Audacity description in Russian. How to use Audacity? Detailed user guide
All sections of the site site
Audacity free download in Russian
Installing Audacity
How to install Audacity on a computer
Finding and downloading Audacity is easy. Type in any search engine
"download Audacity" and you will see a bunch of links to the site of this program.
There's a choice for all operating systems Windows, Mac or Linux
True, often I'm having trouble installing Audacity.
Therefore, do not smack the fever? look at the special
video tutorial on installing Audacity on a computer.
Audacity is a program for recording and processing sound.
In this video tutorial below, you will see how to download and install the program.
on your computer, as well as how to set up this sound editor after installation.
There are many settings in the program, so watch this video tutorial below
and after watching it you will be able to adjust and adjust
settings no problem. Lesson author Anton Kremenetsky
Did you like the video tutorial about the sound editor guys from the PC-vestnik website?


If you didn't find what you were looking for on this page, you can
use the search form throughout the site.
Enter one search word or a combination of several,
and click "find". Who seeks will always find:)
editing audio files, recording new files from the line input of the sound card (Line In), microphone input (Mic In), digital input from CD, AUX inputs, sounds in operating system from other programs that reproduce any sound, software media players, etc. With Audacity you can convert WAV to MP3, WAV to OGG, MP2 to MP3, MP2 to WAV, MP2 to OGG, MPA to MP3, MPA to WAV, MPA to OGG, MP3 to WAV, MP3 to OGG, M2A to MP3, M2A to WAV, M2A to OGG, AIFF to WAV, AIFF to MP3, AIFF to OGG, OGG to WAV, OGG to MP3, AU to WAV, AU to MP3, AU to OGG. All specified formats for import into the program (WAV, MP2, MP3, MPA, M2A, OGG, AIFF, AU) can be edited using the processing filters built into the Audacity program (or just filters, for those who already have experience with audio file editors). These filters in Audacity are:
amplify, bass boost, change pitch, change speed, change tempo, click and pop removal, dynamic range compressor (compressor (dynamic)), echo (echo), equalization (equalizer), fade in (smooth increase), fade out (smooth decay), fft filter (fast Fourier transform filter), invert (invert), noise removal (noise removal ), normalize, nyquist prompt filter, phaser, repeat, reverse, wahwah, cross fade in, cross fade out damping), delay (delay), gverb (reverb), hard limiter (hard limiter), high pass filter (high pass filter), low pass filter (low pass filter), sc4 filter (stereo compressor with advanced settings), tremolo (tremolo effect).
Audacity is free and supports the following languages: Arabic (Arabic), Bulgarian (Bulgarian), Catalan (Catalan), Chinese (Traditional) (Chinese Traditional), Chinese (Simplified) (Chinese Simplified)), Czech (Czech), Danish (Danish), German (German), English (English), Spanish (Spanish), French (French), Italian (Italian), Lithuanian (Lithuanian), Hungarian (Hungarian), Macedonian (Macedonian), Dutch (Dutch), Norwegian (Norwegian), Russian (Russian), Slovenian (Slovenian), Finnish (Finnish), Swedish (Swedish), Ukrainian (Ukrainian). It is very convenient to use the Audacity program on mother tongue, but in our tutorial we will use English terms and designations.
Below is the main contents of the Audacity manual, we recommend starting with
During the installation of the "audacity-win-*.*.*.exe" file, the program will ask you to confirm the interface language. To understand the basics in this manual and match the screenshots, terms, effects, and user actions, you can select English ("English"). Subsequently, you can change the language of the program interface by selecting the language convenient for you at any time in the "Preferences" menu.
After starting the Audacity program, we see the main program window. It contains the main menu with sections "File" (File), "Editing" (Edit), "Tracks (Project)" (Project), "Creation" (Generate), "Effects" (Effect), "Analysis" (Analyze) , "Help" (Help), toolbars for basic editing functions, sound file time bar, free space for edited audio tracks. We recommend using the values shown in the screenshots in this Audacity manual.

Before you can start using Audacity, you must first set up the program's Preferences. To see the "Options" window, please select the "Preferences" item in the "Edit" menu, or simply press the keyboard shortcuts in the Latin keyboard layout "CTRL + P". In most cases, editing "Parameters" needs to be done once for future use.
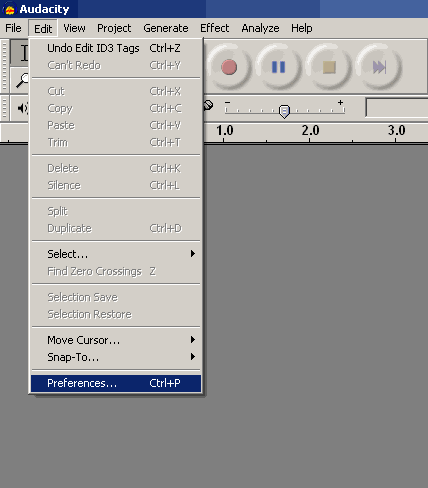
Devices tab (Audio I/O tab). On this tab, select the device in the "Playback" - "Output" (Wave mapper) list, or the name of your sound card in the system, if your PC has more than one sound card, and you know exactly which card You need to output sound, ie. connected to monitor acoustics, headphones.
In the "Recording" device list, select "Sound remapping program - Input" (Wave mapper) or the name of the sound card from the list - in this case, do not forget to connect the audio signal source to the inputs of the selected sound card. If your plans do not include audio recording , then you do not need to make any connections to the sound card inputs. Specify a number in the "Channels" list more than two (2 channels (Stereo)), if you plan to record a signal from a multi-channel source. The default number of channels is "2 (Stereo) (2 channels (Stereo)) will suit us just fine.
The checkboxes "Play other tracks while recording new one" and "Software Playthrough (Play new track while recording it)" may also be available to the user, it is better to leave unchecked, they are needed by users with some experience using Audacity.
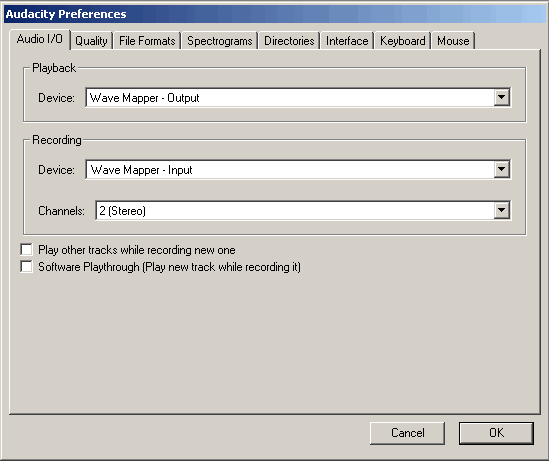
The "Quality" tab. Audacity supports "Default sample rates" which must be set from the list: 8000 Hz, 11025 Hz, 22050 Hz, 32000 Hz (Digital radio broadcasting in some cases), 44100 Hz (Audio CD recording standard) - shown with red arrow, 48000 Hz (standard DVD Video audio sampling rate) - shown with green arrow, 64000 Hz, 88200 Hz (Audio CD double sampling rate), 96000 Hz (DVD Video double audio sampling rate), "Other" (Other ) (Any sample rate of your choice, option for advanced users). For basic editing tasks, specify the sample rate and work with it - 44100 Hz for Audio CD, 48000 Hz for DVD, the final result will be good quality. If you plan to record a project with multi-channel sound, and you have a professional sound card that supports 96 kHz sound format with 24 bit resolution, specify these values on the "Quality" tab, the recording result will be better, do not reduce the Sample Rate to the final frequency (for DVD, Audio CD, etc.). If you plan to work with increased sample rates in your Projects, use the values obtained by multiplying the final sample rate by 2 or 4, - 96 KHz for DVD, 88.2 kHz for Audio CD. Remember that the size of the Project on your hard disk will grow by the same multiplication factor. And, in conclusion, it is worth noting that the use of a double sampling rate is justified if your sound card is built on an ADC / DAC (Analog to Digital Converter, Digital to Analog Converter) with the same sampling rate. Consumer sound cards operate at 44.1 and 48 KHz and below, sound cards with 96 KHz processors cost over $300, so it's up to you.
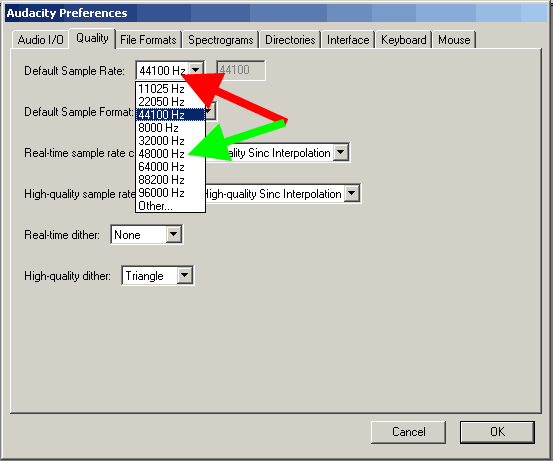
Default sample format parameter. By default, Audacity uses 32-bit. If you do not need such precision, specify 24 bit or 16 bit. By specifying a reduced bit depth, you will save space on your hard drive when working with the Project. For consumer segment sound cards, specify 16-bit bitness, if your sound card supports 24-bit sound, specify it, do not forget to check the box in the Windows Control Panel settings (either for the Sound Remapper or for the Direct sound mode) in accordance with instructions for the sound card - this option must be configured by a user with experience in using the program. However, the default bit depth of 32-bit will be used in our tutorial.

Parameter "Conversion in real time" (Real time sample rate converter). For fast modern processors, it is better to select "High quality Sinc interpolation" for best results.

High quality sample rate converter option. Select the "High quality Sinc interpolation" value even if you do not have the most modern processor - this option will help you get the best result when saving your Project to the final file with the specified Sample Rate.
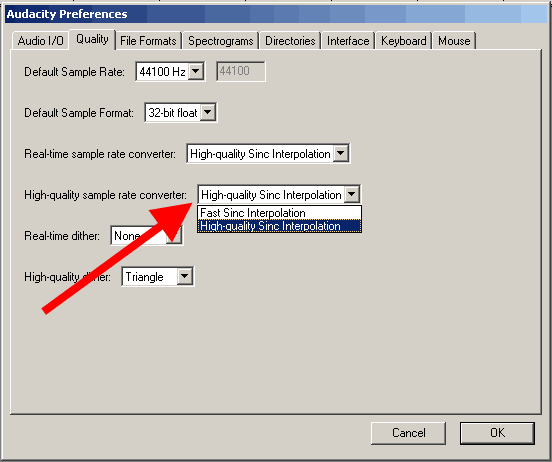
"Real-time dither" parameter. We do not need it - select "No" (None)

"High-quality dither" parameter - for the best accuracy, select "Triangle" (Triangle)

Import/Export tab (File Formats). To speed up work with uncompressed files, check the "Read directly from the original file (faster)" checkbox. Another available option - "Make a copy of the file before editing (safer)" will allow you to work with the original file without affecting it, avoiding any edits in it

The "Uncompressed export format" determines the format when exporting from the Audacity Project after editing is complete - "WAV (Microsoft 16 bit PCM)" is fine in most cases.
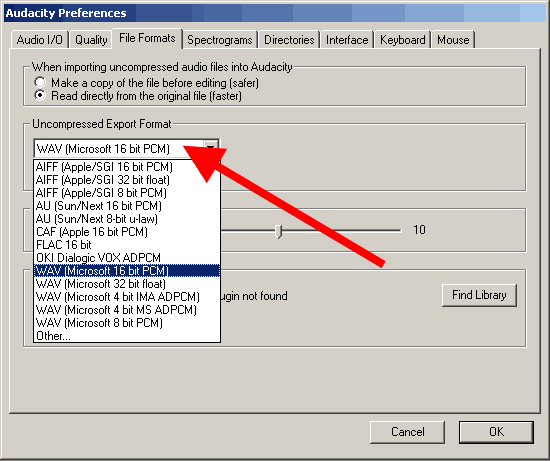
Indication in the list "Other" (Other) "Export format of uncompressed audio data" can be used by advanced users, then the parameters "Header" (Header), Sampling frequency become available to change. In the "Other" mode, you can select a 24-bit sample rate value for export.

Export settings for OGG files. (OGG export setup). Here is the most interesting. If you have found the above settings so far, then for the Beta version of the Audacity program, the interface is slightly different, and in the Beta version, export to AAC, AC3, AMR, WMA formats using the FFMPEG library is also available. The FFMPEG library is connected in "Parameters" - "Libraries", by the "Download" button - download from the official site, by the link "Go to the download page" look for "FFMpeg Binary compatible with Audacity 1.3.13, 2.x or later on Windows ", install, specify the path on the "Libraries" tab.
OGG compression is more optimal than MP3 compression, and lower bitrates produce better results. When exporting to OGG format - value 0 will give a bitrate of 64 kbps, 5 (default) will give 160 kbps, 10 - 500 kbps
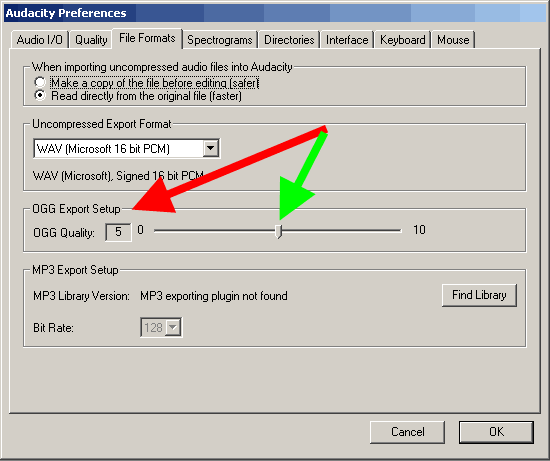
MP3 Export Setup. To export to mp3 format, we need to install an additional Lame library - "lame_enc.dll". During the installation of Audacity, this library is not installed, so for a stable version of Audacity, you can . After downloading the lame_enc.dll library and extracting it from the ZIP archive, click the "Find library" button, specify the path to the "lame_enc.dll" file on your hard drive - shown by a green arrow.


MP3 export options - Specify "Quality" (Default bitrate). After that, the "lame _enc.dll" library will be connected with the version (v3.97, red arrow) to the Audacity program, you need to specify the bitrate for exporting to MP3 format, for the stable version it is shown with a green arrow. If you have a Beta version of Audacity, the settings for exporting to MP3 format are set by clicking the "File" - "Export" menu of the "Options" button

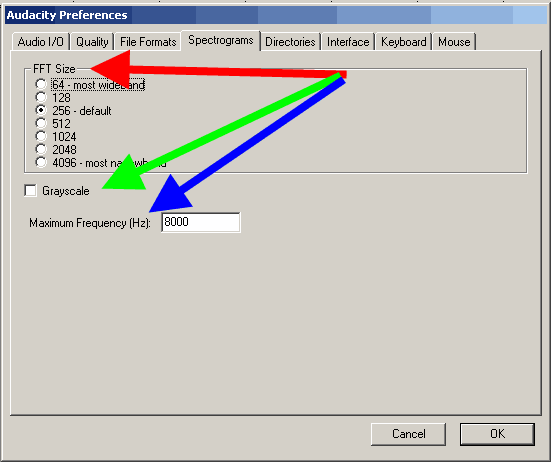
The "Spectrograms" tab. Specify the default value - "256", as shown by the red arrow, if necessary, check the box "Show spectrograms in grayscale" (Grayscale) - shown by the green arrow, and select the maximum frequency to be displayed in the spectrogram (blue arrow). this frequency is 8000 Hz, it's okay, this is the limit for the displayed frequency of the spectrogram, to fully display the frequency range, you need to know the sample rate in the Project and divide it by 2. For example, for the Sample rate 44100 Hz, the frequency range is from 0 to 22050 Hz, this is the rule discrete mathematics.
The "Directories" tab. Specify a path to store Audacity's temporary files (red arrow) with enough free hard disk space. The available free space is shown as " free space:" (Free Space)

The "Interface" tab. On this tab, the user can change the settings for the interface of the Audacity program. The default settings shown in the screenshot suit us quite well, here you can also change the interface language of the Audacity program to your native one, if necessary. Changing the value "Minimum of dB mode display range (db)" helps to set the accuracy of drawing the spectrogram on your screen - for example, it can be useful for editing 24-bit audio files.

Tab "Keyboard" (Keyboard). On this tab, you can set "Keyboard Shortcuts" for frequently used operations in Audacity.
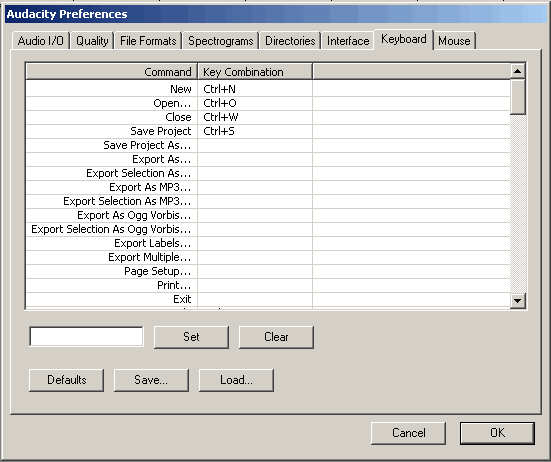
Let's look at the example of the Keyboard shortcut for the command "Export to MP3" (Export as MP3). Select the required command from the list, then press "CTRL + SHIFT + M" (red arrow) in the Latin layout. After that, click the "Set" button to add a new keyboard shortcut to the list of options

The result of adding a new Keyboard Shortcut will be shown in the list of commands.

The Mouse tab shows the mouse actions available to the user in Audacity. This is the last tab of the "Parameters", then click "OK".

The Audacity control panel contains buttons and tools:
"Selection Tool" - this tool is used to select the waveform graph using the mouse and keyboard shortcuts "Shift+Left", "Shift+Right", "Shift+Home", "Shift+End". By holding down the "Shift+Left" or "Shift+Right" keys, you can highlight the desired range of the waveform graph, depending on the one you have chosen. The combination "Shift+Home" highlights the waveform graph from the current cursor position to starting position sound track. The combination "Shift+End" highlights the waveform graph from the current cursor position to the end position of the audio track. You can also use to change the selection area. To use this tool, press the "F1" key.
The "Envelope Tool" helps to change the level of a part of the waveform graph using the mouse or by selected points. To use this tool, press the "F2" key.
The "Change Envelope (Pencil)" (Draw Tool) helps to change individual samples in the waveform graph - used by advanced users of the Audacity program. To use this tool, press the "F3" key.
The "Zoom Tool" helps the user to change the scale of the waveform graph by left clicking (Zoom in) and right clicking (Zoom out), or by holding down the "Shift" key and pressing the left mouse button, the "Zoom out" mode is enabled. ". To use this tool, press the "F4" key.
"Move" (Time Shift Tool) shifts the graph of the waveform to the left or right, producing a time shift for the audio track. To use this tool, press the "F5" key.
"Multi-Tool Mode" combines all the above tools, it requires the skill of using the above tools, called by pressing the "F6" key.

The Audacity edit toolbar includes the following operations:
Operations "Cut" (Cut), "Copy" (Copy), "Paste" (Paste) are the main ones when editing in Audacity.
Trim outside trims the audio signal to the left and right of the selected portion of the shape graph.
"Create silence" (Silence) creates a signal with zero level (silence) in the highlight area of the waveform graph.
Buttons "Cancel" (Undo) and "Return" (Redo) cancel and return to the step the editing operations performed by the user of the program.
The "Zoom in" and "Zoom Out" buttons are given to users who prefer to call commands from the editing panel, rather than keyboard shortcuts and mouse clicks.
By pressing the "Fit selection" button, the zoom scale of the waveform graph is selected so that its selected part fits across the entire width of the program screen.
Clicking the "Fit project in window" button scales the waveform graph so that the entire duration of the Project over time (frames, samples, etc.) in Audacity is displayed across the entire width of the screen.
"Audacity mixer toolbar" is intended for:
adjusting the signal level of the output and input device, as well as displaying the name of the devices.

"Audacity indicator panel" (Audacity meter toolbar) contains:
the left indicator to display the level of the reproduced signal, and the right indicator to display the level of the recorded signal, for which it is possible to select the "Enable monitoring" mode. For each indicator, it is possible to turn on the "Vertical orientation" (Vertical stereo), or "Linear" level (Linear)" modes, although the use of the "dB" scale mode mode is closer to real audio equipment.

Audacity is a free audio editor, which, however, has quite a lot of features. In this article, we will look at the basic techniques for editing music tracks, as well as the location of the main functions and tools of the editor.
The editor exists in two versions: installation and portable. The second does not require installation and can be run from a USB flash drive.
After launching Audacity, we need to open the track. To do this, use the "Open" and "Import" functions, which are located in the "File" menu.
The import function is used for some file formats that refuse to open. Also, import is used when adding tracks to an existing project (when something is already being edited).
Our track is displayed on the waveform. Most likely you will need to select various parts of it (to cut, remove noise or apply effects). To make it easier to select, use scaling.

To cut, copy or paste a section of a track, use the buttons shown in the screenshot below. When you hover over a button, a tooltip appears explaining the button's function. In any case, if it is not clear, you can try, and then just cancel the action using the key combination Ctrl + Z. Use the play button to indicate the boundaries of the area.

The Effects menu is probably the most interesting place in Audacity. There is a fairly large list of effects that will help you give your favorite tracks originality. The effects are well described in this article (with sound examples).

To save the result, use "File - Export". The "Save" item is used to save the Audacity project in *.aup format, that is, you will not receive an audio file. When exporting, you can use formats such as MP3, WAV and other popular ones.
Audacity is a popular software that is great for both amateur recording and professional audio modeling of text and music written by composers and poets.
The great thing is that this program allows you to do all this at home. However, some users may experience difficulties when working with the interface of this utility, and therefore we will consider in more detail the question of how to use Audacity, especially since there are not so many instructions in Russian. We do not pretend to be a detailed guide, but we will write down the main points.
Introduction to the program
When you first start this sound editor, the user will see something like the following picture on the screen:

To get started with Audacity, simply connect a microphone to your computer () and click the "Record" button.
In the upper figure, this is a red circle under the number 1. In this case, an audio track immediately appears on the screen, and the user will be able to visually observe the process of recording his speech in the form of an image on the screen corresponding to the tempo and timbre of the voice of sound waves.
In order to pause the recording, it will be enough to press the "Pause" button, which is indicated by the number 2.
During a pause, the vocalist has the opportunity to take a breath, drink water, recover with strength, and then continue recording directly from the place where the recording of the track was stopped.
To continue working, it is necessary to press the "Pause" button again, and the recording will resume again.
When the work on the audio podcast is completed, it will be enough to click the "Stop" button (yellow box at number 3), after which the recording will immediately stop.
In order to listen to the resulting recording, the “Play” button (marked 4) is used.
If the resulting audio podcast is long enough, you can use the Rewind and Forward buttons to jump to the beginning or end of the recording. They are numbered 5 in the figure above.
When you start recording again in the Audacity sound editor, it will be carried out from a new sound track. At the same time, the program makes it possible to process and edit each audio track separately, as well as move sounds relative to different tracks:

Moving tracks in a podcast
When creating a podcast that consists of multiple audio clips, it is often necessary for the user to make the next audio clip start right after the previous one ends. All individual tracks in Audacity are located on the timeline, and can move along it to the left or right. In order to move tracks along the timeline, the Timeshift tool is used (double arrow at number 6 in the figure below).

After selecting this tool, select the desired track by clicking on the image of the sound waves corresponding to it, and holding down the left mouse button, move the selected element to the left or right along the timeline to set it to the desired location.
In addition, the Audacity sound editor has the ability to change the order of the tracks in the working window. The Timeshift tool is also used for this: to change the order of audio recordings in working area you should click on the desired track and move it up or down, while holding it down with the left mouse button.
Track control panel
If, after recording several tracks, turn on the “Play” button, then all of them will be played at the same time. If this is not necessary, then you need to press the "Solo" button in the audio recording control window. In this case, only those tracks for which this function is selected will sound during playback in the speakers.

In the case when there is a need to listen to all tracks, except for one (or several), then unnecessary recordings are excluded from playback by pressing the “Mute” button for them.
The track control panel contains many useful features to work with records. If you click on the small black arrow pointing down, a list of options will appear on the screen.

In this case, the first three parameters are the most useful for managing tracks. These include the ability to create a track name, as well as other ways to move records up and down within the workspace. However, assigning a name to each specific entry can be very useful when the user is working with large quantity tracks, as this case it becomes difficult to distinguish them one from the other simply by the visual image of the sound waves corresponding to each track.
The track control panel also contains two sliders (“worms”):
- The first one, located above, contains the signs "+" and "-". It allows you to control the volume level of the track, increasing and decreasing it accordingly. This volume control option can be useful if there are tracks in the audio project that are played much quieter than the rest of the tracks, or vice versa drown them out with their more powerful sound. Volume control makes it possible to solve the problem with such troubles and even out the sound level of the entire podcast.
- The next slider labeled "L" and "R" applies only to those tracks that were recorded in stereo, and allows you to adjust the volume of the sound that will come from the left or right speakers, respectively. This effect is called panning. By moving the slider to the right, you can increase the volume of the sound coming out of the left speaker and decrease the volume from the right speaker, and vice versa.
In addition, the track control panel makes it possible to automatically sort tracks by start time or by name, without resorting to manually moving them in the workspace space. In order to sort all the tracks in the current audio project, you must select the menu item "Tracks" ("Tracks"), and then "Sort" tracks by ... "(" Sort tracks by ... ") and a choice is made from the two proposed options.

Sorting tracks by start time can be useful for aligning all tracks in the same order they will play in the current podcast project.
Sorting by name is most useful when the podcast contains many tracks with similar names. For example: Entry1, Entry2, Entry3, Interview1, Interview2, etc.
Conclusion
As you can see, the Audacity sound editor is quite simple and easy to use. And with some basic skills, even a novice user can easily create their own high-quality audio recordings.
Audacity is one of the most widely used audio editors and is popular due to the fact that it is free. Here you can process the musical composition the way you want. It is quite simple and understandable thanks to its friendly interface and Russian localization. But still, users who have never dealt with it before may have problems. The program has many useful features, and we will try to tell you how to use them. We have selected the most popular questions that users have during their work, and have tried to answer them in the most accessible and detailed way.
Like any audio editor, Audacity has tools "Crop" and "Cut out". The difference is that by clicking on the button "Crop", you will delete everything but the selection. Well, the tool "Cut out" will already delete the selection. Audacity allows you not only to trim one song, but also add fragments from another song to it. Thus, you can create ringtones for your phone or make cuts for performances.

For more information on how to trim a song, cut a fragment from it or insert a new one, as well as how to glue several songs into one, read the following article.
Voice over music
With Audacity, you can easily overdub one recording over another. For example, if you want to record a song at home, then you need to separately record the voice and separately the music. Then open both audio files in the editor and listen.

If the result suits you, save the composition in any popular format. It's like working with layers in Photoshop. Otherwise, increase and decrease the volume, shift the records in relation to each other, insert empty fragments, or shorten the protracted pause. In general, do everything to get a quality composition as a result.
Noise Removal
If you recorded a song, but there are noises in the background, remove them using the editor. To do this, you need to select a section of noise without a voice in the recording and create a noise model. Then you can already select the entire audio recording and remove the noise.

Before saving the result, listen to the audio recording, and if something does not suit you, adjust the noise reduction parameters. You can repeat the noise reduction operation several times, but in this case it is possible that the composition itself will suffer. See this tutorial for details:
Saving a song to MP3
Since Audacity does not support the MP3 format by default, many users have questions about this. In fact, MP3s can be added to the editor by installing the additional Lame library. It is downloaded using the program itself or manually, which is much easier. Having loaded the library, you will only have to tell the editor the path to it. Having done these simple manipulations, saving all edited songs in MP3 format will become available. More detailed information you will find the link below.

Sound recording
Thanks to this audio editor, you do not need to use a voice recorder: you can record all the necessary sounds right here. To do this, you just need to connect a microphone and press the record button.

We hope that after reading our article you were able to figure out how to use Audacity and get answers to all your questions.




