Bitten a little spider what to do. How to treat a spider bite wound
On vacation or at home, no one is immune from such a problem as a spider bite. The main difficulty in providing first aid is that after an incident it is difficult to determine the type of arthropod and to take appropriate measures.
Spider bite
This kind of creature, in any case, releases a certain amount of poison on the bite. This is a natural mechanism designed to protect and to obtain food. Most spiders inject poison into the body of the victim with neurotoxins that cause paralysis of the nervous system.
Spider bite - symptoms
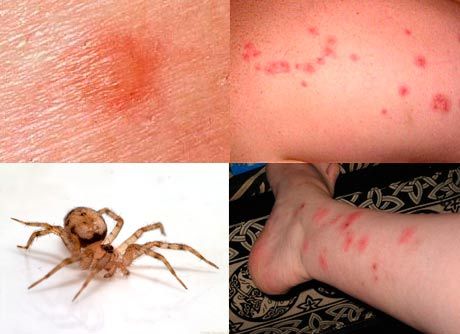
Directly during the bite, mild short-term pain may be felt, like after a shot with a thin needle. A small white spot with pinkish or red edges immediately appears in the injury site.
Subsequent symptoms of a spider bite:
- muscle pain, seizures;
- swelling and flushing of the face;
- general weakness in the body, aching joints;
- temperature rise.
For the bites of various species of spiders are characterized by special features, which will be discussed in more detail below.
Spider jogger - bite
This arthropod was named because of the pattern on the abdomen in the form of a cross. Its poison with epieurotoxicity is not dangerous to human life and health, but can cause discomfort for several days.
The bite is surrounded by a spot of pink or reddish tinge, in the center there is a slight swelling. As a rule, no special treatment measures are required, the poison will be completely eliminated from the body within 24 hours. You can impose a special ointment to relieve swelling and inflammation.
Home spider bite
Typically, such creatures do not bite, they live in remote places and are not at all aggressive. There are several types of domestic spiders, but the distribution is mainly black, they are small in size.
The bite of the arthropod in question can lead to a slight edema and pain tolerance, no more. To relieve symptoms, it is recommended to apply something cold to the injury site or compresses with cool water.
Tarantula spider bite
The presented type of spiders is very popular in domestic breeding, respectively, its bites are not dangerous for humans, in general, it does not even release poison. The only problem may be the risk of infection by the pathogenic bacteria of the injury site.
Hermit spider bite
In contrast to the above-described subspecies of spiders, the hermit is very dangerous. It is small in size and has a characteristic pattern on the upper part of the body in the form of a violin.
The hermit's bite is almost imperceptible, and the symptoms begin to appear noticeably only on the second day. Among them are dense formations under the skin that swell. Itching builds up, the seals begin to harden, and the surrounding tissues die off. Necrosis develops so quickly that it affects even the muscles and deep layers of the skin. In some cases, spider venom infects the kidneys, nervous system and can lead to death.
What to do when a hermit spider bites?

It is worth noting that a hermit bite necessarily requires the introduction of an antidote, so you should immediately seek help from doctors.
Black widow spider bite
This is probably the most dangerous spider, especially females. Karakurt is painted black, on the abdomen there is a bright red mark. This arthropod produces, when bitten, a strong neurotoxic poison that quickly paralyzes the nervous system, leading to soft tissue necrosis and gangrene.
Rescue the victim can only be in a medical institution by injection of an antidote.
However, most of them have chelicera, by means of which poison is introduced, short or too fragile to bite through the skin. Severe systemic reactions often develop from the bite of brown spiders ("violin", "guitar", brown recluse of the Loxosceles species) and widow spider (black widow - karakurt, Latrodectus). Brown spiders live in the middle west and south of the central regions of the United States, except for the coast and the states bordering on Canada, as well as occasionally imported with clothing or in baggage. Widow spiders live throughout the United States. A few poisonous species commonly referred to as (Brazilian) Spider Soldiers are not characteristic of the USA, but can be imported with food and other goods or for the purpose of selling spiders as new-fangled pets. Spider bites cause<3 смерти в год в США, обычно у детей.
Only a few poisonous spiders have been studied in detail. Poisons with necrotizing components and neurotoxic (in widow spiders) are of great importance. The most toxic component of the venom spider-widow poison is peptides that violate neuromuscular conduction. A special fraction of brown spider venom, which causes characteristic necrotic disturbances, was not isolated.
Symptoms and clinical picture of a spider bite
Brown spider bites are most common in the United States. Some bites are painless at first, but the pain, a very strong and gripping entire limb, develops in 30-60 minutes in all cases. The area of the bite becomes erythematous, with a bruise and may itch. A common itch may also begin. At the site of the bite, a central blister forms, often surrounded by irregularly shaped bruises (such as a bull's eye). Damage may resemble pyoderma gangrenosum.
Most bites leave small scars, and some even a large skin defect that can seize a muscle. Loxosselism - a systemic syndrome caused by the poison of spiders from the Loxosceles genus, may not appear until 24-72 hours after the bite and is rare. Systemic effects (arthralgia, myalgia, generalized rash, convulsions, hypotension, disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombocytopenia, hemolysis, renal failure) can lead to death.
The widow spider bites usually cause an immediate sharp burning sensation. Within 1 hour after the bite, the constant local pain, profuse sweating, and erythema can increase. The pain can be dull, aching and disproportionate severity of clinical signs. Abdominal pain can be severe, imitating a sharp stomach, rabies or tetanus. Death is extremely rare. Symptoms subside after 1-3 days, but residual cramps, paresthesias, agitation and weakness can persist for weeks and months.
The tarantula bites very rarely, it is not poisonous, but an angry spider can shed its needle-sharp hairs. They act as foreign bodies to the skin or eyes and can cause mast cell degranulation and an anaphylactoid reaction (for example, urticaria, angio-edema, bronchospasm, hypotension) in sensitized people, who usually keep spiders at home and communicate with them daily.
Diagnosing Spider Bites
- Clinical evaluation.
- Careful consideration of alternative diagnoses.
Patients often mistakenly believe that they were bitten by a spider. Typically suspected diagnosis is based on the history of the disease and physical signs, but confirmation is rare, because it requires witnessing the bite, determining the type of spider (the spider is rarely caught intact), and excluding other causes. In non-endemic areas, brown spider bites do not need to be diagnosed without determining the type of spider. Many patients mistakenly attribute the much more common methicillin-resistant infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) to an infectious skin disease to the bites of brown spiders. Such infections should be excluded, as well as other conditions that mimic spider bites. Severe cases of latrodectism must be differentiated from acute abdomen, rabies or tetanus.
When identifying spiders take into account their habitat and signs. Widow spiders live outdoors in protected places (piles of stones, firewood, hay, outbuildings) and feature a red or orange hourglass mark on their stomachs. Brown spiders live in domestic areas in hidden places and have a mark in the form of a violin or cello on the dorsal segment of the cephalothorax from the eyes to the stomach. This mark is difficult to see even on an intact spider.
Spider Bite Treatment
- Normal wound treatment.
- Delayed excision of necrotic tissue with brown spider bites.
- The introduction of calcium gluconate and possibly an antidote for latrodectism.
The treatment is the same for all spider bites and includes cleansing the wound, topically applying ice to reduce pain, the elevated position of the affected limb, the prevention of tetanus and the observation of the patient. In most cases, for the treatment of local reactions of these measures is sufficient.
For brown spider bites, limit the intervention to standard wound care and take the usual most appropriate measures to reduce the risk of infection.
- Ulcers should be cleaned daily; apply antibiotic ointment to the injury site: for example, polymyxin / bacitracin / neomycin may be used.
- Rash caused by urticaria can be treated with antihistamines, topical corticosteroids or both.
- Necrosis caused by a brown recluse spider needs to be cleaned and bandaged. Surgical excision, if necessary, should be postponed until the demarcation line of the area of necrosis is fully designated, and this process can take weeks.
No intervention will reduce the incidence or improve the outcome of a brown spider bite. Usually, proposed or poorly understood treatment options are controversial or can be harmful. Dapsone, is used until inflammation disappears with ulcers\u003e 2 cm in size, but its benefits have not been proven. The benefits are different, dose-dependent hemolysis almost always develops; agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia and methemoglobinemia have also been described. Local injection of corticosteroids in the area of necrosis also proved to be useless.
Latrodectism at the beginning is treated symptomatically. Myalgia and muscle spasms from a widowed spider bite are poorly stopped by muscle relaxants and opioid analgesics. A 10% calcium gluconate solution, slowly injected intravenously with a bolus of 2 to 3 ml, can relieve pain for a while, but requires constant cardiac monitoring. Aged patients<16 лет или >60 years, as well as with hypertension and with symptoms of severe poisoning must be hospitalized. For patients with severe latrodectism, there is an antidote made from horse serum. It can be administered as early as possible if the symptoms are severe, but can be effective up to 36 hours after the bite. The clinical response can be violent.
Bites of other arthropods
In the USA, the most common are bites from arthropods that are not tick-borne, including sand flies (a species of midges), gadflies of Scaptia beyonceae, gadflies (horse or black flies), midges (Simuliidae, detachment of Diptera), real flies (lighter, flies, autumn flies), mosquitoes, fleas, conical (kissing) bugs, lice, bed bugs, wheeled and some water bugs. All these arthropods, except for wheel and water bugs, are blood-sucking, but are not poisonous.
The saliva of arthropods varies considerably in composition, the damage from bites varies from small papules to large ulcers with edema and acute pain. Dermatitis may develop.
The location and appearance of the blisters and lesions sometimes help to determine the appearance of the bitten insect. For example, a midge usually bites in the neck, ears and face; flea bites are multiple, with feet and feet being predominantly exposed to bites; Bedbugs bites are often located on the same line and are usually localized on the body.
The bite site should be cleaned and put a cream or ointment with antihistamines and corticosteroids to get rid of itching. For severe hypersensitivity reactions, treatment is necessary.
Many of us have spiders cause really strong, inexplicable fear, and about 4-6% of the population of our planet suffer from arachnophobia - the fear of spiders to such an extent that it significantly interferes with living.
And this is no accident: spiders are the oldest inhabitants of the Earth, their age is estimated at hundreds of millions of years, and the number of species currently living on the planet is estimated at 3-4 tens of thousands of species, all of which are poisonous to one degree or another. Poison is an integral part of their way of life, because all spiders are hunters that kill a victim with a special substance that is released when they bite. In the world there is only 1 type of spider, the diet of which consists of the leaves of plants, all the rest are predators, and sometimes they do not disdain even each other.
Spiders are everywhere - in the woods, in the meadows, in the steppes and gardens, and even in houses and garages, so the chance of being bitten by carelessness is always great - no one is immune from this. You can minimize the risk of attacking animals, hymenoptera (bees and wasps), and even snakes, but spiders are creatures that are guided solely by instinct, and therefore are almost always unpredictable.
One thing is certain: if in relation to its victims (creatures that the spider eats) its bite is an aggression, an attack, then in relation to a man the spider bites are almost always defensive, according to the principle “the best defense is an attack”. The bite a person receives, when accidentally disturbed by a spider, steps on him. However, quite a few of them bite through human skin: it is thick enough for spider fangs, because they are intended to attack mainly insects. Only some large spiders are dangerous, and we will talk about them today.
What is dangerous spider poison?
The main principle is this: the further south, the more spider species, and the more dangerous they are. Although all spiders are poisonous, however, the strength of their poison is very different, and therefore it makes sense to pay attention only to those whose bites are painful or are fraught with dangerous complications. The fact is that when you bite, the problem is not only the poison itself, but also an allergic reaction to it, which is observed in some people, as well as the infection in the wound.
What are the consequences for the body is fraught with a dangerous bite?
- First of all, it is a hemolytic effect (effect on the blood), the result of which is the death of the affected tissues - areas where the poison has entered (necrosis).
- Secondly, many poisons act as neurotoxins, that is, they affect the nervous system, violate neuro-muscular mechanisms. This is the most common method of action on the victim among spiders, designed to paralyze it.
Symptoms and effects
Symptoms of bites are quite different depending on the type of spider that attacked. However, it is possible to identify a number of common signs by which it can be determined that it was the spider that bit you, and not anyone else: the fact is that the spider bite itself is sometimes not noticed, because it is not always painful, as when stinging wasps and bees, symptoms begin to appear only after a time, usually - during the first 20 minutes, sometimes - during the day.
So, the common signs of spider bites can be considered: 
- the appearance of a small, no larger than a coin, white spot at the site of the bite (in the area of poison injection) with red or pink edges;
- formation of a blister-blister speck framed by a swollen and reddened area in the form of a large circle (when a hermit spider bites, the central area has a bluish tint, the first ring around it is white, and the outer one is red);
- swelling and redness can be observed not only in the area of the bite, but also on the face;
- the bite often grows numb and becomes dense (for example, with a bite of karakurt);
- the bite itself is single, for a larger spider is not technically capable, so if there are several bites, then this is either someone else, or there were more than one spider (but this is impossible not to notice, and you will know for sure that it was the spiders that suffered);
- the pain increases gradually, and does not burn immediately, as with the bites of hymenoptera;
- another local reaction is burning in the area of the bite;
- itching appears as a reaction to the poison, often it spreads throughout the body, and a rash can also be observed;
- another common reaction to the toxin in the body can be considered the emergence of symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, indigestion and stool;
- often there is a general depression of the condition: drowsiness, weakness, body aches;
- fever, chills, sweating, and increased saliva production are often noted;
- it is possible to change the color of urine to pinkish or red;
- hemolytic poisons affect blood and pressure: it falls or grows;
- when a spider bites, whose poison has a neurotoxic effect, spasms, muscle aches and cramps are observed;
- fainting or dizziness may also occur.
What spiders look like: we define the type of abuser
In order to properly provide first aid and treatment, you need to know what kind of spider has bitten the victim. Even if you do not have time to notice the "attacker", knowing the symptoms and the ability to distinguish oh can help in a difficult situation.
Home spider bite
These spiders get their name because they always live near the human dwelling, or directly inside. In appearance, these are small gray, black or brown creatures that bite extremely rarely - unless you have noticed and crushed it. This happens, for example, at night when spiders are active and people are sleeping - in a dream you can try to drive away the creature traveling through you and get a bite in return.
The bite itself can be painful, but not for long (not more than a day) and not very intense. In addition to minor edema, none of the listed general symptoms is usually observed (unless the person is allergic to toxin). What to do with the bite of a spider living at home? The best help would be to put ice or a cold compress on the affected place.
Bite cross
 These spiders are very common on the territory of our country, and at least once in life everyone has come across it, even a convinced resident of the megalopolis who does not leave it for a minute. The name of the spider was due to the light cross on the back.
These spiders are very common on the territory of our country, and at least once in life everyone has come across it, even a convinced resident of the megalopolis who does not leave it for a minute. The name of the spider was due to the light cross on the back.
He bites only by accidentally turning up a person who has shown negligence towards the spider (you can stumble upon it, for example, collecting mushrooms, walking in the woods, working in the garden). These spiders grow all summer, and by September can reach impressive sizes.
Is the cross spider dangerous for humans? Only in part: the poison of the spider (it belongs to the category of hemolytic) is slightly toxic to humans. The bite will be a little painful, accompanied only by burning, aching, headache, which pass within 24 hours. If you are allergic, you will need the help of a doctor!
Tarantula bite
Although the spider has a very unpleasant appearance, it does not pose a mortal danger. In addition to the poison, small hairs that the spider drops on the victim after being bitten have an irritating and allergenic effect: they develop pain syndrome and an itchy skin rash, and other allergic symptoms may also appear.
Tarantula lives in grooves in the steppe and desert, active exclusively at night. It feeds only on insects, so the intensity of its poison is calculated on them, and in humans it can only cause soreness, redness and burning as a local reaction. Within 3-4 days everything goes away, however, allergy sufferers may have serious complications, so they need to immediately consult a doctor.
Tarantula bite
 This spider is one of the subspecies of the tarantula, the most threatening in appearance: shaggy, with long legs, large size. Interestingly, this is a long-living spider, females can live up to 40 years, and they live in holes dug by them in the ground. According to the intensity of exposure, its poison is comparable to that of wasps and bees, and therefore tragic cases are possible only if there is an allergy to the bite or its infection. Usually, the symptoms are standard: pain, swelling and redness.
This spider is one of the subspecies of the tarantula, the most threatening in appearance: shaggy, with long legs, large size. Interestingly, this is a long-living spider, females can live up to 40 years, and they live in holes dug by them in the ground. According to the intensity of exposure, its poison is comparable to that of wasps and bees, and therefore tragic cases are possible only if there is an allergy to the bite or its infection. Usually, the symptoms are standard: pain, swelling and redness.
Although many tarantulas scare their "appearance", there are quite a few people who keep these spiders in the house as exotic pets. It is funny that domestic spiders get used to their owners and even bite them without injecting poison, “dry” - and then only if they are negligent, embarrassed when handling the spider.
Hermit Spider: Bite Dangerous?
It is brown with a beautiful pattern in the form of a violin on the back. This species is not distinguished by aggressiveness, bites only when a person’s actions threaten him: they attack, they wave their arms and legs near his home, etc. And the habitat itself chooses a secluded one: under the cupboard, in the crevices of the walls and floors, under various boxes, etc. - so not to notice it is really easy.
Despite its small size and not the most formidable species, it is this spider that possesses the dangerous poison of a hemolytic nature, destroying red blood cells - red blood cells. At first, you will not even notice the bite, or you will feel a slight discomfort, such as a burning sensation and the formation of a small blister. However, much more serious reasons for anxiety appear during half an hour: the pain becomes severe, accompanied by itching, fever and muscle pain (as if with the flu), as well as nausea and vomiting. The site of the bite itself hardens and compacted, it is also possible subsequent necrosis at the site of the blister and the appearance of ulcers that heal heavily.
Reported cases of death were attributed to the violation of the heart and kidneys. Because of the severely tolerated effects, the hermit spider bites need immediate assistance and often hospital treatment.
Karakurt bite
This is one of those spiders whose bite is also especially dangerous. It dwells in the south of our country - a small, black with a white mark on the abdomen. Like almost all other spiders, he bites only when a danger has arisen for him (for example, when he is attacked). The moment of the bite itself is not painful, after it a small spot forms on the skin. However, after just 10-15 minutes, the person begins to feel severe pain, and not only in the area of the bite, but also in the stomach, chest and lower back. Of the above symptoms, almost everything is observed with a karakurt bite: headache, dizziness, weakness, and heart rhythm disturbances, shortness of breath (up to the cessation of breathing), and nausea with vomiting.
The danger lies in the high toxicity of the venom-neurotoxin, which provokes general intoxication, which can even cause the death of a person. Therefore, the answer to the question “What to do when a spider bites?” Is one: immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to the hospital.
Black widow bite
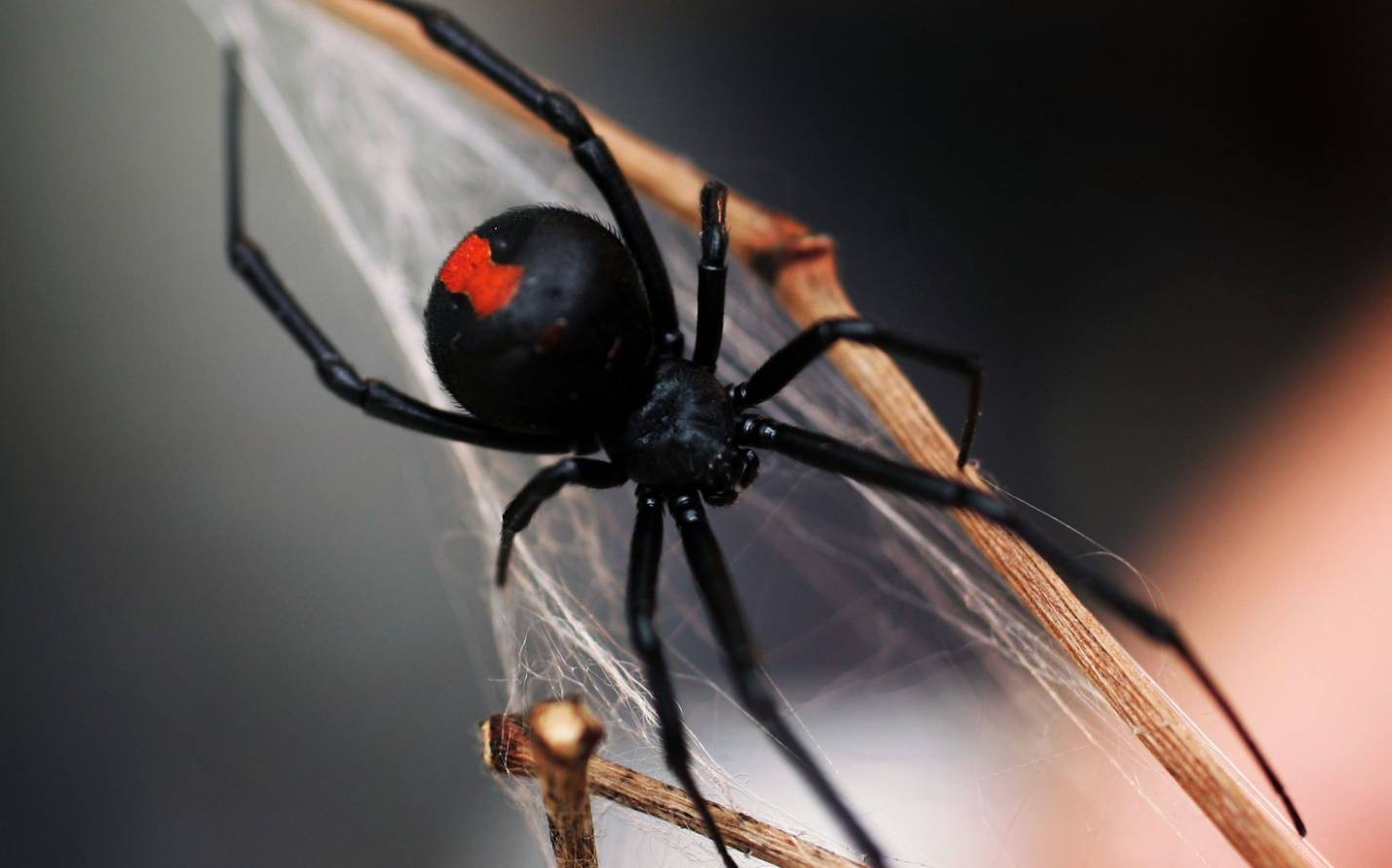 So eerily called karakurt female - black spider, young individuals which have red spots on the abdomen. They are larger than males and more aggressive, and even within the limits of their own species: after mating, it simply devours the male, hence the name.
So eerily called karakurt female - black spider, young individuals which have red spots on the abdomen. They are larger than males and more aggressive, and even within the limits of their own species: after mating, it simply devours the male, hence the name.
The black widow's bite itself is more painful than that of a karakurt male, and it feels like a noticeable injection, a couple of hours after which very serious consequences develop: besides the above, the complex syndrome caused by neurotoxin develops: a person becomes agitated, he is thrown sweat, pressure rises, salivation increases, itching spreads to the whole body, eyelids and limbs swell and become heavy, temperature rises, muscle spasms occur throughout the body, pain may occur, similar to I'm on the symptom of appendicitis, difficulty breathing. As for the site of the bite, the soft tissues simply atrophy and gangrene occurs when infected. In short, in the sense of the consequences, the black widow's bite is one of the most dangerous spider bites, which can even end in death (although this is rarely seen in young children, weakened or elderly people). However, if in the first hours after a bite to have time to enter the serum, the consequences can be minimized - the only trouble is that it is not always available in hospitals.
What to do with a bite: first aid
What to do when a spider bites, how to help the victim and to maximize and alleviate the manifestations of intoxication?
- First, the wound needs to be washed with clean water and treated with an antiseptic, because, in addition to the toxin, it can be infected, and then the consequences will be caused not only by poison, but also by contamination of the wound.
- Secondly, carefully examine the site of the bite and observe what is happening in the dynamics, in order to determine by symptoms who has bitten and assess the degree of danger.
- If the spider did not escape, take a picture of it from a distance to show the doctor.
- With shortness of breath and loss of consciousness (as well as if a child or a pregnant woman is injured), an ambulance should be called immediately, if the symptoms are serious, but not threatening yet, just get to the doctor as soon as possible.
- The bite is anesthetized with ice or a cold compress from clean running water so as not to infect the wound; the same remedy (cold) will slow down the absorption of the toxin.
- We accept any antihistamine (anti-allergen): Suprastin, Zodak, etc.
- If possible, move less so as not to intensify the spread of poison through the body.
- Above the bite, which fell in the limb, you can impose an elastic bandage or not too tight bandage from the bandage; It would also be good to give limbs a high position.
- Drink a little more to get the toxin out faster with urine.
- Do not scratch the bite so as not to infect the infection.
All further actions in accordance with the symptoms will produce doctors.
Take care and be healthy!
Spiders are the most ancient inhabitants of the planet, according to estimates of arachnologists, these arthropods appeared on Earth more than 400 million years ago. To date, there are about 40 thousand species of spiders, but only a few of them represent a danger to humans.
Almost all 30,000 species of spiders are poisonous. However, the fangs of most of them are too short or fragile to bite through the skin. Serious systemic reactions are most characteristic of the bites of brown spiders [for example, the brown hermit - a member of the genus Loxosceles) and karakurt spiders (Latrodectus)]. The most dangerous are the bites of Latrodectus mactans - female karakurt, called “black widow.” Brown spiders are found in the Middle, Western, Southern and Central parts of the United States. They are rarely found in the coastal and bordering states of Canada, except when they are carried with clothing and luggage. In the US, karakurt is found everywhere. For several poisonous species (for example, Pamphobeteus, Cupiennius, Phoneutria), the United States is not considered a homeland, but they are imported as rare pets.
The poisons of only a few spiders have been studied in detail. The most important effects of poison are necrosis (brown and some domestic spiders) and neurotoxic effects (karakurt). It is believed that the most poisonous component of karakurt poison is a peptide that disrupts neuro-muscular transmission. In the brown spider, a specific fraction of the venom that produces characteristic necrotic damage has not been identified.
These types of arthropods, as a rule, are common in the southern regions with a warm climate, they hide in places where people rarely happen or just where you can hide - in woodpiles, barns, storerooms, in the crevices of the earth, among the dry grass of last year. A spider bite is not an attack, but rather a defense by dangerous arthropods. For a person, a spider bite is a threat in terms of exposure to the poison itself, an allergic reaction to the introduction of a poisonous substance or infection of a wound after a bite.
Poisonous spider bites
It should be noted that any spider is a priori poisonous, since arachnids are predators and poison serves as a weapon for them, a way to get food for themselves, and also to defend themselves. The bites of poisonous spiders can be both deadly and unpleasant, but not a threat to trouble. Almost all spiders have glands that secrete poison, which can be divided into two types - hemolytic and neurotoxic. The most common are spiders, which secrete neurotoxins, paralyzing the nervous system of the intended victim. Small spiders are not dangerous, as they simply can not damage human skin or the skin of an animal, and the toxic substance released will be too small to cause any complications. Larger bites of poisonous spiders can actually be dangerous, especially when it comes to karakurt or the brown recluse spider.
What does a spider bite look like?
How to distinguish a simple scratch, which is not uncommon in garden work or hiking, from a bite of an arthropod? First of all, you need to know how a spider bite looks and how it feels:
- The first sensation is like a shot by a thin needle. Quite often, a person does not feel a bite at all.
- A small speck of white color (not exceeding the size of a five-kopeck coin) is immediately formed on the site of the damage. The edges of the white spots are most often pink or red.
- After a few minutes (from 5 to 20), the symptoms begin to grow.
- There are sudden pain in the muscles, possible convulsions.
- The face is very red, may swell.
What a spider bite looks like depending on its type:
- The bite of a tarantula and some other species looks like a small spherical spot (swelling). The skin around the puncture is bloated in the form of a blister, the color is most often pale with reddish edges. After an hour or two the blister may burst, turning into a wound. If the blister is not treated in time, it can be transformed within an hour into an erosive wound, that is, into an ulcer.
- The bite of a brown recluse spider also looks like a blister surrounded by a bluish-purple, white and red border of an irregular shape. Often, such a bite is called the "bull's eye" or "target", so similar to the damage pattern with these images. The bubble quickly grows in size, bursts and a wound forms, more like an ulcer.
- The bite of karakurt is most often not visible at all. It feels like a flea bite or a mosquito bite, a microscopic speck of red may appear, which disappears literally before our eyes.
Brown spider bites are most common in the United States. Some bites are initially painless, but pain, severe and covering the entire limb, develops within 30-60 minutes in all cases. Erythema and ecchymosis appear in the area of the bite, itching is possible. Itching may also spread throughout the body. Often surrounded by an uneven ecchymosis area, a central blister ("bull's eye") forms at the site of the bite. Damage may be similar to pyoderma gangrenosum. The central blister becomes large, filled with blood, torn, and in its place remains an ulcer on which a black scab forms; he is eventually rejected. Most bites leave a small scar, but some may leave a deep defect that involves muscles. Loxosselism (systemic syndrome-induced poison) is detected only 24–72 hours after the bite, but not always. All previously registered deaths are caused by the systemic effects of poison (eg, fever, chills, nausea and vomiting, arthralgia, myalgia, rash, convulsions, hypotension, DIC, thrombocytopenia, hemolysis, renal failure).
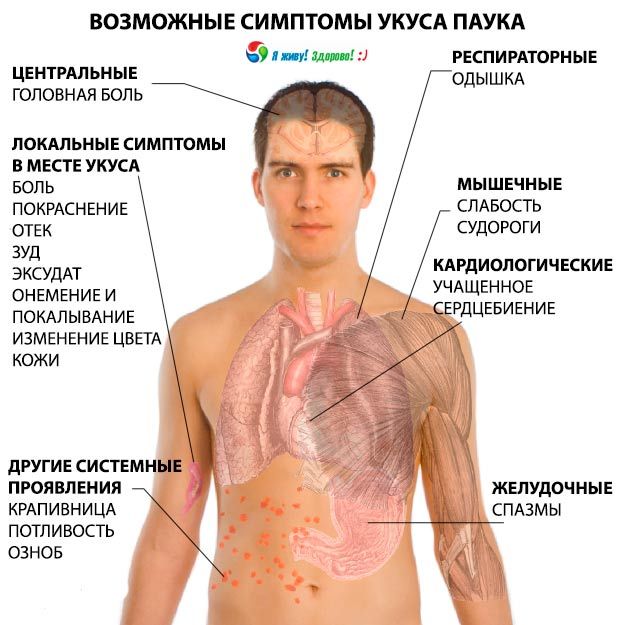
Symptoms of a spider bite can be varied. If you know for sure, or even simply suspect that the bite has taken place, and you cannot differentiate it from an insect bite, it is better to be safe and consult a doctor. Also, the help of a specialist (most often emergency) is needed when the following symptoms of a spider bite appear:
- A purple, bluish speckled area, surrounded by a white and then a red ring, formed around the bite point. In toxicological practice, this symptom is called "red, white, blue." This is a clear sign of a poisonous hermit spider attack.
- The body of the injured person is covered with a rash.
- Muscle spasms appear, right up to cramps - in both the legs and the arms.
- There is a feeling of numbness at the site of injury. To touch the bite site is slightly compacted. This most often indicates the attack of karakurt.
- The symptoms of a spider bite, which are manifested by pain in the right hypochondrium, are also a clear sign of a karakurt bite. Such pains are very similar to an attack of an inflamed appendix.
- The headache increases, the temperature rises sharply.
- Accompanied by aching joints, general weakness.
- Urine can get a non-characteristic color, most often pink or even red.
Black widow bites
Black widow is called female karakurt. The female is usually noticeably larger in size than the male, moreover, the black widow was not called her by chance - after mating, the female mercilessly devours the arachnid in love.
The black widow spider bite is considered one of the most dangerous, sometimes fatal, among all the injuries a person can get from arthropods. The wound is almost invisible, it feels like a light injection, the symptoms also appear not immediately - after a couple of hours. Black widow bites usually cause an immediate sensation of a sharp bite.

Within an hour, poisoning can cause local pain, sweating, erythema, and piloerection at the site of the bite. The pain can be both dull and acute, it may not correspond to clinical signs. Latrodectism - systemic syndrome caused by neurotoxic components of the venom appears excitation, anxiety, sweating, headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, hypertension, hypersalivation, general weakness, common erythematous rash, itching, ptosis, swelling of the eyelids and extremities, shortness of breath, increased skin temperature in the affected area, as well as painful cramps and tension of the muscles of the abdomen, shoulders, chest and back. Abdominal pain can be severe and similar to appendicitis. Latrodectism is rare and most often develops in children or elderly patients suffering from chronic diseases. Deaths are very rare. Symptoms subside within 1–3 days, but residual cramps, paresthesia, anxiety, and weakness may persist for several weeks and months.
The most effective way to neutralize the black widow spider bite is considered a special serum, which is not always available, especially in the first hours after the attack.
Tarantula bites
Tarantula is strongly associated with poisonous spiders, but this view is somewhat exaggerated. Indeed, the tarantula spider bite can cause some painful symptoms, but deaths are extremely rare and are most often associated with combination with other internal pathologies.
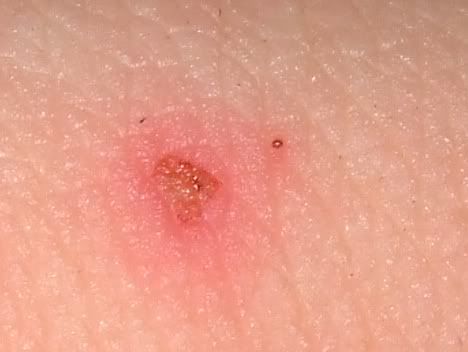
The tarantula is a spider of steppes and deserts that lives in depressions, sometimes reaching up to one meter. In the daytime a tarantula is almost impossible to meet, since it is a purely nocturnal predator. The notorious danger of a tarantula, first of all, concerns insects that the spider prefers to feed on. In humans, the tarantula spider bite causes pain and a burning sensation at the injury site. Tarantula bites are extremely rare and non-poisonous, but an angry spider can shed needle-like hairs that end up as foreign bodies in the skin or eyes and can cause mast cell degranulation and pseudo-anaphylactic reaction (for example, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm, arterial hypotension) sensitive people, usually spider owners, who contact them daily.
Local edema develops, a small rash may form around the wound. The bite of a large tarantula is accompanied by hyperthermia, headache paresthesias, and general weakness. Death is extremely rare and is associated with a general allergic reaction to toxins and anaphylactic shock. A simple tarantula spider bite disappears without a trace within 3-5 days.
Tarantula bite
The bite of a spider tarantula does not bear mortal danger to humans. Given that the new fashion for breeding as pets of these spiders is becoming widespread, the attack of the tarantula has already been “tested” by many owners, everyone has remained alive and healthy. Seeing a doctor after a bite is most likely due to a precautionary measure or ignorance of the properties and abilities of your pet. The spider tarantula is dangerous for small animals in the wild. The tarantula hunts frogs, lizards and small birds. The poison of the spider does not kill the victim, but only paralyzes it, since it refers to neurotoxic substances. The tarantula spider bite is also possible as a self-defense, which is the cause of the attack on the person. The pet tarantula often bites the host in a “dry” way, that is, it does not release poison, but only damages the skin. Mechanical damage to the skin is a relative hazard in the sense of infection by bacteria. This danger is fairly easy to eliminate by treating the wound with an antiseptic.
Karakurt spider bite
A karakurt spider bite can be deadly for both humans and animals. Under natural conditions, karakurt eats mainly small insects. A karakurt will not attack a person on his own, he bites only in cases when he is disturbed or is attacked. The most poisonous are karakurt females, which emit a strong poison that causes atrophy and gangrene of soft tissues.

Also, the bite of a karakurt spider may be accompanied by a general intoxication of the body with a fatal outcome. The most characteristic symptoms are severe diffuse pain, spreading throughout the body, chills and cold sweat, cyanosis of the skin, convulsions, asphyxiation, paresthesia, and possible coma. The reaction develops within a few hours, less often within a day. The karakurt spider bite is dangerous because of its neurotoxic effect, which paralyzes the human central nervous system.
Crosshair spider bite
Spider crosses are ubiquitous; it is one of the most common arthropod species in the world. The name of the spider was due to the characteristic mark on the body - on the belly is clearly visible pattern in the form of a cross. The color of the spider can vary depending on the environment - so the spider is masked, waiting for its prey. The bite of a spider spider can be dangerous for many animals, since the venom contains temperature-resistant hemolysin (a substance that completely destroys red blood cells). However, not all animals can be affected by this poison, large dogs, sheep, cows, horses are resistant.
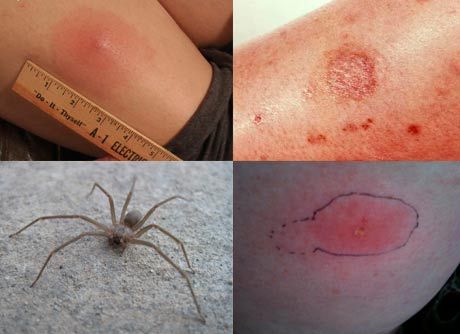
The bite of a spider of a krestovik for a person does not pose a mortal threat, however, the appearance of a headache, aching joints, and a burning sensation can cause a lot of trouble to the bitten one. The eiperotoxin, which the spider releases, is absorbed and removed from the human body within 24 hours, the bite site may retain some swelling for several days.
Hermit spider bite
The hermit spider bite is extremely dangerous for both humans and animals. Hermit spiders are common mainly in the US states, as well as in Australia, where they were brought from the US with transport cargo. The distinctive visual mark of the hermit is a drawing on the back, resembling a violin. These spiders are small in size, so a person often does not even notice them in the house or in nature. Spiders prefer to hide in the old boxes under the cabinets, in the cracks of the walls and floors.
![]()
It is dangerous because it is practically invisible and does not cause even the slightest sensation of pain. Symptoms of damage develop only on the second day, when the poison is already distributed throughout the body. Severe itching, thickening and visible swelling. Then the tumor ulcerates, the soft tissues begin to necrotize (die off). The ulcer is difficult to treat, necrosis affects the very deep layers of the skin. In addition to external manifestations, the hermit spider bite is accompanied by typically flu-like symptoms - fever, aching joints, runny nose, cough and general weakness. Individual cases of severe intoxication can disrupt the kidneys, heart, and lead to death.
Home Spider Bites
Domestic spider is divided into several species - black, gray, brown and others. Most often in life there is a kind of black domestic spider - Badumna insignis, which prefers to live both inside the home and outside - in window frames, building walls, in logs or trunks of trees, that is, everywhere where it will not interfere with weaving its web. Home bite spider bites are extremely rare, a person needs to really try to get a similar injury. If the trouble happened, then the bite really hurts, but the pain is tolerable.
A slight swelling may also develop in the microdamage zone, symptoms of dizziness, nausea and increased body temperature are extremely rare. Strong intoxication does not cause the bites of the house spider, it is enough to attach ice or a cold compress to the puncture site, usually all traces disappear within 24 hours.
Diagnosing Spider Bites
Patients often suspect a spider bite is mistaken. The diagnosis is usually based on the patient's story and physical signs, but is rarely confirmed, since this requires witnesses to the bite, identification of the spider, and the exclusion of other causes. There are the following conditions that mimic the spider bite:
- the bites of ants, fleas, bedbugs, ticks, flies and beetles;
- skin damage [eg, toxic epidermal necrolysis, chronic migrating erythema, nodular (nodose) erythema, sporotrichosis, simple chronic herpes or periarteritis nodosa];
- infectious diseases (for example, common gonorrhea infection, septic embolism with endocarditis or intravenous drug addiction, skin anthrax, skin abscess with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus);
- trauma (for example, subcutaneous injection of the drug, self-induced wounds);
- panic attack.
Severe cases of latrodectism may be similar to appendicitis, rabies or tetanus. Spiders are identified by location and appearance. Karakurts live outdoors in protected places (for example, piles of stones, bundles of wood, a haystack, buildings) and have a red or orange hourglass on the abdomen. Brown spiders live indoors in protected places (for example, in clothes, behind furniture, under baseboards), on the dorsal side of the cephalothorax there is a figure in the form of a violin.
Effects of a spider bite
The most dangerous consequences after a spider bite are tissue necrosis, wound infection, and arachnosis or loxosselism, which most often develops after hermit spider bites. Arahnoz is characterized by rapidly developing necrosis of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and nearby soft tissues. The consequences can also manifest as a deadly systemic syndrome that begins as a fever, accompanied by diffuse myalgia, arthralgia, seizures, a sharp drop in blood pressure, hemolysis and heart failure.
Platelet hypercoagulation syndrome - disseminated intravascular coagulation (disseminated intravascular coagulation) - is also quite frequent consequences of the attack of karakurt or hermit. Summarize the consequences in this way:
Weak, non-threatening effects:
- Tolerable pain at the site of injury.
- Hyperemia of the skin.
- A small tumor in the puncture zone.
- Itching, burning.
Effects that are felt during the week:
- Pain.
- Swelling and swelling, not transient for 3-5 days.
- Itching and redness.
- Digestive Disorder.
- Transient convulsions.
- Drowsiness and general malaise.
Consequences that are considered threatening:
- Sharp pain, intensely spreading throughout the body.
- Rapidly developing tumor.
- Generalized convulsions.
- Disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, indomitable diarrhea.
- Constant drowsiness, weakness, explained by a steady decrease in blood pressure.
- Renal failure.
The effects of a spider bite can be significantly less dangerous if provided with timely adequate assistance.
First aid for spider bites
Help with spider bites should be consistent with the appearance of the venom and symptoms. It is not always possible to consider arachnida, for example, karakurt, since signs of a puncture appear after a few hours, when the spider has already gone. However, by determining the nature of the puncture by the appearance of the skin, it is possible to provide the necessary, adequate assistance for spider bites.
- At the puncture site should put a cold compress, better ice.
- Children under 16 years old and older people are subject to immediate hospitalization.
- When attacking karakurt, specific serum is injected intravenously. Before the introduction of funds spend skin test or fractional sensitization for more adequate perception of the body serum.
- It is advisable to conduct antihistamine therapy.
- In severe cases involving cardiac or renal failure, cardiologic drugs are administered, usually intravenously, respiratory analeptics, myelorelaxants, and glucocorticosteroids.
- Detoxification. It is carried out using infusion therapy (drip injections of saline solutions, glucose to maintain electrolyte balance).
- Non-humanized tissues after a bite of a hermit spider are treated and removed. The treatment of necrotic ulcers is quite long and, as a rule, is performed on an outpatient basis.
Assistance with spider bites, first of all, must be timely, the choice of the method or sequence of actions depends on what kind of spider a person has bitten.
Spider bite treatment
Treatment is the same for the bites of all types of spiders, including debridement, analgesia, limb elevation, tetanus prophylaxis and dynamic observation. These measures can successfully cope with most local reactions. Ulceration should be treated daily, you can use ointments with antibiotics (for example, polymyxin B, bacitracin + neomycin). Ulcerations are treated with antihistamine drugs, topical glucocorticoids, or a combination thereof. The necrotic lesions observed with the bites of brown spiders are sanitized and bandaged. In some cases, when necrotic areas\u003e 2 cm in diameter, 100 mg of dapsone is administered orally once a day, until the inflammation subsides, but its effectiveness has not been fully proven. Local injection of glucocorticoids is useless. Surgical excision should, if necessary, be postponed until the necrosis zone is completely delimited (a process that can take weeks).
Systemic manifestations of karakurt bites are first treated symptomatically. Myalgia and muscle spasms from black widow bites respond poorly to muscle relaxants and narcotic analgesics. Slow administration of 2-3 ml of a 10% solution of calcium gluconate intravenously can quickly reduce pain, but it requires constant cardiac monitoring. Patients younger than 16 years or older than 60 years with hypertension and signs of severe poisoning should be hospitalized. Horse antidote is used in patients with severe latrodectism. It should be administered within 30 minutes; the reaction can have dramatic consequences. Dose for children and adults - the contents of 1 bottle (6000 units) in 10-50 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution are administered intravenously for 3-15 minutes. The manufacturer recommends skin tests before prescribing an antidote, but these tests do not always predict adverse reactions (for example, acute anaphylaxis).
If the bite caused by karakurt, a hermit spider, is promptly examined and undergoes specific therapy, as a rule, rehabilitation is not required thereafter. However, due to the strong general intoxication and weakness of the body, it will not be superfluous to strengthen the immune system and slightly support the organs and systems with vitamin therapy. In addition, gastrointestinal symptoms and diarrhea sometimes occur. In this case, it is worth two to three weeks to observe a sparing diet, excluding protein foods. If the arachnid attack causes an allergic reaction, after a spider bite it is necessary to conduct a course of antihistamine therapy. Neurotoxic poison, which can cause functional disorders of the central nervous system, is excreted with the help of drug therapy, copious drinking is shown as an independent action, and bed restraint is desirable. All actions aimed at eliminating the consequences should be adequate to the main symptoms.
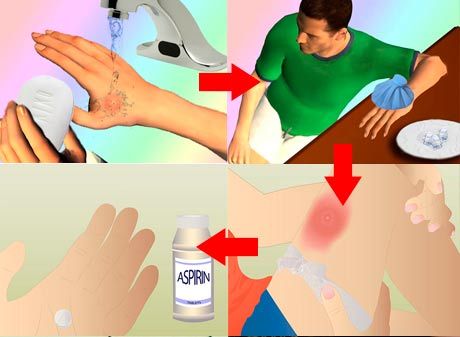
If a spider has bitten a child or an adult, and no one is insured against it, the first aid provided in a timely manner can save not only health, but sometimes the life of a bitten person. Therefore, you should remember the proposed algorithm to know what to do with spider bites:
- If the bite is characterized as not too dangerous, the site of injury should be washed with running water, preferably with soap, in order to avoid possible infection of the wound.
- The bitten limb should be immobilized (immobilized) to reduce the possibility of spreading the poison.
- Leg or arm can be pulled with an elastic bandage or material just above the bite. In this way, the zone of venom is localized. The bandage should not be too tight so as not to disturb the general blood supply to the limb.
- A cold compress should be applied to the puncture site, preferably ice.
- What to do when a spider bites, knowing that it is an intoxication of the body? Of course, drinking plenty of fluids will help, which will speed up the elimination of toxins.
- With mild symptoms of headache and a slight increase in temperature, paracetamol can be taken.
- With the appearance of a slightly pronounced allergic reaction, you can take a non-prescription antihistamine drug - Allergostop, Loratadin, Agistam.
What to do with spider bites if symptoms cause concern? The answer is unequivocal - first aid or independent immediate access to a doctor. Especially worth hurry in such cases:
- If the spider has bitten a child (age up to 16 years).
- Symptoms of a bite develop rapidly, the condition worsens dramatically.
If you know (or suspect) that the bite was produced by a Karakurt or a brown recluse spider. Treatment of these bites requires the introduction of serum (antidote).