for the benefit of the whole planet? This project will not only cool and slow down the volcano, but also extract a significant amount of environmentally friendly heat.
Drilling process

Scientists suggest that for cooling, you do not need to dive directly into the hearth, which would be extremely dangerous and would cause depressurization. To cool the magma it will be enough to reach the walls of the hearth, located at a depth of 10 kilometers. At this depth, geothermal waters heated by magma flow.
These waters, in and of themselves, cool the magma well, absorbing its heat, but this is not enough, so NASA experts plan to add cold water under extremely high pressure.
To accidentally not damage the roof of the magma chamber, which, again, is extremely unsafe, NASA offers to drill rocks under the hearth.
Cost

If this project is approved, its cost will be approximately three and a half billion dollars. It is not cheap, however, on the rescue of the United States in particular and the planet as a whole, the space agency offers not to save. In addition, the price of the project to protect the state from the threat of destruction is only 0.6% of the country's total military budget.
NASA assures, however, that their plan will pay off over time. All this excess heat, extracted from drilling, must go somewhere, so why not use it to supply the surrounding cities with electricity?
Anyway, this project has a sad side. The fact is that even with approval and funding, sufficient cooling of the magma will take several centuries. This means that those people who came up and started the process will never know its result.
NASA scientists report that the eruption of a super volcano is much more dangerous for mankind than a collision of the Earth with an asteroid. The increased danger of supervolcanoes is seen in the fact that their eruption is considered a much more likely event (although, as we shall see later, this controversial statement), as well as it can not be known in advance as about the approaching asteroid to our planet, and take timely measures. However, other researchers consider such fears to be excessive, and the proposed ways of "cooling" super-alkanes - unrealistic.
The so-called "super-volcanoes" do not differ in principle from ordinary volcanoes. This is generally not a scientific, but rather a publicistic term, which became popular after the release in 2000 of the BBC documentary series on a powerful volcano. Usually, a volcano is known as a super volcano, capable of producing a volcanic eruption of 8 VEI, the Volcanic Explosivity Index, proposed in 1982 by American volcanologists Christopher Newhall and Stephen Self. Eight points on this scale means that the volume of matter ejected during the eruption of the volcano should exceed one thousand cubic kilometers. For comparison, Tambora volcano erupted from 150 to 180 cubic kilometers in 1815, Krakatau in 1883 was only 12 km³, Pinatubo in 1991 - 10 km³ (photo of this eruption is shown on the title page), Vesuvius in 79, according to scientists - 3 km³, Eyjafjallajökull in 2010 - and at all 0.25 km³. Eruption of 8 points on the VEI scale is sometimes called a mega-eruption.
In the historical period, mankind did not face mega-eruptions. But geologists recognize their traces well. Therefore, we can establish that over the last 485 million years (from the Ordovician period), super volcanoes erupted 47 times. People found the last of these eruptions, but at a very early stage of history.
Approximately 26,500 years ago, there was an eruption of the Taupo volcano on the island of North in New Zealand. It has its own name - the eruption of Oruanui. The total volume of erupted substances was 1170 cubic kilometers. In the central part of the island, the height of the layer of volcanic ash was not less than 200 meters. If this happened in Moscow, then from the main building of the Moscow State University only a part of the spire would stick out on the surface. Later, about 180 BC. the volcano Taupo erupted again (the eruption of Hatepe). This time everything was more modest, but on a global scale it was a serious eruption: about 120 km³ of discarded material, which corresponds to seven points on the VEI scale. People at this eruption were not harmed, as New Zealand was inhabited only in 1250 - 1300 years, but the Chinese chronicles kept mention of the red color of the sky at that time. After that, Taupo erupted in 260, even weaker, and since then there have been no eruptions. In the caldera of the volcano is now the same lake - the largest in New Zealand, an area of 616 square kilometers.
View from space to Lake Taupo
Another mega-eruption, which people found, happened about 75,000 years ago. The volcano of Toba in the north of Sumatra erupted. The emission is estimated at about 2800 km³. Traces of volcanic ash from Toba are found in central Africa, and when drilling ice cores in Greenland and Antarctica it is noted that in the period during which this eruption occurs, the content of sulfur compounds in the Earth's atmosphere has sharply increased. It is believed that the dust released into the atmosphere made it difficult to access the sun's rays and caused a "volcanic winter" that lasted from six to ten years. And the general cooling of the climate lasted about a thousand years, although it is unclear how much it is due to the eruption of Toba, since the eruption occurred already during the glacial era.
A number of scientists believe that the Toba volcano threatened the existence of people. After its eruption, the Homosapiens Only a few thousand people fell sharply. The so-called "bottleneck effect" - the depletion of the gene pool due to the decline in numbers - in the early history of mankind is confirmed by genetic studies . Once in the remote antiquity of people there were no more than ten thousand. But there are researchers who do not agree that it was connected with You. Paleoclimatologists argue about the magnitude of the decrease in the average temperature on the Earth under the influence of volcanic ash. Anthropologist Michael Petralgia discovered that in southern India traces of people's presence are found in layers of deposits both before and after a layer of volcanic ash from Toby. On the other hand, the local inhabitants really did not have to die right after the eruption and for the years that remained, gradually dying from the cold and hunger, could leave their artifacts in the upper layers of sediments. While the linkage of the decline in the human population and the Toba volcano remains a hypothesis, although very likely.
Volcanic activity in the Yellowstone National Park of the United States was known for a long time, but the supervolcan caldera was discovered there only in the 1960s by geologist Robert Christiansen. Later, its existence was confirmed by comparing Christiansen maps with pictures of the national park territory made from space. Caldera occupies about a third of the park's territory. Geologists found that there were three catastrophic eruptions in Yellowstone. The first happened about 2.1 million years ago. The volume of emissions reached about 2,500 km³. As a result of the eruption, the Island Island Park caldera originated in the states of Idaho and Wyoming. Its size is approximately 80 by 65 kilometers. The next eruption was the weakest of the three. The remaining caldera - Henris-Fork, measuring 29 by 37 km - lies inside the caldera Island Park. The volume of the ejected material was 280 km³ (VEI 7).
Finally, the last eruption of the Yellowstone super volcano, which formed the current caldera, occurred about 640,000 years ago. It was more powerful than the second, but weaker than the first eruption. The volume of igneous material is estimated at 1000 km³, a layer of volcanic ash covered a significant part of North America. Lava Creek tuff formation that arose after the eruption has a capacity of up to 200 meters.
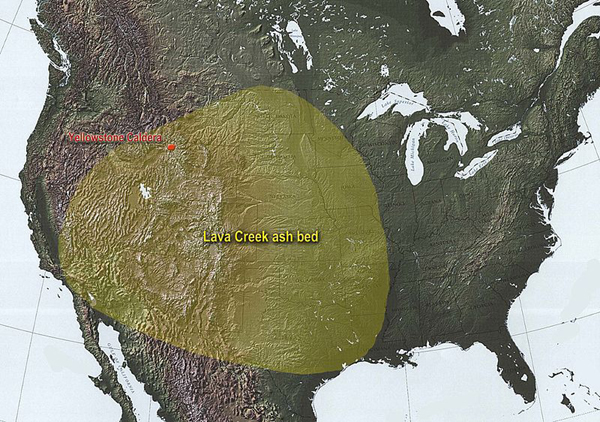
The ash layer of the third eruption of the Yellowstone Super Volcano
It is worth mentioning and another super volcano in the US - the caldera of Long Valley in the eastern part of California. Its size is 32 by 18 kilometers. There was a caldera as a result of an eruption, which occurred about 760 thousand years ago. Most likely, this eruption was a little under 8 points on the VEI scale, the amount of emissions is estimated at 750 km³. But the seismic activity in the area of Long Valley is very high, and hence the volcano can wake up again.

Map of the Long Valley caldera
Altogether, there are about twenty super volcanoes on Earth. Millions or thousands of years they are dormant, making themselves known by the exits of volcanic gases (fumaroles), geysers, mud boilers. But there is a risk that they will again show what they are capable of. And the greatest concern among NASA researchers is the Yellowstone Super Volcano. In its vicinity, there are 1000 to 2000 earthquakes every year, although most of them have a magnitude of 3 and are felt only by instruments. The Yellowstone plateau rises at a rate of 1.5 centimeters per year, indicating an increase in magma pressure. Maximum speed the rise was in 2004 - 2008, when it was more than seven centimeters per year.
Estimating the potential capacity of the Yellowstone eruption, they say that lava flows will destroy everything within a radius of 97 kilometers, and Wyoming and neighboring states will cover a meter layer of volcanic ash. But these events, catastrophic on the continent's scale, are inferior to the consequences of a possible eruption for the whole Earth. If enough ash and gases are emitted into the atmosphere, the Sun may disappear for several years, and "volcanic winter" - drag on for decades, millions of people will starve.

The geological structure of the Yellowstone Super Volcano
True, not everyone is inclined to perceive the threat of Jelouston so sharply. In 2005, the US Geological Survey, Utah State University and the Yelouston Volcanological Observatory ( YVO) announced the , that "they do not see evidence that in the foreseeable future there will be another such catastrophic eruption in Yellowstone. The periodic intervals of these events are neither regular nor predictable. " Although in 2013, scientists from Utah found that the accumulation of magma under Yellowstone is much larger than it was thought, YVO commented on it's like this: "Despite the fascination, the new results do not imply an increase in geological hazards in Yellowstone and, of course, do not increase the chances of a" mega-eruption "in the near future."

The north-eastern part of the caldera these days
Small earthquakes, earth fluctuations, and also gas emissions in Yellowstone are ordinary events and do not reflect forthcoming eruptions. Data on seismic and volcanic activity can be observed in real time on the YVO website. The probability of a catastrophic eruption in Yellowstone can be estimated based on the time intervals between the three mega-measurements of the past. In this case, the chances that it will occur in a particular year are 1 out of 730,000, or 0.00014%. This is comparable to the probability of a collision of the Earth with a large asteroid.
Mega-eruption is unlikely to come tomorrow, or in ten years, or in front of the present generation of people. But it can happen both during the 21st century and later. Therefore, scientists believe that it is necessary to prepare for such a threat now. And they prepared an action plan. About him told Brian Wilcox ( Brian Wilcox) from the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena. It was this speech that drew attention of the press to the super-volcanoes in recent days. In the caldera Yellowstone volcano Wilcox and his associates suggest drilling wells to heated rocks. There they intend to pump water, which, when heated, will cool the volcano, and at the same time serve as a source of energy in geothermal power plants.
However, for many geologists such a proposal, for sure, will cause a skeptical reaction (Wilcox himself a specialist in robotics). Implementation of the plan will require expensive drilling of superdeep wells, and even through hot, soft rocks. When the temperature and pressure become close to magmatic, the well will quickly close with minerals crystallized from the liquid. Even if these difficulties can be overcome by spending a huge amount of money, it is not a fact that the amount of water that people can pump into the wells will effectively cool the magma.