A spider with a large white belly. Flower yellow spider: cobweb is not its element
Spider caracurts are among the most dangerous creatures on earth. Despite its small size and non-threatening appearance, the poison of Karakurt is 15 times stronger than the poison of the rattlesnake and 50 times the poison of the tarantula. For a horse or a camel, the bite of karakurt is often fatal.
Spider caracurts are among the most dangerous creatures on earth
Without prompt medical intervention and professional help, meeting with a person can also result in a fatal outcome, although such cases are extremely rare. The black spider causes mystical associations due to the presence of 13 spots of bright red color on the body and cannibal family traditions. Kalmyk shamans use a dangerous creature in certain ceremonies. There is a common opinion that Karakurts live only in deserts and do not pose a threat to residents of central and even southern steppe and forest regions, but this is not so. Recently migration of biting "robbers" to the north is obvious, and the warming of the climate has led to the fact that the karakurts are recorded in regions that have never been observed before.

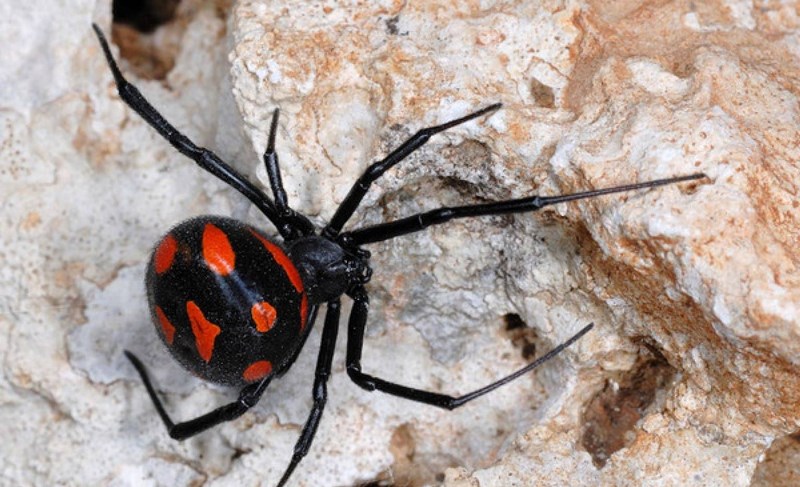
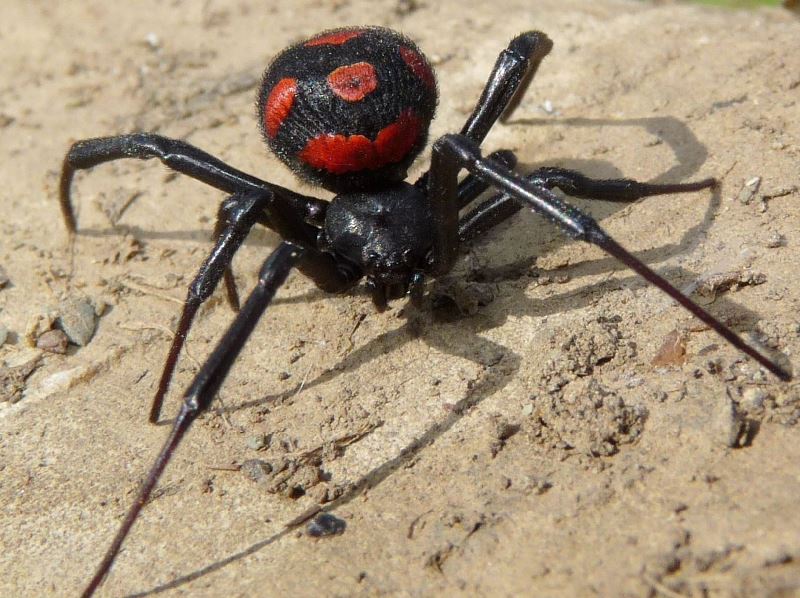
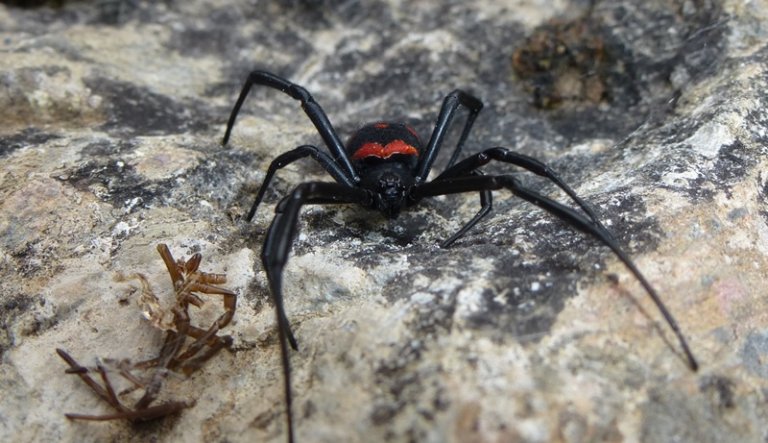
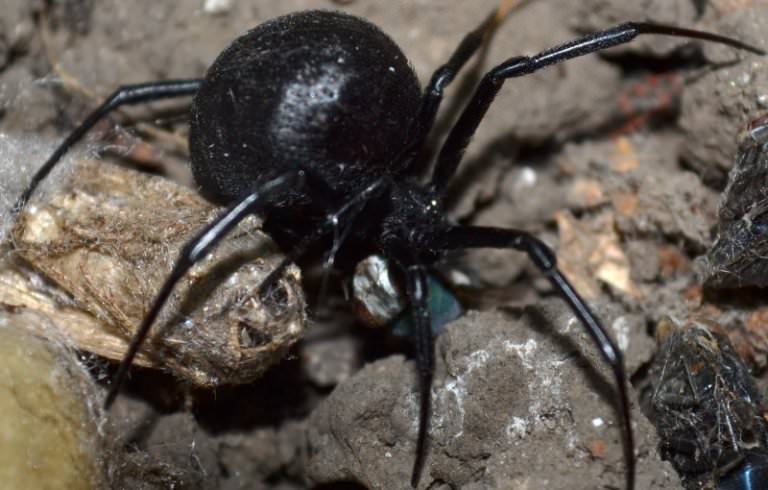
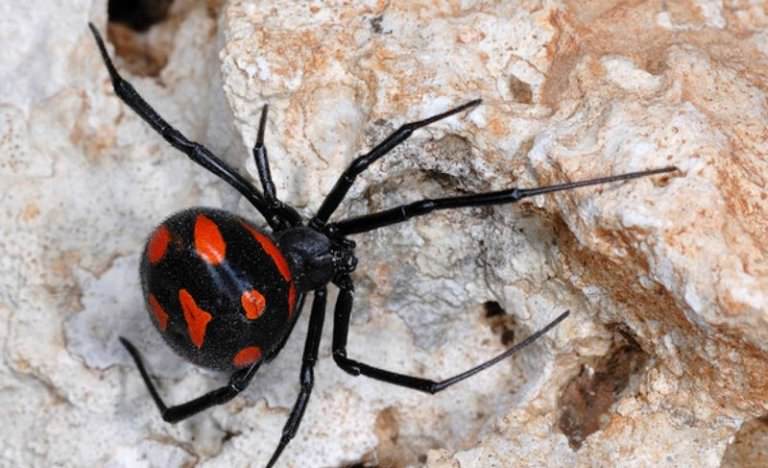
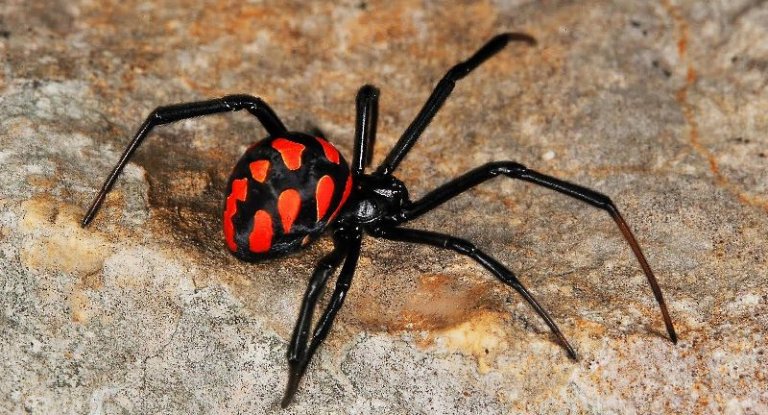
The poisonous spider caracurt belongs to the spider's family of spider-taunts from the genus of black widows. In translation from the Turkic language, the name is literally translated as a black worm. Latin name Latrodectus tredecimguttatus reflects external signs - 13 points on the back and the essence of a spider (biting robber). Like a karakurt, sometimes called a steppe spider? In size, the spider belongs to the average arachnids. The size of the male is 4-7 mm, the female of the Karakurt is 2-3 times larger and can reach 20 mm. The body of the eight-legged spider is black, with a pronounced abdomen. On the upper side of the abdomen, both the male and female have red spots or dots. On the lower part of the abdomen, a clear scarlet pattern is visible, resembling the shape of an hourglass. The point on the abdomen often has a white halo. Adult individuals (males) can be completely black. Karakurt is a predator, feeds on insects, for the capture of which a web is used.
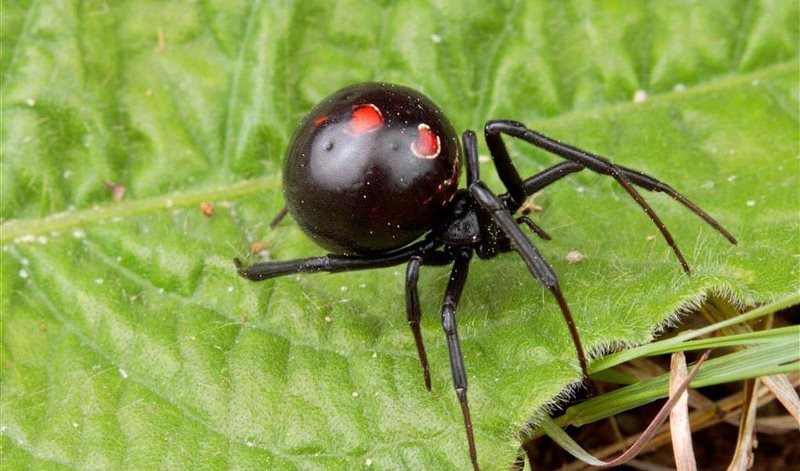 Despite its small size and non-threatening appearance, the poison of the Karakurt is 15 times stronger than the poison of the rattlesnake and 50 times the poison of the tarantula
Despite its small size and non-threatening appearance, the poison of the Karakurt is 15 times stronger than the poison of the rattlesnake and 50 times the poison of the tarantula White karakurt, also referring to spider-snares, has a white or yellowish color. There is no figure in the form of an hourglass or spots on the body, but there are 4 grooves forming a rectangle. White spiders are much less poisonous, their bite is not dangerous for humans, although the poison of white karakurt is toxic in its toxicological properties and peculiarities of influence on the human and animal organism with the poison of the black widow. White caracurts can be found on the territory of Russia and nearby countries, but the main habitat is located to the south - in North Africa, the Middle East, and also in Central Asia. Let's focus on the black widow's karakurta as the most dangerous representative of the tenetniki, which you can meet at the domestic resorts.
The whole house in wool?
Many people are afraid to start pets, because they are constantly a lot of wool. The last invention - special glove , which will easily collect the coat of your pet, and he will not mind. Watch our video on how to use this glove and how it can help you:

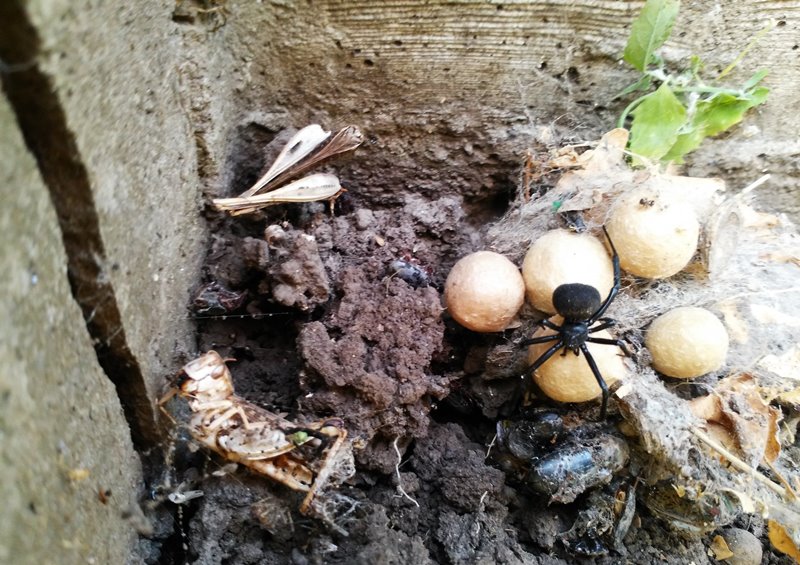
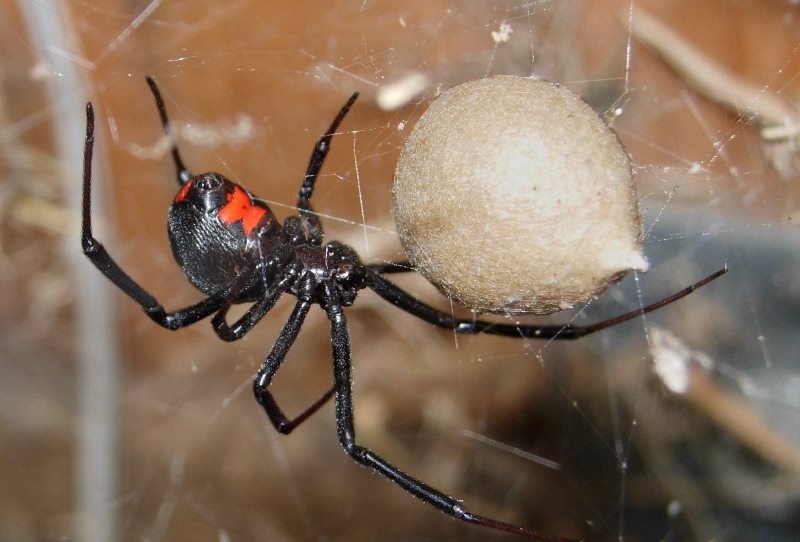
Karakurty differ fertility, in the southern regions there are periodic bursts of fertility, which lead to an increase in the number of people affected, the loss of livestock. Poisonous spiders in Kazakhstan and the Crimea each year attack dozens of people, but severe consequences are extremely rare. The female lays more than 1000 eggs a year, which are placed in a protective cocoon. The spiders born continue to live inside the cocoon and leave there only in the next spring. Sexual maturity occurs 2-3 months after the spider leaves its original dwelling. Eggs are deposited in holes on the ground or in holes of rodents. Fertilization occurs in the hottest months of the summer. After mating, the female of the karakurt feeds on the male, although there are exceptions - for unknown reasons the female can both destroy the male before mating, and leave it alive after fertilization.
Gallery: Spider Karakurt (25 photos)










Spider Black Widow or Karakurt (video)
Habitat and biological enemies
The strip of Karakurts' residence is occupied by the Crimea, the south of Russia and Ukraine, the Astrakhan steppes, Kazakhstan, Central Asia, the Middle East and North Africa. When migrating to the north, spiders reach the Saratov region, the Southern Urals and even the Moscow region, but they can not settle in the northern regions, in the winter spiders die. To live caracurts choose dry steppe areas and arable land, wastelands, solonchaks, slopes of gullies, ditches, the ruins of abandoned settlements, cracks of mud houses. A spider can also be found in populated areas, in suburban areas, sometimes it penetrates into a person's home. The peak of activity is during the period of fertilization - June-August.

The natural enemies of Karakurts are:
- sheep and goats, on which the bite of karakurt does not work;
- wasp-sniffs, injecting their poison into spiders, which paralyzes them;
- insect-riders, laying their eggs in cocoons of karakurt;
- hedgehogs that are not vulnerable to spider attacks.

Flocks of sheep or herds of goats are used to trample down the nests of Karakurts, the Crimean peninsula is thus cleared of poisonous creatures during periods of sharp amplified breeding or when cleaning pastures for horses, cows and other domestic animals. With outbreaks of spider births, they are capable of causing significant harm to livestock, therefore, the implementation of preventive measures is necessary.

Danger to humans
As a rule, males and young individuals do not pose a danger to humans, since they can not bite the skin with their weak jaws, although individual cases of attacks are known. The danger is presented by adult females, especially in July-August. You can distinguish the female by color. Males have red spots with white rims, females do not have fringes. Sometimes in females, red spots change to yellow bands. Female have long legs up to 30 mm and much larger than males.

The attack is very fast. Karakurt attacks only for self-defense purposes. Nature has endowed the spider with such a strong poison that it can capture the burrows of small rodents who do not enter into conflict with it and immediately liberate their territory. A predator can attack when he only seems to be in danger, so it is better to avoid contact with him. The difficulty of detecting danger lies in the fact that the caracurts do not weave their net in a classical form. The filaments are arranged horizontally, the web does not have a characteristic pattern and is chaotic in nature. Attacks occur most often at night and on vacation, when you can accidentally crush karakurt or disturb the web.

The spider's bite is not painless, but it does not bother you very much. The place of bite is marked by a small red speck, which disappears after a few minutes. After the poison has acted, the bitten person in the damaged place starts to test strong pains. There are specific psychological and physiological reactions.

In the first minutes and hours after the bite, poisoning is characterized by the following symptoms:
- strong mental excitement;
- a sense of fear of death, panic;
- spasms and choking;
- severe pain in the abdomen, chest and lower back;
- the feeling that the legs are being taken away;
- cyanotic complexion;
- shallow breathing, dizziness;
- sometimes cramps of hands and feet, tremors, vomiting;
- increased heart rate, arrhythmia;
- retention of urination and defecation;
- increase in protein in the urine.

After the initial reaction of the body, the person becomes lethargic, apathy, weakness, depression, sometimes delirium, but severe pain persists. A few days later, a red rash appears on the body. Lethal outcome is possible in especially dangerous cases with general weakness of the body and lack of qualified medical care, especially if the patient has cardiovascular diseases. With a favorable course, recovery occurs 3-4 weeks later.
Beware of karakurt (video)
Treatment and prevention
The most elementary and known since ancient times method of treatment of a bite of a poisonous spider, supported and official medicine, is moxibustion. The poison of a predator is sensitive to heat and when it is heated it is destroyed, losing its toxic properties. Therefore, immediately, within 2 minutes after the attack, the damaged place must be burned with a cigarette, match or otherwise. The spider does not have powerful jaws, the depth of the bite does not exceed 0.5 mm, so immediate cauterization gives a strong effect. In any case, at the first opportunity it is necessary to apply to a medical institution.

As special measures, anti-carcurt serum is used, which is administered intramuscularly. Serum removes the main symptoms of poisoning, the recovery period is reduced to 3-4 days.

The disadvantage of the facility is its high cost. In the absence of a special substance, intravenously administered:
- novocaine;
- calcium chloride;
- magnesium hydrogen sulphate.
- 33% ethyl alcohol;
- 2-3% solution of potassium permanganate.
The victim should be given water, rubbed with alcohol, enemas are recommended. As an anesthetic, you can use a universal remedy: Analgin, Dimedrol, Ketanol.

In cases of residence in the habitat of Karakurts, care must be taken when cleaning the living quarters, especially in adobe houses, to pay attention to the presence of cobwebs on homestead territories. When leaving for nature, you should follow certain rules:
- do not spend the night in the open air in the habitats of poisonous spiders;
- do not touch the inside of the tents;
- to examine the place of spending the night or rest, paying attention to pits and natural depressions in the ground, mink rodents, and in case of having to cover them with earth;
- use cover clothing, wear a hat;
- periodically, and without fail, before going to bed, carefully examine the tent, sleeping places, clothes, shoes and other property;
- use the canopy, tucking it under the bed;
- dig a tent by making a shallow groove;
- do not remove shoes;
- when a caracurt is found, do not touch it, if the spider is on clothes - shake or knock it down.
To prevent the loss of domestic animals, the soil is treated with hexachlorane and other poisons.
Attention, only TODAY!
Some spiders are so small that they can fit on a pinhead; Others are so great that they can hardly fit on a soup plate. There are smooth-skinned spiders, there are thick and shaggy ones. The general structure of the body in all spiders is similar. Some people scream in fright at the sight of a spider sitting in a tub or crawling on the wall. But you should not be afraid. Most spiders just hurry to find a nook to twist the web and catch tasty insects, and are not going to attack people at all.
The domestic spider is just one of 40 LLCs of spider species that live on our planet almost everywhere, except in the polar regions. They are quite ancient inhabitants of the Earth - spiders appeared, according to scientists, more than 300 million years ago. The spiders that appeared in ancient times for millions of years of evolution have changed little. The evolution of spiders is nothing more than the perfection of their tenacity, that is, the web. The patina is the liquid secret of special glands located on the abdomen. In one outlet duct several different types of glands are opened, enabling the spider to weave a web of various types - from rigid supporting threads to fibrous soft protection of the cocoon. So the spider carries a whole life with itself a whole weaving factory producing threads of all sorts and purposes! In this, spiders are like human beings: they create their own habitat for themselves, and do not adapt themselves to circumstances.
Both in females and in male spiders, the body consists of two main parts - the cephalothorax (connected head and thorax together) and the abdomen. The female has an abdomen larger than the male, because the female must lay a large number of eggs. The spiders do not know how to fly, and they do not have wings either. But the spider has eight long legs, thanks to which it can quickly run and deftly climb. Special bundles of hairs on the legs help him to rest on smooth surfaces and even walk on the ceiling. Most spiders have eight eyes - two of them look ahead, four point up and two look at what's behind them - so do not expect to sneak up on the spider From the back! However, the multi-eyed spider is rather short-sighted. Nevertheless, he can orient himself - and in time to detect insects - with the help of organs of touch. These organs - the so-called palps - are located in the front of the body and resemble a pair of short legs. With their help, the spider can even catch smells. With jaws or muzzles, it can bite the shell of the body of the insect and inject the poison into the victim. After this, the spider eagerly sucks the liquid contents of the prey's body. In the back of the body of the spider, under the abdomen, are the cobwebs. With the help of these bodies, he weaves his net for catching insects.
 Spiders are surprisingly skilled weavers, they can very quickly weave a thin, but strong network for catching insects that feed on. A victim caught in a web is unlikely to escape. When the Scottish King Robert Bruce in 1314 was hiding in a cave the night before the Battle of Bannockburn, a spider caught his eye, unsuccessfully trying to tighten the cobweb in the cave. The spider did not abandon its attempts until it was successful. Encouraged by the example of a spider, the king showed the same tenacity in the battle the next day - and won!
Spiders are surprisingly skilled weavers, they can very quickly weave a thin, but strong network for catching insects that feed on. A victim caught in a web is unlikely to escape. When the Scottish King Robert Bruce in 1314 was hiding in a cave the night before the Battle of Bannockburn, a spider caught his eye, unsuccessfully trying to tighten the cobweb in the cave. The spider did not abandon its attempts until it was successful. Encouraged by the example of a spider, the king showed the same tenacity in the battle the next day - and won! Many spiders weave a large round web to catch flying insects. Probably, you happened to see in the garden a round web spanned between trees and bushes. There is such a web in the house - usually it is stretched between the ceiling and the cord of the chandelier. It seems that the web appears from nowhere, as if by magic; in fact it is not so and the spider needs to do a lot of work to spread its net. What does the spider do first? First, he selects the point to which the upper part of the web will be attached, and lets out one single thread. After that, he sits and waits until a light breeze blows the thread to the opposite fixing point. The produced thread extends from one point to another, the threads cross until a web frame is obtained. After this, the spider stretches the radial strands leading from the frame to the center. Then he starts spinning circles that run from the center and intersect with the radial lines until the whole pattern is completed. All this time the spider uses a temporary spiral as the "forests" on which it works. When the network is completed, it eats the temporary spiral. Now it's time to rest and wait until an incautious insect gets into the web. The spider uses its thread to tie the spoiled prey, for example a fly. But not every web is done that way. For example, a glove-spider lives in a spider's cocoon, most of which is underground. The part protruding to the surface resembles a finger glove. The spider hides inside and draws insects adhering to the web directly through the walls. Other spiders weave some kind of funnel, also leading to the underground den. Here the spider waits for the victim who had a carelessness to wander into the web.
Disguise.
Some spiders can masquerade as completely unexpected objects - for example, under droplets of bird droppings. Others can change color. The bush needs to merge with the surrounding environment in order not to frighten off the potential victim and not to become prey to predators. Many spiders have a dull color - brown or black, due to which they are almost invisible against the background of the soil. However, even striped or mottled spiders can perfectly disguise themselves and in some cases become almost invisible. For example, a black and white zebra spider lives on the stone walls of buildings, perfectly merging with the surrounding environment. The filodromic boxes are round in shape, they are woven from black and white cobwebs , sometimes with the addition of garbage. If you look at the cocoon from a distance - neither give a pile of bird litter. Excellent disguise!
In other spiders, the surface of the body is cone-shaped, uneven, which provides them with perfect camouflage on tree trunks. There are even spiders (for example, an amazing spider-crab) that can change their coloration to the color of the environment. They do not need to weave cobwebs to catch prey, they can safely wait until an unsuspecting insect approaches itself. For example, a yellow flower can serve as a good shelter for them. The crab-tree is magically turned yellow and merges with the petal on which it sits. And when the insect crawls closer, the spider-invisible grabs it-and the dinner is ready!
 Marriage games.
Marriage games. A male spider, caring for a spider, must be careful. Pauchikha is not particularly picky and can take him for prey. She is twice as big, and maybe even bigger, and is more likely to dine with a male than to show tender feelings. Therefore, the spider has nothing else to do but show remarkable bravery and do a number of tricks, to subdue her heart and persuade her to marry her. What are these tricks? Strange as it may seem, but you can dance, play serenades, give gifts - just like men-men do, caring for women. First you find the female by smell. Further, bend the body and stamp your foot, hoping that your dance will please the spider and it will allow you to come closer. You can still step on the edge of its web and pull axial strings in a certain rhythm - just like a musician doing a guitar string does. This is a musical the message will notify her that you are not a prey at all. Instead, you can catch an insect and wrap it around your own web. It is hoped that the female will be interested in the gift and will allow her to come closer without attacking the male. She can even respond by waving her paws and palps in the air, and take several steps to meet her.
However, after pairing, the spider will face a terrible danger from the spouse. Despite all attempts to gain its location, the male spider still seems to be a good snack. It is common knowledge that a spider of the form "black widow" sometimes eats its spouse, and representatives of many other species at the first opportunity, follow her example.
An attractive smell.
Many female spiders actually produce a web with a special smell. By this smell, males can recognize a spider, belonging to the same species as them, and start performing a marriage ritual. (A spider will never mate with a female of a different species.) The smell does not last long, but it's for the best - the spider will not have to go on a false track and try to care for a female already married. Some male spiders can mate with several females, but from this they become weaker and can please one of their spouses for dinner, being unable to escape from it.
Most spiders, before they eat prey, kill or paralyze it with poison. The bite of some spiders can be dangerous even for a man. If a person is bitten by a poisonous spider, then a terrible pain arises, a sweat streams on the skin of a bitten person, it tones. But then a doctor appears, he brings the necessary medicines and saves the victim of a spider bite from a serious disease, and maybe even from death. Fortunately, not all spiders have such a strong poison, besides they do not attack first. In this case, in everyday life, you are unlikely to be bitten by such a spider. However, you can not rely on the fact that if you are attacked by a poisonous spider, a doctor will definitely be there. Therefore, take precautions, traveling in countries where such spiders are found.
All spiders have jaws, or wedges, with which they sacrifice a bite. Therefore, never bother spiders, as some of them can bite defensively, and the bite can be painful, if not fatal.
However, one of the spiders, namely the tarantula, was completely unfairly branded as a killer. Perhaps it was because of his terrible name. Just listen to this word - "tarantula": a terrible furry monster, ready to pounce and inject a deadly poison. Yes, the tarantula is really big and furry, but its bite is about as dangerous as a bee sting, which for most people is completely harmless.
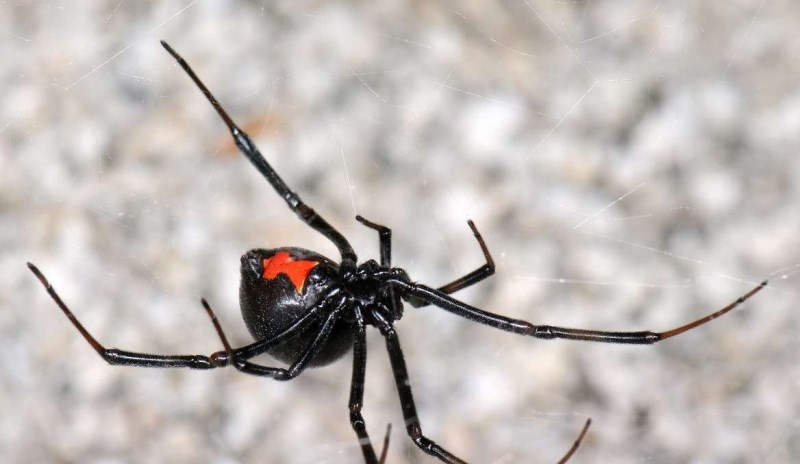
The real horror is inspired by the spider "black widow". The name "black widow" was received because sometimes a spider after mating devours a male. This spider is not large - its body length does not exceed 15 mm - however its poison is fatal and much stronger than, say, the poison of the rattlesnake. 15 minutes after the injection of the poison you feel pain - first in the bite, then it spreads to the stomach, and after and throughout the body. It becomes difficult to breathe. It can be recognized by the characteristic red mark in the form of an hourglass on the back; this mark is in many "black widows", although not in all. Among other poisonous spiders you can name a brown hermit spider and a wandering spider from Tropical America.
 It is often possible to meet a spider, weaving a cobweb in the bathroom. And do you know that some spiders spend most of their life under water? Next time, when you find yourself at a pond with calm water, try to observe. Look, there are no splashes on the surface of the pond, as if pointing out that someone is going to get to the surface. Possibly, these are signs of living in a pond of a water spider, quietly living under the water in a house built by himself. Sometimes water spiders have to rise to the surface , but most of the time they spend underwater, waiting for prey. Some water spiders are also called spiders-fishermen. These spiders are quite large and can even grab a tiny fish and eat it if they do not have the patience to wait for an incautious insect. The water spiders should not be taken into hands because they can bite, and their bite is usually poisonous.
It is often possible to meet a spider, weaving a cobweb in the bathroom. And do you know that some spiders spend most of their life under water? Next time, when you find yourself at a pond with calm water, try to observe. Look, there are no splashes on the surface of the pond, as if pointing out that someone is going to get to the surface. Possibly, these are signs of living in a pond of a water spider, quietly living under the water in a house built by himself. Sometimes water spiders have to rise to the surface , but most of the time they spend underwater, waiting for prey. Some water spiders are also called spiders-fishermen. These spiders are quite large and can even grab a tiny fish and eat it if they do not have the patience to wait for an incautious insect. The water spiders should not be taken into hands because they can bite, and their bite is usually poisonous. The water spider builds its underwater dwelling in a rather cunning way. First, it weaves a web, which lies flat beneath the surface of the water. Then emerges to the surface and grabs his air bubble with his hind legs. Very carefully the spider places the air bubble under the spider web, sliding down the stem of the water plant. It can do this up to a hundred times until the air gathers under the cobwebs and gives it the shape of a thimble. Now the spider can safely live under water, grabbing and eating incautious insects. The water spider is very prudent. The air in its "diving bell" lasts for 4-5 months. This means that the spider can remain under water throughout the winter.
Water spiders are so sensitive to all sorts of vibrations that they can easily detect signs of movement on the surface of any insect's water. Having caught this signal, the spider leaves its bell and pounces on the prey, first grabbing it with its legs, and then sucking at its poisonous jaws. But the spiders are fishing on the floating leaves on the surface and dive to grab the victim. However, the web and the air "bell" are not designed for catching prey - they serve as a cover for the spider itself. The water spiders hunt mostly at night, but always return to their bell to eat the caught prey.
The most complex networks are weaving spiders, but some spiders do not like to weave, and do not spend any time on anything except a cocoon. They are called "spiders-dinosaurs". These are, for example, spiders of the family of sidewalks, or spiders-crabs. They got their name because they looked like crustaceans: their front two pairs of legs are almost twice as long and more massive than the two rear pairs. Because of this disproportion, the spider must move cautiously, sideways, in the manner of a crab. Although the runner is unimportant from the sidearm, he does not suffer from it at all. For hunting, he usually chooses a flower cup. He pulls several safety threads so that his casual wind does not throw him to the ground, he spreads the front legs to the sides and stops - he waits for the prey. Stillness and bright coloring make it like a part of a flower, invisible to the eye of a possible victim. Usually the prey becomes a bee or a fly, sitting down to drink a cool nectar. As soon as the victim touches the flower, the spider's legs immediately close, pulling it to him, followed by an instant bite in the articulation of the head and chest of the insect. Along with the poisonous components, digestive enzymes are injected into the victim's body, which digest all the tissues of the victim's body, and the spider can only drink the resulting nutrient broth. The empty skin of the paclibo takes off from the flower, or leaves it as a "duck duck" to lure other flies and bees! In early spring, lanky males come to females, their pedipalps second pair of limbs on the cephalothorax spiders, have extensions in which they even before they go in search of females, store sex products. A few weeks later, females build flat cocoons on leaves and stems of flowers - within a month the testes will develop here. Having appeared on light, spiders will lift a spider's cover of a cocoon and will run in the different parties.
The nearest relatives of the boats are representatives of the family of philodromids, also wanderers and homeless pilgrims. Most spiders of this family are hunters daytime, and only one - philodrome nightly prefers sunset hours. Most often it is possible to meet this spider sitting on a bark of a tree or a wall of a wooden shed, with the background of which it almost completely merges due to gray with pestrinami coloring. But the most surprising in the guise of a spider is its flat body: it seems that he was under the wheel of the car, even the feet are flattened and pressed tightly to the surface of the tree. This form of the body helps quickly hide in narrow cracks, where no one will climb through.
In the thickest thickets of grasses bordering the edge of the forest, a relative of side-boats sits - the micro-mammata is green, a spider about the size of a centimeter. Usually he sits on a long leaf of cereal, stretching in front of him four longer legs, and watches prey. If a fly flies by, the spider pushes away from the sheet with his feet, doing somersaults in the air, and lands on the back of a fly. At the same instant, he strikes a bite and, while holding the fly, manages to get hold of the free legs for the leaves of the plant. And all this happens in a split second! Then the spider selects the leaf more conveniently, where it takes time and sucks up the fly.
For some spiders that do without cobwebs, their homes are vertical surfaces - tree trunks or house walls: there are a lot of booty, and opponents do not bother. Horseshoe spiders do not differ in large sizes, their body length rarely exceeds 1.5 cm, and painted they are modest: in black and gray tones with a white pattern on the upper side of the abdomen. Males of horse-breeders are spiders, although hawking networks are not set, but their territory is guarded jealously. It is not large - 30 x 30 cm. The spider sits in the center of the possessions and protects them from encroachments from the male neighbors. But the female came to its territory - and hostility is replaced by cordiality. The owner takes short steps towards her. Coming closer, the spider begins ... a dance number consisting of alternating strokes of legs, interrupted by a strong trembling of the entire body. The female watches favorably. A neighbor in the meantime decides to quickly examine other people's possessions. Our hero, having left the surprised lady, rushes to put things in order. Spiders weave for a moment in a ball, and then an outsider jumps out of it and shortly escapes away. Here on the wall a fly fell. Quite to not give out its presence, the horse leapt to the prey and froze. He must carefully calculate the throw. The spider breaks out of its place in its famous jump (for which he was called a "skunker"), but the fly that has noticed the movement takes off. The skunk grabs her legs already in the air and, describing the semicircle, falls swiftly down, hanging on a safety net, previously fixed on the wall. After hanging, the spider intercepts the prey with the first pair of head limbs - chelicerae and "moored" to the wall with free legs. Now you can gently pull the fly to your site and have lunch.
Spiders, mentioned above, do not weave networks in principle, using cobwebs only in emergency cases. There are among the spiders and those who have just started to master the basics of weaving. They do not yet have a complex web of webs, although they already use cobweb structures. These are, for example, wolf spiders.
The most famous representative of the family of arachnids is the tarantula. In Russia, the Dzhungar and Narbon tarantulas live. The Yaron tarantula is inferior in size to the Dzhungar, its body is about 2 cm in length, it is painted in gray with a coffee-colored pattern. His long legs are covered with alternating black and light rings. On the lower side of the body, in the region of the cephalothorax and the upper part of the abdomen, there is a black contrasting spot. This spot is the protection of a spider: a frightened tarantula rises to its hind legs, revealing the chelicera, and demonstrates a black spot that visually increases the dimensions of the body together with the legs that are raised above the head. In the dark hole, the spot is also an additional masking. If the spider feels that someone has taken to his hideout, he stands on his hind legs, cuddling up against the wall, and waits for an insecure insect to creep past, and then attacks from the rear. The Narbon tarantula settles on the dry slopes of the hills, where it digs shallow, 20-30 cm, mink, the bottom and walls of which are lined with a thin layer of cobweb. From the hole outlet of the burrow there are several threads in different directions - they are signal strings, that someone came. The tarantula sits in the hole, putting the two front legs on the thread, and if it finds the signal suitable, without hesitation for a second, jumps out, grabs the insect and drags it to the hole.
The female tarantula is a very caring mother. She uses several cobwebs to attach a cocoon with masonry and carries it everywhere with her. About a month later, it's time to be born to kids. If earlier the female often left the mink to wander around the neighborhood, now she becomes a homebody. The spider braids small hemispherical tent that will not allow the offspring to scatter in different directions. Having taken a place in the center of such a hemisphere, the female tears the wall of the cocoon and puts it next to her. Young spiders, just getting out of the egg, carefully climb on the legs of the mother on her back, and the female patiently waits, not moving at times for two days, until all, even the weakest, will take their places.
Numerous kids wear a live fur coat back and abdomen of mother. The female sits on the ground for the first few days, waits until the bright integument spiders get stronger and pour black color. For several weeks she does not eat, only drinks a lot, and only then dares to intercept the small prey. If the female makes a halt, the toddlers slide down to her feet and crawl under the protection of her mother, but the female stands off, as if they are on command, occupy their places of origin. When the time comes for spiders to become independent, the female increases the route. Stop, one or two spiders from the back with the back leg will fold - and again in the way. So all the children gradually settle down and begin an independent life. With the arrival of cold weather, children fall into a hibernation - only with the coming of next year, and even in a year they will turn into adult spiders.
 By mid-summer, young spiders reach sexual maturity. Lanky males lose their peace and leave their homes in search of females. Searches can last a week and two, all this time the spider almost does not eat, he does not have time to hunt: he is looking for. Finding the mink of a female, the male carefully touches the signal strings, as if he is ringing a doorbell. Immediately from the hole appears a larger female, and the male begins his presentation. Such a passionate dance more than a single spider will not see! The male lifts the front legs and starts to make them fast-quick rotational movements, as if the bicycle pedals are twisting, so the black and light rings on his legs merge into a continuous wheel.
By mid-summer, young spiders reach sexual maturity. Lanky males lose their peace and leave their homes in search of females. Searches can last a week and two, all this time the spider almost does not eat, he does not have time to hunt: he is looking for. Finding the mink of a female, the male carefully touches the signal strings, as if he is ringing a doorbell. Immediately from the hole appears a larger female, and the male begins his presentation. Such a passionate dance more than a single spider will not see! The male lifts the front legs and starts to make them fast-quick rotational movements, as if the bicycle pedals are twisting, so the black and light rings on his legs merge into a continuous wheel. But the famous tarantula was not for interesting behavior. Glorified his poison, which has long been attributed to the deadly power. Curiously, the treatment from this poison was considered a special dance, named after the spider tarantella. The virility of the dance was explained simply: a man sweats, and then with all the poison and goes out, danced all evening - next morning he's healthy! The legend is beautiful (and the dance too), but to reality all this has no relation. The bite of the tarantula is completely harmless, it looks like a bee sting - so that the bitten need not "dart" the poison.
Life on the surface of the river.
On a summer day on the surface of a quiet sleepy water in the river you can see a large spider running along the water with such ease, as if under it the earth's firmament. This Dolomedes is trimmed, one of the most interesting representatives of a spider's tribe. The males of dolomedes are painted bright brown, surprisingly deep and sated. Most often the spider chooses for its habitat either a branch lying on the surface of the water or the edge of water where a small arachnoid canopy is weaving. If the shore is too smooth, the spider builds a dam of webs of dry leaves fastened together and moored to the shore. On this raft, he sits, placing several legs on the signal threads of his small web, and one - gently touching the surface of the water. So the spider determines the fluctuations of the water, turning the whole water mirror of the reservoir into a large signal network. It is worth the predator to catch the excitement of the water floundering on the surface of the fly, as he instantly leaves his sentinel and runs like a bedbug, on the surface of the water to the victim, here the spider boldly attacks the prey - strikes the bite and drags it onto the raft. If the extraction was stronger, he goes to a clever maneuver: grabbing her stronger hooks chelicera, diving under the water, carrying away the victim behind him. Under the water, the body of the spider is covered with a silver "spacesuit", created from the air, detained by hairs on the body. This air will not only help him stay for about ten minutes under the water, saving him from suffocation, but will also allow him to easily surface when production stops resisting. In early summer the Dolomedes mother acquires a cocoon, she stops eating and completely devotes herself to children. After losing the cocoon , the female can easily take in pedipalps any round object and continue to "grow" it, at the anticipated moment of the appearance of the spiders patiently waits, when its piece of cotton wool will be exposed to the light of the cubs. After lying day beside a silent piece of cotton wool, the female considers her duty fulfilled and begins to feed, preparing for the laying of the second cocoon ...
And now we are talking about spiders that can create real tent - complex, skilfully woven networks. This is, for example, tegenaria.
There is no need to go far to search for tegenarii: their favorite refuge is dark, damp cellars and cold cellars. And the spiders themselves seem to have lost their colors from their underground life - their ash-gray body is covered with a discreet mottled pattern. The spider reaches a centimeter in length, its long slender legs, like the whole body, are covered with sparse long hairs, which makes it seem not "fluffy", but frighteningly hairy. It builds its own web of tegenaria in the corner, whether it's the angle of a staircase or a room. The network is a flat triangular pad that hangs in the air and the "top" begins necessarily from the corner of the room. In the narrow site of the network is a living spider tube with two holes - the main and spare, in case of flight. The spider sits in the living tube, exposing the two front legs to the arachnoid carpet, where the signal threads are intertwined. Feeling the jerks of a shadow, he runs with incredible speed to the prey, which, after a short struggle, drags him into his pipe.
Getting used to living in the darkness of the cellars, these spiders are guided ... by their feet! Their sensitive limbs catch the direction of the filaments that go to the entrance of the burrow, and along them, like a train on rails, the spider unerringly finds its way to its shelter. And yet, the spider's carpet of tegeneri can not yet be called a truly complex structure, and not so much it is tied to a wicker house. This is just a transition from stray spiders-non-genders to sedentary and hostile tenetnik.
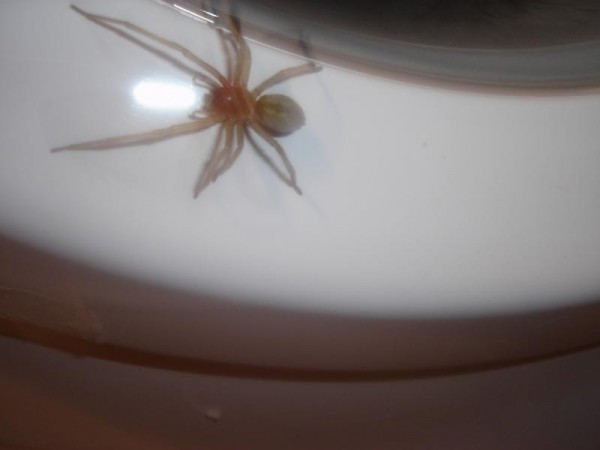
Karakurt is perhaps the most famous spider in the world. It is large enough: the body of a female, for example, reaches the size of a hazelnut. It is painted black with a red patch on the abdomen in the form of an hourglass - this is a sign of the "virulence" of the karakurt and its relatives.
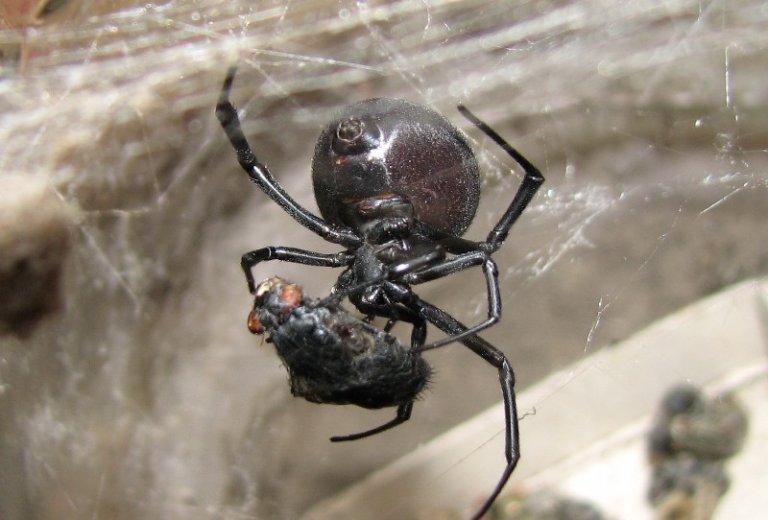
At first glance the web of karakurt has no structure and is a chaotic intertwining of threads stretching from the bush of grass to the ground itself. But what for us - chaos, for a spider - a native home, and it is with an amazing ease is guided by the intricacies of threads. On the tents, the spider sits upside down and most often rests under a canopy of leaves in anticipation of prey. Here the network has trembled from jerks of the grasshopper entangled in it, and there and then the spider hurries to it. He snacks some threads, providing better access to the prey, and is taken by the back legs to throw sticky lunettes. If the extraction is large, the karakurt acts differently: without approaching the victim, it sprinkles it with a liquid cobweb that, when frozen, permanently hobbles the insect. Once the prey is immobilized, the spider makes a bite and again continues to throw cobweb arcanes. Then, having had a bite of the rest of the restraining threads, he, fixing the cocoon with prey with his back legs, takes him to the corner where he usually takes his meals. There he inflicts a few more bites in the most diverse parts of the insect's body, apparently, for faster and more uniform dissolution of the tissues. And after half an hour he starts sucking the victim.
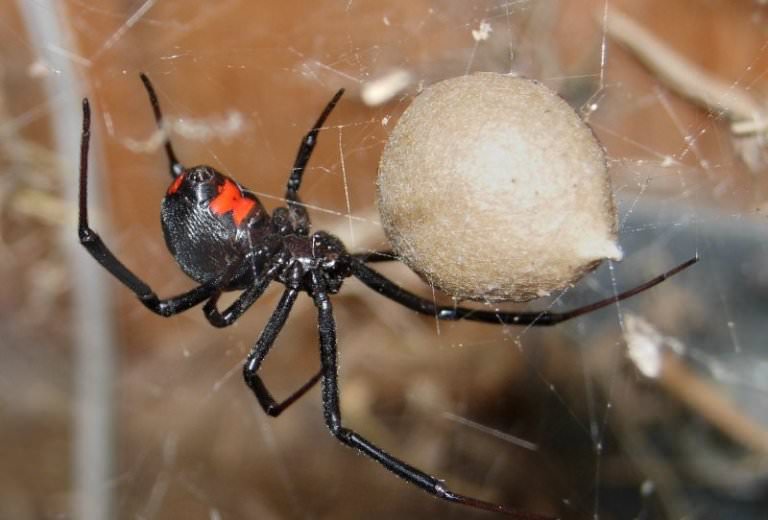
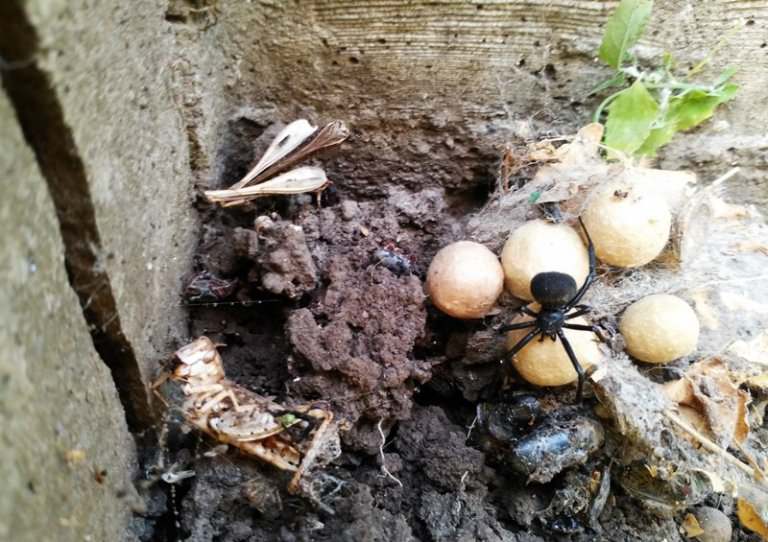
The spider grows, sheds, and, at last, comes the time of the penultimate moult of females and the last molting of males. The females become black, but the males do not want to lose the paint: there is nothing to boast about the females! Now, having left their tent, the females are sent to a new migration. Wherever the young spider goes, she always pulls a thread behind her. It is on these strands that the male finds it. On the road, females spread temporary tensions, the last time they molt - here the males also favor them! After uncomplicated courtship, mating takes place, which often ends in tragedy: the female eats a legitimate spouse. Hence the other name of the spider is the "black widow." The carapace tree eats the male, because in order to lay eggs, it badly needs protein. When the egg laying time comes, the female swaddles them into globular cocoons that hang in a secluded mouse hole all winter, until next spring. The maternal instinct of female Karakurts is striking. Sharp, rough hooks-chelicera and a strong anterior pair of limbs - pedipalps, which could kill a huge grasshopper a minute before, turn into soft mother hands with the appearance of offspring. The female carefully removes the cocoons from the cobweb to carry them away from the sun to the shade or, on the contrary, to take out the warm under the first rays of the sun.
Karakurt is widespread in Central Asia, the Crimea, Southern Europe, mainly in the steppes. But sometimes it can be found in our central strip. How did the southern spider turn out to be near Moscow? In the early spring, from the cocoon of Karakurt, suspended somewhere in a mouse hole or other secluded place, spiders begin to rush towards the first spring sun. In these small fragile glossy black creatures, covered with white specks, it is not easy to guess the deadly spiders. The babies weave their first tent, on which they rest together for several days, gain strength, and there comes the time of the first migration. Spiders try to escape far from their native cocoons, even climb on tall spikelets of grasses and bushes, to let out of the abdomen spider web, fly away to it to the far edges. The meaning of migration is not only in the development of new lands, it is also a mixture of different populations of karakurt, which allows avoiding fatal degeneration. Sometimes the wind carries a weightless web for hundreds of kilometers - and there are Karakurts in the suburbs. Alas, here they will die with the onset of colds: the northern climate is too harsh for them!
Karakurt is known as a cruel and dangerous creature. Not only sheep, but even camels perish from the bite of the karakurt, and at least every 20th person perishes from bitten people! In severe cases, poisoning karakurta causes nausea, headache, convulsions and loss of consciousness, the work of the heart and respiratory organs is disrupted. What should I do if I bite the karakurt? The most effective method in the first minutes after a bite is moxibustion with a burning match. The burn is, of course, painful, but compared to the consequences of a bite - trifles. The spider bites shallowly, and in the first minutes the poison penetrates only to all layers of the skin and from the heat it breaks down . But only 5-10 minutes after the bite, this method does not work: the poison will get into the blood through the microvessels of the skin. In this case, you need to make a cold compress to slow the spread of the poison, and immediately get to a doctor who will inject serum and prevent paralysis.
What is the probability, after encountering a spider, to get a poisonous bite? A spider bites a person only in one case - if he by negligence or curiosity presses him with his fingers or clothes. Because it is enough not to take karakurt in your hands and do not spend the night in the open air. Pasterns, who have to spend the night in the steppe on the ground, lie down, carefully wrapped in sheepskin. The smell of sheep's skin frightens away the Karakurts.
Circular networks.
It is enough to go up to the attic or just look into the dark corner of the entrance, as a large circular network with a huge and scary spider sitting in its center rushes into the eyes. It makes a careless move - and the spider falls down with a stone, leaving the web. The circular network is the top of the development of the spider's shadow, the most complex, the most economical and at the same time the most effective. This is a real masterpiece of spider architecture. Everyone knows a diadem with a cross - he settles near human habitation. His brown abdomen is decorated with a white cross-shaped design, for which the whole genus of these spiders has its name. More often than not, the science does not move, sitting in the center of its own circular grid and waiting for the prey. If you patiently watch it, you can see the very process of creating a tenon. First of all, the spider connects various supports with different threads: tree branches, a fence or a window frame (these supporting threads are called the frame of a shade). Then he pulls the radial threads and ties them with circular fastening threads. The distance between the fastening rings is within 10 cm. This is the basis for a shadow from a dense, elastic web. The next stage is the construction of trap rings. Their spider makes of a thin elastic web, hung like a garland, with droplets of sticky secret. It moves in a circle, fixing the thread on each radius, creating a dense and strong network. When the tails are built, there is the final touch - to stretch the signal thread from the center parallel to the right radius. On it, like a fireman on a wire, the spider instantly moves from its shelter to the tent , if there is an occasion.
Very similar to the cross spider of a shark. Dimensions, it is only slightly inferior to the crosses, but the brightness of the color is superior. Its greenish-yellow body has on the upper side of the abdomen a picture in the form of a green leaf, and the body itself is densely covered with hairs. The circular network of the sharkleipher is slightly different in structure, it has an "empty zone" without trapping radii, a ring 10 cm wide encircling the center. This network structure is by no means a simple fad of the architect! He hangs the tent not in attics, like a diadem cross, but in
fields and forest meadows, where strong gusts are constant. The hole in the center is the insurance against the rupture, so that the wind of the tide, like a sail, does not pull, but freely pass through them. The aculepists acquire a cocoon at the very beginning of summer - at this time, near their circular nets, you can see a shiny golden ball suspended on fastening threads. If it receives a ray of sunlight, it begins to shine strongly, turning only into a sunlight flare. This is a completely different masking principle, using the reflection of light. It turns out that a sharkepeare is not only an architect, but an optician!
In Crimea, another representative of the circular spirits lives - the lobed arpyopa. Her abdomen has protuberances on both sides, why the spider's body resembles some strange fruit in its shape. The spider is painted not strikingly: the cream body on top has a metallic luster; When the spider is hanging in the center of its tent, in the bright sun it seems only a glare of the sunbeam. In the circular network of this spider, hanging low over the ground, very wide mesh: not for small flies, it is calculated, but for grasshoppers and kolylok.Samy arhipop compared with females just dwarfs. Having fallen on the web to his beloved, the male does not even risk being eaten-the fish simply does not notice it.
No matter how brave and resourceful the spiders-tenetniki are on their webs, they do not know how to hunt or care, they are afraid of every bug and try to hide from every shadow. A circular network is the only world in which they can live and create for themselves. The spider web, like any masterpiece, has a special, unique style, and a connoisseur will always determine which spider created these tents.
Eight-legged giants.
Not all spiders in order to survive, began to experiment with tent. Some have done easier: they just took it and ... grew up! This strategy was chosen by the tarantula spiders: the length of many representatives of this group reaches 10 cm, and the range of the paws is 15-20 cm. The gigantic size is already in itself both protection and help in fighting multi-legged game. The most famous tarantulas are brahypelm - the creatures are quiet. They live in a small hole, only a little braided spider web, and occasionally they go out hunting. The foot of the giant brahapelma is not audible - its quiet steps and smooth movements, hidden by the cover of the night, allow you to get to the cricket cricket unnoticed. If the spider will feel the slightest movement, then for a moment it stops, setting out its furry legs in front of him, listening to the smell of prey, and then makes a lightning attack, grabbing the game. And just as quietly, stealthily, will hide back to his hideout under the snag so that they can have a quiet supper. If he is caught off guard by an enemy - some small predator, then the spider will stop for a moment, letting the attacker get closer. And then the rear legs will rise and they will quickly rub their abdomen quickly. From these movements break loose fragile hairs covering the body of a spider - and a cloud in the air. Getting into the respiratory tract of the beast, they cause irritation - the predator sneezes, can not stop, and the spider slowly and importantly leaves away.
There is an opinion that tarantulas eat almost exclusively small birds. However, in reality they, like their smaller relatives, prefer insects, crickets and cockroaches. The second myth concerns the virulence of all turtles without exception. But most of them are not poisonous: their bite, though painful, does not threaten the unfortunate. Unfortunately, there are very poisonous spiders among the tarantulas, first of all inhabitants of the crowns of tropical trees - in comparison with their bite, the bite of the karakurt will seem an easy trouble! Not surprisingly, these spiders are colored in the evocative colors - bright yellow, red, etc. They are not hiding to anything, their color they signal: "Do not touch me, I'm very poisonous!".
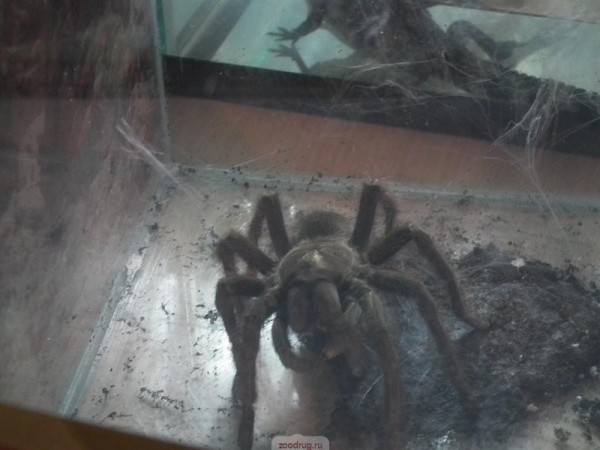 Tarantulas have a special structure of chelicera: they are directed "hooks" not inside, like other spiders, but forward, like the teeth of a poisonous snake. A tarantula bird produces an unpleasant impression: its hairy body reaches a length of 10 cm and rests on 4 pairs of shaggy paws. Like most other spiders, the tarantula produces silk with the help of special spiderwebs. He mulled the mink in which he lives. A spider-tarantula even makes a "cover" for his home. He makes it from the ground, mixed with pressed silk, and fixes it on the original hinge. When a spider is harassed, it clings to the inside of this lid to prevent the enemy from entering. Spider-tarantula is a good hunter. He waits for prey, hiding at the exit from the mink. As soon as the spider notices the future victim, he jumps out of the burrow, rushes to the prey and bites her with two venomous teeth. His teeth are injected with a poison that can paralyze small animals. Tarantula spiders live about 17 years. Some researchers believe that females live to 30 years old, males are less. During the mating season, the male knocks on the lid of the females burrow. The lizard comes out, both partners approach and mate. The lion lays 200 to 1,000 eggs, and then envelops them with a silk cocoon Eggs ripen in 20-30 days. Hatching spiders in the process of growth pass through several lines. The age of puberty comes to 2-3 years. The adult spider-tarantula can do without food for more than a month. The record is 3 years. Despite the fact that the spider-tarantula has many eyes, it is short-sighted and practically sees nothing. In addition, he also does not hear anything and does not feel anything. This spider is oriented in space, catching the hairs of the body of the vibration of the surrounding world.
Tarantulas have a special structure of chelicera: they are directed "hooks" not inside, like other spiders, but forward, like the teeth of a poisonous snake. A tarantula bird produces an unpleasant impression: its hairy body reaches a length of 10 cm and rests on 4 pairs of shaggy paws. Like most other spiders, the tarantula produces silk with the help of special spiderwebs. He mulled the mink in which he lives. A spider-tarantula even makes a "cover" for his home. He makes it from the ground, mixed with pressed silk, and fixes it on the original hinge. When a spider is harassed, it clings to the inside of this lid to prevent the enemy from entering. Spider-tarantula is a good hunter. He waits for prey, hiding at the exit from the mink. As soon as the spider notices the future victim, he jumps out of the burrow, rushes to the prey and bites her with two venomous teeth. His teeth are injected with a poison that can paralyze small animals. Tarantula spiders live about 17 years. Some researchers believe that females live to 30 years old, males are less. During the mating season, the male knocks on the lid of the females burrow. The lizard comes out, both partners approach and mate. The lion lays 200 to 1,000 eggs, and then envelops them with a silk cocoon Eggs ripen in 20-30 days. Hatching spiders in the process of growth pass through several lines. The age of puberty comes to 2-3 years. The adult spider-tarantula can do without food for more than a month. The record is 3 years. Despite the fact that the spider-tarantula has many eyes, it is short-sighted and practically sees nothing. In addition, he also does not hear anything and does not feel anything. This spider is oriented in space, catching the hairs of the body of the vibration of the surrounding world. Large tropical tarantula spiders can be kept in aquariums provided they are often cleaned. Aquariums should consist of:
1 Cover.
2 Asylum under stones.
3 The bottom is covered with gravel.
4 Electrolamps for heating.
5 A cactus or other tropical plant.
6 Sponge in a saucer with water - spiders do not drink water, but moisten their mouth parts.
Feed live insects, especially locusts and crickets. Spiders regularly shed, and at this time they change color and become inactive. Small spiders, including braided nets, can be caught and kept for several days in plastic or glass vessels with perforated lids. You need live insects, branches to attach nets and moist plant leaves. Some spiders can be "tamed" by giving them flour worms.
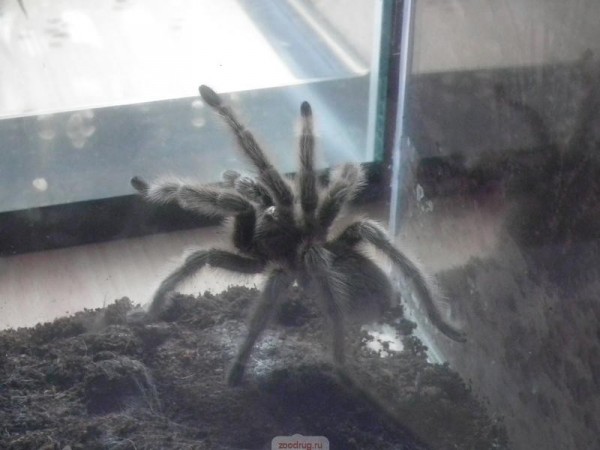 Tarantula spiders are found in different climatic zones (from semi-deserts and deserts to tropical forests). Their range is from South America to Australia, as well as the south of Europe and the USA.
Tarantula spiders are found in different climatic zones (from semi-deserts and deserts to tropical forests). Their range is from South America to Australia, as well as the south of Europe and the USA.
How to stop being afraid of spiders.
There are a lot of people who spider, to put it mildly, dislike. And they are panic-stricken, just ready to pass out. The scientists even came up with a special name for this common phenomenon - "arachno-phobia", ie, "fear of spiders"! arachnophobia, there are special computer programs. At first, they show drawn conventionally pretty "cartoon" spiders, then the images become more realistic and detailed, they are replaced by fragments of popular science films about the life and habits of spiders.
Tarantula spiders
Interest in arachnids as pets has increased markedly, especially in the last quarter of the 20th century. But in the distant past there were brave souls who kept these extraordinary animals. Thus, Henry Walter Bates, mentioned by us, saw how the little Indians, who helped the scientist in collection collections, were tied with a thread of a huge tarantula around the "waist" and "walked" him like a little dog.
It is known that in 1862 on a ship laden with coal, a spider-tarantula was found, apparently, got on the ship "hare". The ship arrived from England and docked in Danzig (now Gdansk, Poland). He lived alive for a year: he ate insects and spiders, but also raw meat.
Of course, this was not the only case. Tarantula spiders repeatedly hit the ports of temperate latitudes, including Russian ones, and entered zoos or museums. They can be found on ... fruit bases or vaults where green bananas ripen, as well as in greenhouses of botanical gardens. Even the famous Swedish zoologist and writer Jan Lindblood received a tarantula spider in a box with bananas in the form of "free application"; although he wrote openly: "I never had a soul to spiders, although I know that large South American spiders are being tamed. I, for example, can not even imagine that a spider crawled on my leg or arm. But in the Butantan Institute in São Paulo, there is a girl who allows a monster about a quarter of a meter long (along with the limbs) to walk along its bare hands. The main thing is to conquer in oneself the fear of an unusual creature. After all, a man in the eyes of a spider, all eight, is also unusual ... "
Psychologists and psychoanalysts use a sophisticated term: "arachnophobia" is the fear of spiders. Usually this fear manifests itself from childhood, if the elders frighten and tease the child with a spider. The patient (or patient), as with other obsessions, imagines that spiders are hiding in his house, and such a patient seeks to get rid of the "threat" at any cost. Fortunately, arachnophobia is successfully treated.
In captivity, tarantulas were fed not only by invertebrates and raw meat, but also by frogs and mice: sparrows were given to him at the Berlin Zoological Institute. From the spider's bite, the sparrow died very quickly. One lover kept the tarantula for about a year. He fed him a variety of small animals. A frog, for example, was chewed by a tarantula in porridge, along with bones. Later in his feces were the bones of this frog with pieces about 6 mm long. After eating enough, the spider stretched out its paws, tightly pressed the belly to the bottom of his home and remained in this position for days on end. Apparently, he was sleeping, digesting a thick dinner. Sometimes the inhabitants of the tropics (although rare people) deliberately bred some spiders at home. During the day, spiders usually hide behind furniture and paintings, and at night clear the apartment of annoying insects.
In the end, the amateurs mastered the technique of keeping tarantulas. Thus, a female caught in Mexico in 1935, lived 28 years. Large tarantulas outgrow sometimes thirty-year boundary.
However, tarantulas in captivity did not multiply for a long time. Their successful breeding in October 1966 produced a genuine sensation among the specialists. It happened at the London Zoo - a couple of spiders came from Guyana a year ago. The female laid 50 eggs in the form of cocoons, pasted them with cobwebs, and hid among the foliage of the terrarium. When spiders appeared, in order to avoid cannibalism and other internecine strife, they were seated in separate large glass test tubes and fed fruit flies - fruit flies.
Subsequently it was found that large female tarantulas of some species lay in the summer from 500 to 1000 eggs in a free cocoon; The female sits on a cocoon, as a hen, or holds a cocoon "in an armful". It is worth disturbing her, as she immediately raises the chelicera in the pose of threat. After three weeks, whitish spiders hatch, but they remain in the cocoon until five weeks. Leaving the cocoon, they acquire a brown color with a black stain on the abdomen. They stay close to the mother for 3-12 days, and then run away.


In addition to feeding Drosophila, the diet includes tiny flour worms and other inactive invertebrates. Young animals are fed daily, adults - every other day. Within three days they increase the size from 4 mm to 16 mm, and weight from 0,0052 g to 0,8 g. By the way, spiders-tarantulas are able to fast till 2 years. During the first three years, spiders molt four times, in the fourth and fifth years - twice, and then annually.
During molting for several hours they are practically motionless and do not respond to visual or auditory stimuli. The same applies to touching. Those tarantulas who are capable of digging burrows, tighten the entrance with cobwebs to avoid enemies, as they are extremely vulnerable during moulting. But pouring, they literally bloom, like a ruddy pie from the oven.
Despite the warm parental love, especially during the first weeks of life, only 0.2% of tarantula spiders survive to maturity.
In the circle of Western "arachnids" is well-known Canadian citizen (Victoria, British Columbia) Rick West; in the basement of his house live are kept 2000 copies of tarantulas, and 3000 are collected in the form of fixed exhibits. He has been engaged in spiders for more than 40 years, and, as a true enthusiast, serves as an inspector of the Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. Although West does not have a scientific degree, he is approached by world-class specialists.
In Moscow, a young amateur Alexander Petrovich Generalov is known, which contains 500 species of invertebrates. Among the favorites of Alexander - tropical scorpions (15 species) and tarantulas (154 species). He was the first in Russia to organize an exhibition of live exotic butterflies; Alexander - a frequent guest of the program "Dialogues about animals." Many animals have successfully reproduced.
I must say that in the US breeding tarantulas is a profitable business. Annually in the town of Orlando (Florida), an exhibition of amphibians and reptiles with an invertebrate section is held. A tiny spider costs $ 150, and customers hope to grow their pets to the age of twenty, which is extremely difficult. In contrast to a worthy, painstaking work - breeding in captivity of any kind - the smuggling of spiders is alarming. One US citizen from the State of California secretly carried 600 spiders, for which he was imprisoned. His failed "business" was estimated at $ 100,000. In addition to living spiders, in the tropics shamelessly traded "souvenirs" for tourists - a prepared spider-tarantula in a glass box. Somewhere in the Amazon basin, a catcher is paid $ 1 for the "head" of a spider, and at a South American airport such a souvenir costs $ 10. They suffer because of busy vehicles. Female of some species (in particular, Aphonopelma chalcodes)go to the highways of the southern states of the United States. They lay between 75 and 2,000 unfertilized eggs in the mink and emit pheromones to attract males. During this period, they are brutally crushed by motorists.
It is not surprising that many species of tarantulas are sharply reduced in numbers, at least one of the rarest - the cave spider (Spelopelma reddelli)from the Mexican state of Oaxaca. Official bodies were forced to restrict trade
effective tarantula (Brachypelma smithi),on the "joints" of which the orange intercepts, also dwelling in the deserts of Mexico and in the south of the United States, adorn.
Among the species of spider-tarantulas, which are not subject to restriction, for zootargeting is interesting Chilean pink tarantula (Phrixotrichus spatulata).He is extremely fond of a novice lover, and therefore we will tell you more about the conditions of his content. These notes, written by the already mentioned Philippe Perser, are intended for the American reader. However, the principles of content can be extended to tarantulas of mountain-desert territories and used for the care of close species.


The creature is, although cute, but inspires inner anxiety. Some kind of unreasonable fear. Especially eerie to watch as a spider with yellow stripes, it is also called osoy, is straightened with defenseless grasshoppers and flies. He will set up a nimble network, sits half asleep, and waits. But as soon as the carefree insect gets in the field of vision, it immediately transforms - briskly attacks, paralyzes the victim with poison and deftly wraps the "dinner" in a cocoon from the web. Is spider-spider dangerous for humans?
At first glance, a very pretty spider ... until you find out that it is poisonous
Dossier on the spider-box
The first question that arises at the sight of an unusual arthropod, is the name of a spider with bright yellow stripes. It is the color that causes confusion - it is called both "special" and "zebra", even "tiger". Biologists have christened the striped spider Arhipopoy.Place in a spider's family
The Arhipop genus belongs to the family of spiders-circuses, has over 80 species. In our area, most often occurs Arhipopa Brunnich, a species named on behalf of a Danish nature researcher. Biological characteristics include several recognizable features.
- Yellow-black-and-white color, consisting of alternating bands.
- Explicit sexual dimorphism - "girls" exceed males in size 4-5 times.
- Predatory habits, the use of poison to paralyze the victims.
- Typical for circular rooks is a cunning radial web, exposed vertically or slightly under a slope.
- Eating of female males after mating.
How does it look?
Look closely at the "portrait" of a spider with yellow stripes on its back from a close distance - the photo below.
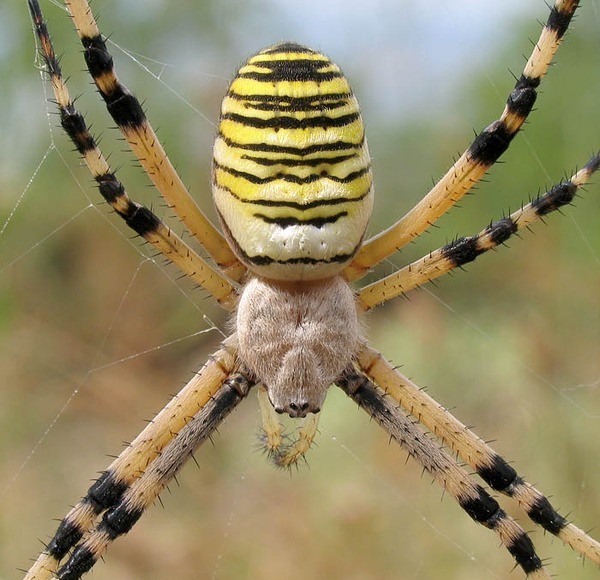 Judging by the size, it is a spider, hanging head down in anticipation of prey
Judging by the size, it is a spider, hanging head down in anticipation of prey
Spider-females are quite large - reach a length of 2.5-3 cm, and taking into account the length of the limbs, even 4 cm. The cephalothorax is "fluffy", covered with dense short hairs of a silvery hue. The abdomen is slightly elongated, in shape and color, like a wasp. The yellow-white background is delineated by thin transverse lines of black color - hence the impression of wide yellow bands on the back. The paws are long, with dark bandages.
Males are small and unattractive, no larger than 5-7 mm in size. The dorsal pattern consists of light yellow and dark strips.
Where does it occur?
The habitual habitat of spiders with yellow stripes is the subtropical and steppe zone. It is due to the love of arachnids to heat. But global climatic changes have led to the fact that the spider-wasp moved to the north, successfully adapted in the suburbs, the Volga region, the central regions of Russia.Ariopa settles mainly in dense, moist thickets of bush, grass. But at the same time he prefers open, sunny places. In the wild - on the fringes of forests, banks of rivers, meadows, roadsides. On the backyard, cottage area of the spider-os can be found in raspberries, thickets of blackberries, in a hedge of thick-leafy climbing plants.
Note! A spider with yellow stripes puts the nets low (30-40 cm above the surface of the soil), pulling the threads of a web between plants, does not like to be disturbed. Therefore, the garden will settle only in places where the hands of the owners do not reach, where the arthropods will not be disturbed by weeding, cutting, loosening.
 The best invitation for arpiope, than thick untouched thickets, you will not think up
The best invitation for arpiope, than thick untouched thickets, you will not think up Lifestyle
Spider-wasps live singly or in small groups, the maximum size of the colony is up to 20 arthropods. They belong to the category of predatory spiders, a favorite diet - grasshoppers, dragonflies, flies. Sometimes bees and wasps enter the net, but then the battle rages against life and death. From the bee (aspen) poison, the hapless hunter dies.
At dusk, a spider with yellow stripes on its back is weaved by nets. He sprawls the radial net, cleverly combining the stems of plants with spiral threads. In the center or in the lower part of the web, a special "decor" is weaved - a stabilizingum - a thickened zigzag thread. Scientists differently interpret the purpose of this "pattern" - for camouflaging, attracting prey, as a sign to kinsmen that the territory is occupied.

 Zigzag pattern in the lower left corner - stabilizingum
Zigzag pattern in the lower left corner - stabilizingum
Interesting! Spider-wasp is one of the fastest weavers. A circular network with a radius of up to half a meter, it creates in 40-60 minutes.
After the works, the arpyopa settles on the stabilizum and patiently waits for the prey. In the victim, the spider sprinkles the poison, which paralyzes and turns the insides into a liquid mass. It is this "broth" that sucks the predator, leaving only the chitinous shell from the insect. To support livelihoods, the spider suffices one successful hunting per week.
 "Lunch" is caught and reliably packed
"Lunch" is caught and reliably packed Features of the life cycle
The life span of large spiders with yellow stripes is 1 year. Sexual maturation occurs in the second half of the summer, July-August - the time of mating and laying eggs.
The fertilized female kills and eats the male, and after a few days begins to weave a cocoon to lay eggs. The larger the arpyopa, the more offspring it produces - the clutches of some specimens reach 400 eggs.
Pauchikha is a caring mother. She weaves a reliable fluffy cocoon, hangs it in a secluded place, guards. Bends the arpyopa before the juvenile appears.
Young (juvenile) spiders hatch in autumn. In a cold climate, they remain under the protection of the cocoon until the spring, then settle and quickly grow up.
Interesting! And did you know that "Indian summer" is the period of settling juvenile spiders. The crumb crawls out of their cocoon, climbs up the hill and spews out the web. The arthropod, taken up by the wind, rushes towards an independent life. It is so small that we see only a weightless spinning in the air.
 Careful mother weaves a cocoon for future offspring
Careful mother weaves a cocoon for future offspring "Relationship" with a person
Although a spider with yellow stripes on its back is classified as poisonous, it does not represent a great danger to humans. First, he is afraid of people and the first will never attack, rather, run away or fall to the ground and pretend to be dead. Secondly, the arpyopa is not able to bite the skin of a person to inject a poison.
But if a spider-owl is taken with a bare hand, an unpleasant and rather painful bite is provided. The redness and itching of the stung spot passes fairly quickly. In allergy sufferers, the reaction can be more turbulent and unpredictable - from a strong swelling of the bite to a rise in temperature and swelling of the airways.
Therefore, it is better to stay away from the beautiful and cunning arthropod. In the garden, the flower garden, he does not belong at all. But if you meet in the forest - let him live!
Video about the spider-ax:
Want to get rid of harmful insects? We recommend professional service of pest control:
- Work experience more than 12 years;
- Departure to anywhere in Moscow;
- Work day and night;
- Modern equipment and powerful insecticides;
- Contract and guarantee.
Spiders were the first among the earliest animals that lived on earth. Despite the fact that the age of life of spiders on the planet is quite significant, fossils of spiders are rare. According to historians, biologists and archaeologists, the first spiders on our planet appeared about four hundred million years ago. The ancestors of modern spiders were a spider-like insect, quite thick, large in size. For a long time this spider-like insect lived in water.
Tarantulas belong to the genus of the higher spiders of the family of spiders-wolves. This species is distinguished by its large body size (long tarantulas can reach 3.5-7 cm), as well as the presence of poison glands. Most often, all large spiders are called tarantulas. This is a very common misconception. For example, the same spider-tarantula, despite its large size, has nothing to do with tarantulas. The habitat of tarantulas is a territory devoid of moisture. More often representatives of this species can be found in the desert sands and steppes. They feed on tarantulas with small insects and animals, attacking them and killing them with poison. Another very common misconception is that the tarantula can pose a threat to a person. Yes, the threat can come, but only for those who are afraid of spiders panicky. The poison of a tarantula can not kill a person. The bite of this spider can be compared to a bite of a wasp or hornet, it can cause swelling or severe pain shock, but not to poison a person.
In the world there are several kinds of spiders that should be feared by man. In the US, only two such individuals live. This is the "brown hermit" (Loxosceles reclusa) and the "black widow" (Latrodectus mactans). The bites of these spiders are deadly because of the poison.
"The brown hermit" can be found in houses in the west of America, they hide in crevices of the sexes. The bites of these spiders never heal. Who wants to look at these terrible wounds - welcome here . So, to know. But I warned you!
"Black Widow" black color with scarlet spots. This kind of spider never attacks a man himself, only if people try to touch him. A distinctive feature of these spiders is an unusually clear pattern on the body in the form of an hourglass:

A photo from here
The female is a very poisonous spider. Males are less common and are safe. The males have four pairs of red dots, located along the sides of the abdomen. After mating, the female devours the male, hence the name "black widow". But even for black widows cannibalism is not found in 100% of cases - it is more a deviation from the norm. The bite of a female is toxic to humans, such a bite is accompanied by local pain, swelling, nausea, difficulty in breathing and sometimes fatal.
Another dangerous spider is Karakurt (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus). It is often found in the steppe zone of Central Asia, as well as in the Caucasus and Crimea. Karakurt - the spider is small, its length does not exceed usually twenty millimeters. The habitat for Karakurts is virgin land, wasteland, banks of irrigation canals and so on. People are prone to bites of karakurt during the migration of females (this is approximately June-July). The most poisonous are sexually mature females, the poison of Karakurt is fifteen times stronger than the poison of the rattlesnake. After a bite on the body there remains a small speck that quickly disappears. Fifteen minutes later, sharp pains begin in the abdomen, lower back and chest, then the legs become numb. The patient becomes sluggish, because of severe pain, does not sleep. Recovery comes in about three weeks, or even more. In severe cases and in the absence of medical assistance, death is already on the second day.
For all of us, the words "spider" and "cobweb" are quite familiar. We well know that a spider is hunting with a spider's web. But it is not always the case. Some spiders do not use cobwebs at all. A vivid representative of a spider that does not use cobwebs is a sidearm. A spider just masks in a flower and waits for prey. Due to their abilities, the spider can move not only forward and backward, but sideways, so it does not take time to turn. And it is these fractions of a second that the victim lacks in order to slip away.
Synema globosum:

A photo from here
Spiders have eight eyes, two of them behind. The name of his spider was for the ability to jump a distance of several times the length of the body. And it's not in the legs, but in the circulatory system. Before the jump, the pressure of the spider increases several times, due to which the hind legs straighten sharply and the spider flies towards the victim, not forgetting to insure themselves with a web.

A photo from here
A spider-wolf uses cobwebs as a rope in order to tie and hang his victim. His legs are fed. A spider-wolf can walk on water and even dive for small tadpoles or fry.
A spider-pirate uses a spider web as an alarm. He stretches it before the mink, and ties the ends to his feet.
Some of the flower spiders are able to change their color for more than a few days, usually between white and yellow, depending on the color of the flower on which they rest.
Another interesting spider is Argyroneta aquatica. It's a water spider. If you translate the name verbatim, you get "someone who has a silver thread." Spider, or rather tell a spider, a very small size, only up to one and a half centimeters in length. However, the bite of this insect is very painful. Spiders live in water, or rather, under water. Habitat - Central and Northern Europe. Under water, each spider has a bag woven from a web. Previously, it was believed that this bag serves to store food and to hide in a moment of danger. And only recently scientists have found out that the primary task of underwater bags is the storage of air. Spiders catch air bubbles under the water and neatly on their paws carry them to their bag, and spiders react very strongly to the composition of air inside the bag.
Taken from here
Peacock spider-male Maratus volans uses dances and bright "outfit" to attract females:

A photo from here
The figure on the abdomen of the spider Cyclocosmia truncata resembles an ancient seal. Its spider disc uses as one of the ways of protection in cases of danger. They lead a sedentary lifestyle, so they do not go far from their minks. During the threat, he crawls into his burrow head first and his hard disk closes the entrance to the shelter.
Taken from here

A photo from here
Unusually look spiked spiders. Spiders are widespread in tropical and subtropical belts. On the edge of their abdomen are six spines. They give the spider a more frightening appearance, which allows scare away potential enemies:

A photo from here
They feed on small insects that come to them on the net. The spider trap is a fairly strong network web, reaching a diameter of 30 centimeters. It has an almost ideal form of a circle, in the middle of which there is a thin network. It serves as the basis for the spider.
Taken from here
The web looks like computer disks:

A photo from here
And now just a selection of interesting and bright spiders in colors.

A photo from here

A photo from here
Red with yellow:

A photo from here
Red with black:

A photo from here
Red with white:

A photo from here
Orange:

A photo from here
(Araneus marmoreus - Marble cross): 
A photo from here
(Brachypelma boehmei):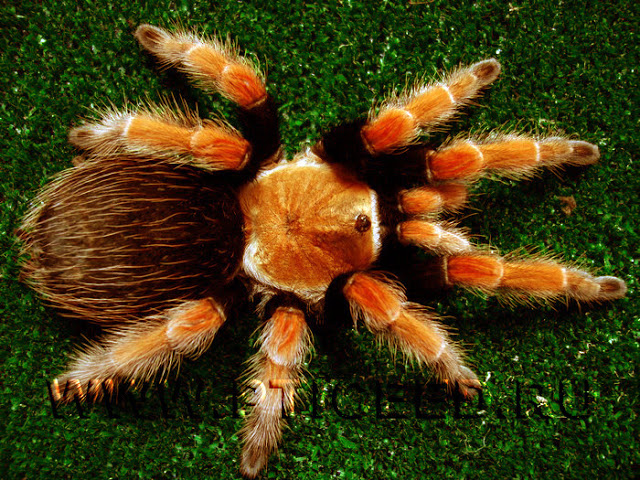 
A photo from here
Yellow:
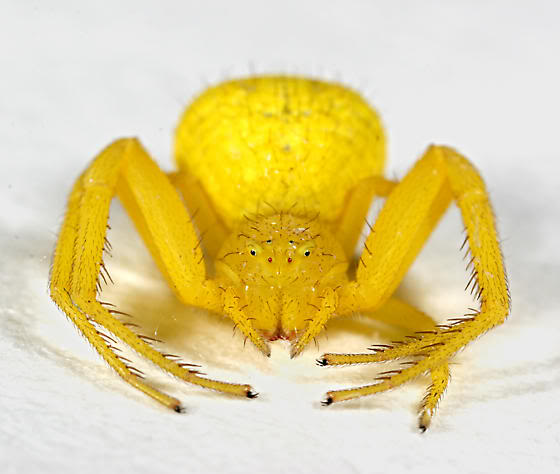

A photo from here
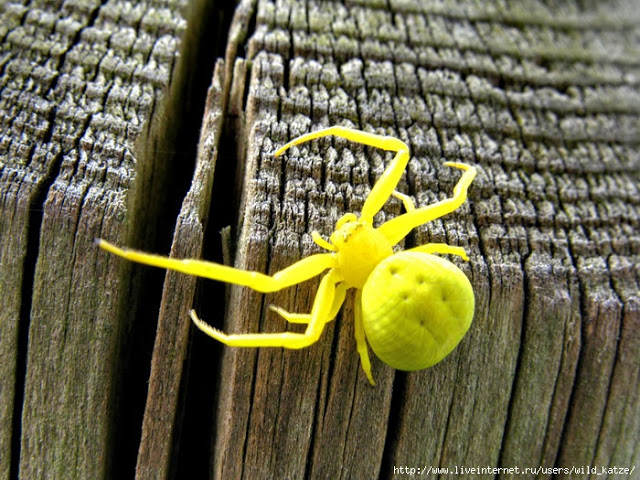

A photo from here
(Gasteracantha arcuata):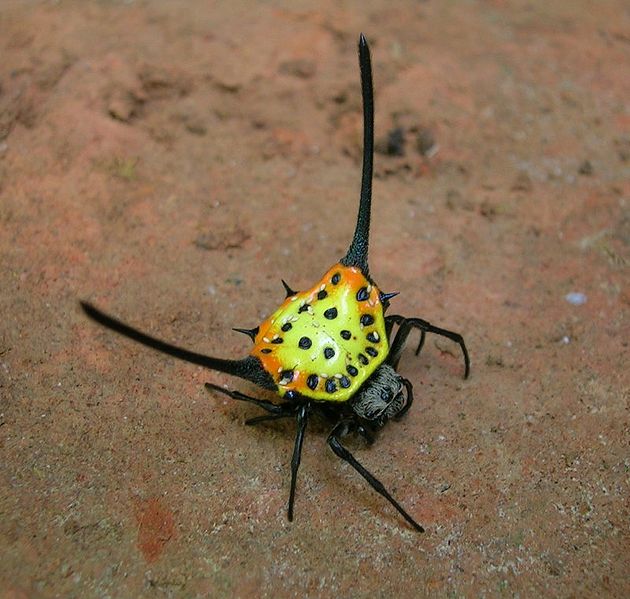 
A photo from here
Green, from emerald to lemon:
(Araneus cingulatus and Mopsus mormon): 

A photo from here and from here
(Grammostola pulchra):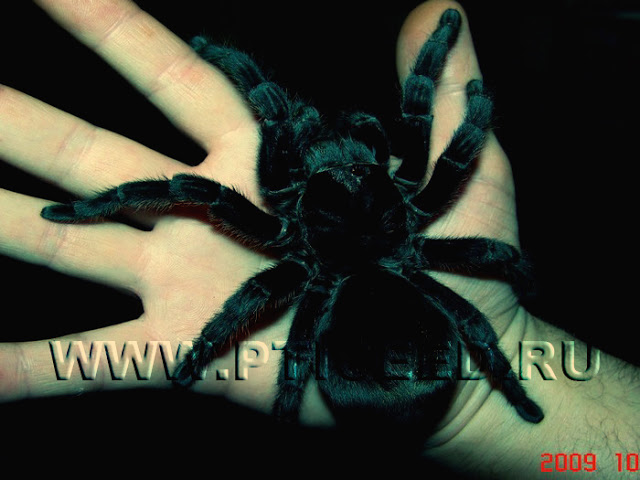 
A photo from here
(Poecilotheria ornata): 
A photo from here
(Nigma walckenaeri): ![]()
A photo from here
(Сolaranea viriditas): ![]()
A photo from here
(Peucetia viridans): 
A photo from here
(Avicularia purpurea): 
A photo from here
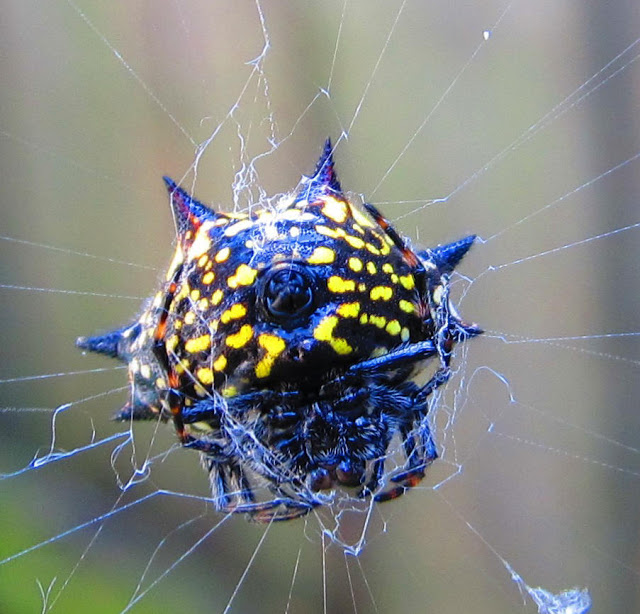

A photo from here
Flower yellow spider refers to a family of spiders-crabs or spiders-boaters.
This name was given to the family for the ability of its representatives to walk sideways. There are about 2000 species of crab spiders, including the floral yellow spider.
This spider does not weave cobwebs, its main weapon is its long front paws and disguise. Most of the time he spends on flowers and there watches prey.
For man, these beautiful spiders poses no danger.
Appearance of a floral yellow spider
There are differences in color and size between females and males. On average, the body length of males reaches about 4 millimeters, and their partners grow to 10 millimeters.
The abdomen of males is white to yellow with long dark strips, and the cephalothorax is black. On the front paws, the males have brown or black stripes, and the hind legs are of the same color as the abdomen.
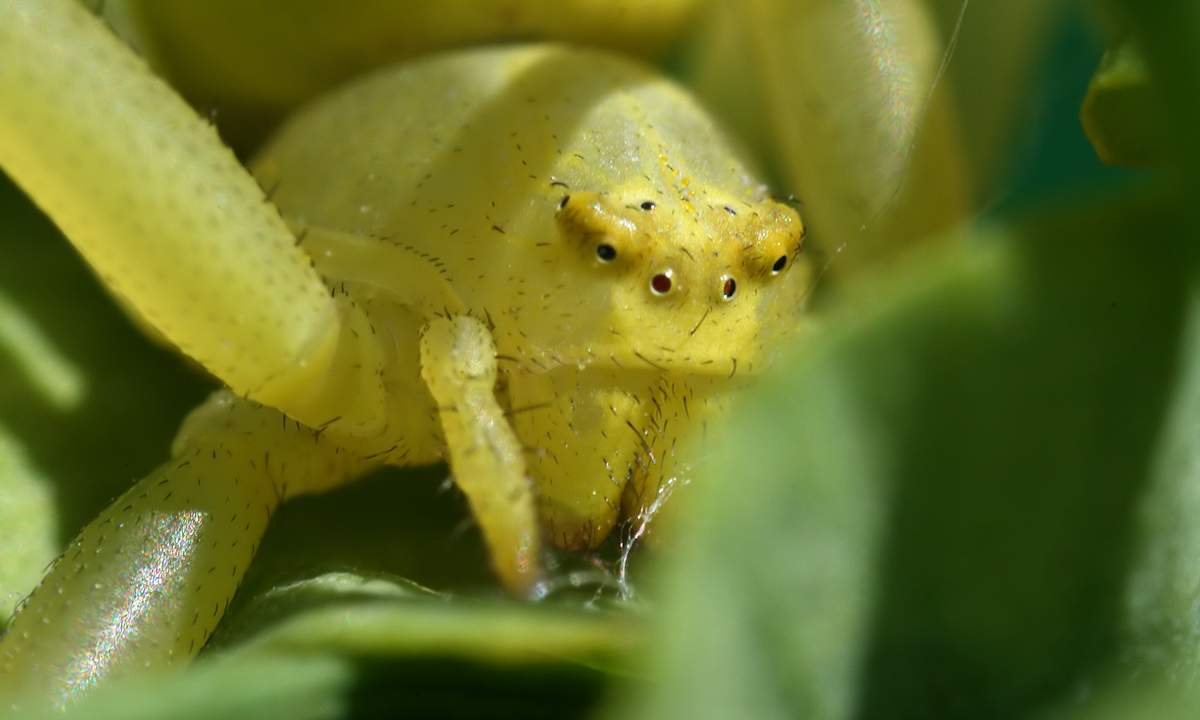 Yellow is only one of the variants of coloring a flower spider.
Yellow is only one of the variants of coloring a flower spider. The female has a body from bright green to bright yellow, and on the sides of the abdomen there are often red stripes.
Distribution of floral yellow spiders
These spiders live from the subtropical to the arctic zone, they can be found in Alaska, and in the US, and Japan, and Portugal. Floral yellow spiders are common throughout Europe, except Iceland.
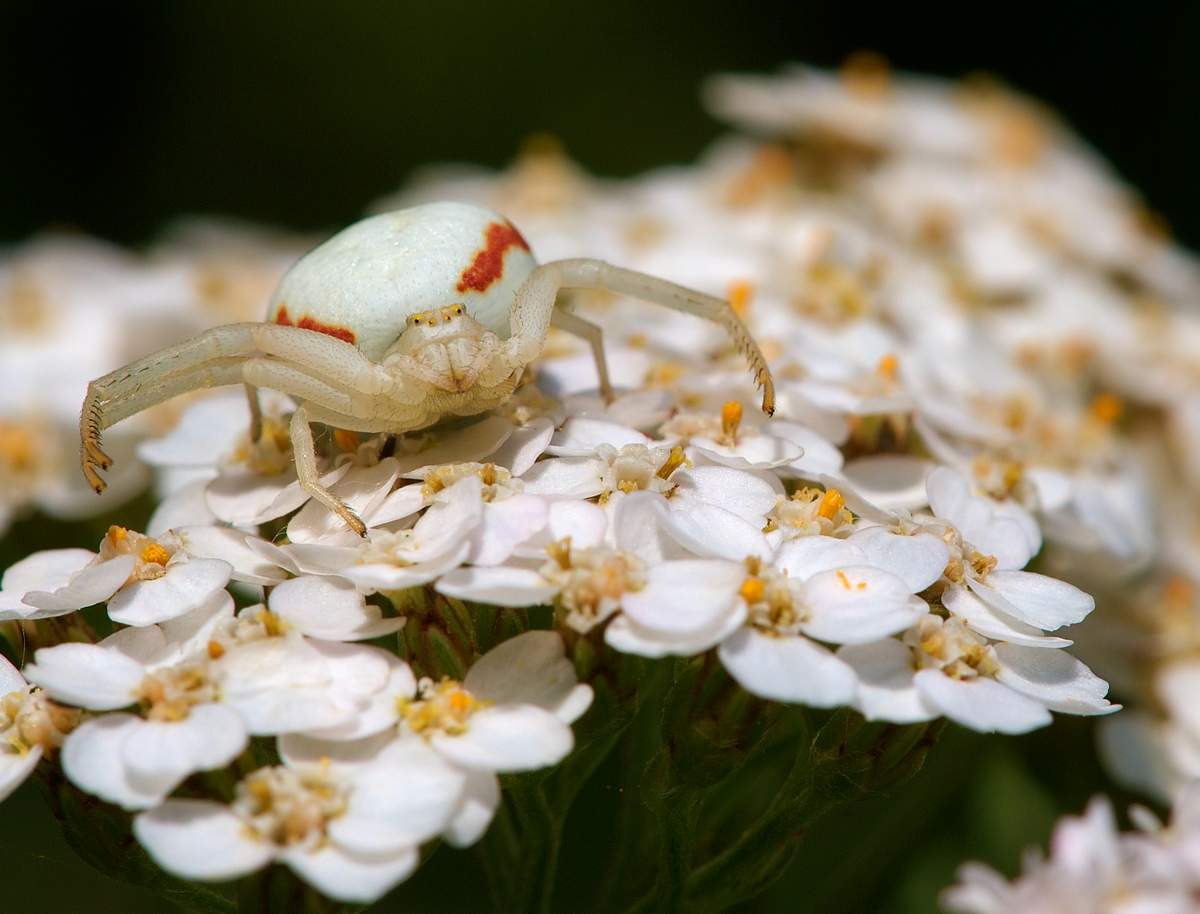

These spiders prefer open areas, where a large number of flowering plants grow. Sexually mature specimens are found in May-June.
Nutrition of flower yellow spiders
Extraction of spiders waiting on the flowers. Depending on the color of the flower, the spider can change its color. This ability is available only in adult individuals. Pigmentation of spiders is controlled with the help of the organs of vision.
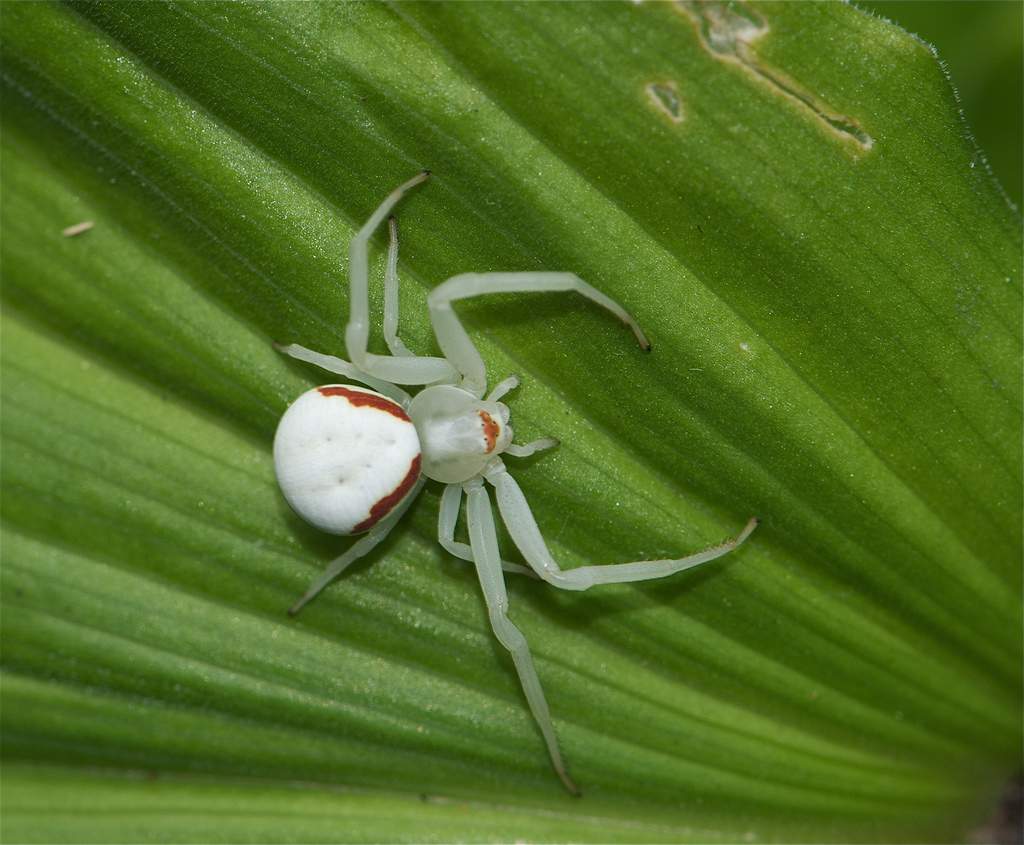 Flower spider - a real predator.
Flower spider - a real predator. The production of yellow flower spiders becomes a variety of pollinators, for example, bees, wasps, and various small beetles. Often the victims are much larger than the hunter himself.
The spider waits for the moment when the victim puts his head in the weave of the stamens, and attacks it, widely spreading his front legs. Grabbing the prey, the spider bites it in the neck area. This bite is poisonous, so caught prey instantly dies.
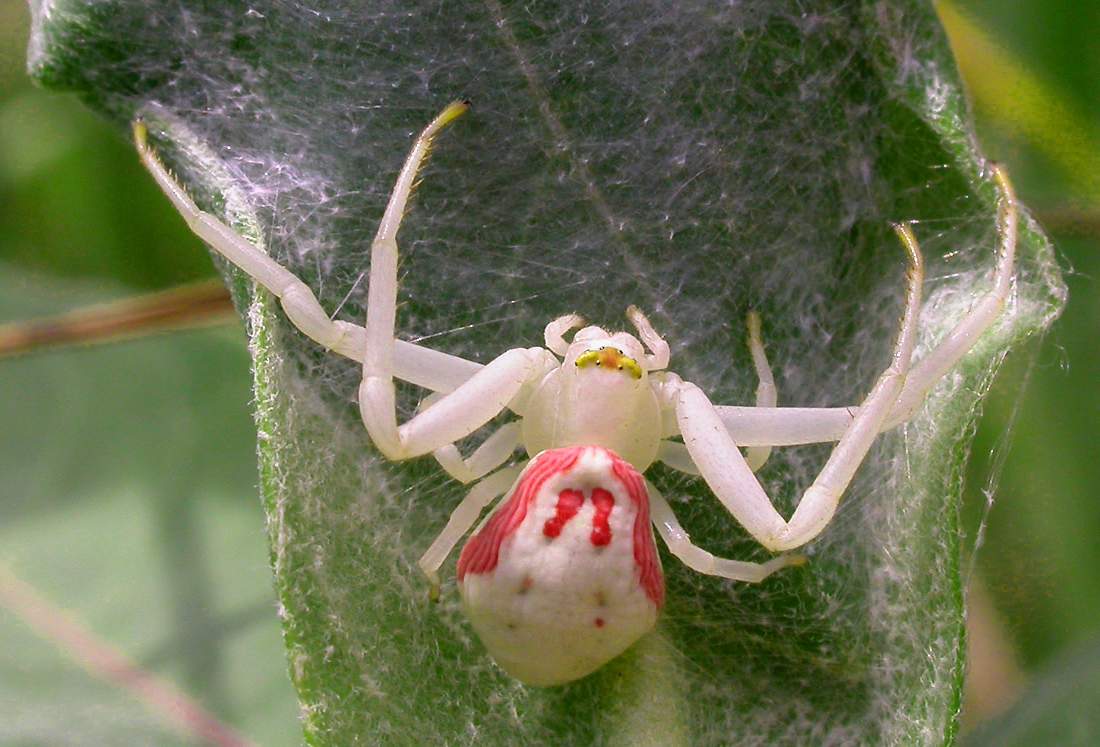

Due to its masking colors, the yellow floral spider remains invisible, being near the victim. As already noted, the yellow color, this is only a special case, the color may vary, depending on the color of the plants.